“The coronavirus nCoV is a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA virus that causes severe respiratory disease in humans and other animals. The HCoV-HKU1 is yet another strain of it has evolved in mammals in recent time. ”
The COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 is spreading lightning fast nowadays, however, other strains of nCoV are now emerging fast and spreading like the SARS-CoV-2. Another viral strain of the family betacoronavirus is now spreading along with SARS-CoV-2.
The cases of HKU1 are increasing faster, though, the first case was reported in 2005 in China. Woo and co-workers reported the first case in humans in 2007. This article has been written keeping in view the current pandemic situation to increase the present database of COVID-19.
Key Topics:
The coronavirus HKU1…
The coronavirus infects both animals and humans due to high recombination frequency and unique replication mechanism. Yet another important factor that makes it more powerful is the largest genome size of it. These factors combinedly allow it to infect a wide variety of hosts.
The present strain of the nCoV was transmitted into humans from mice, accidentally, their infection cycle is similar to the SARS-CoV-2. It affects the upper respiratory tract and causes cold, fever, pneumonia, and lung bronchiolitis. HCoV-HKU1 is classified into the group 2a coronavirus.
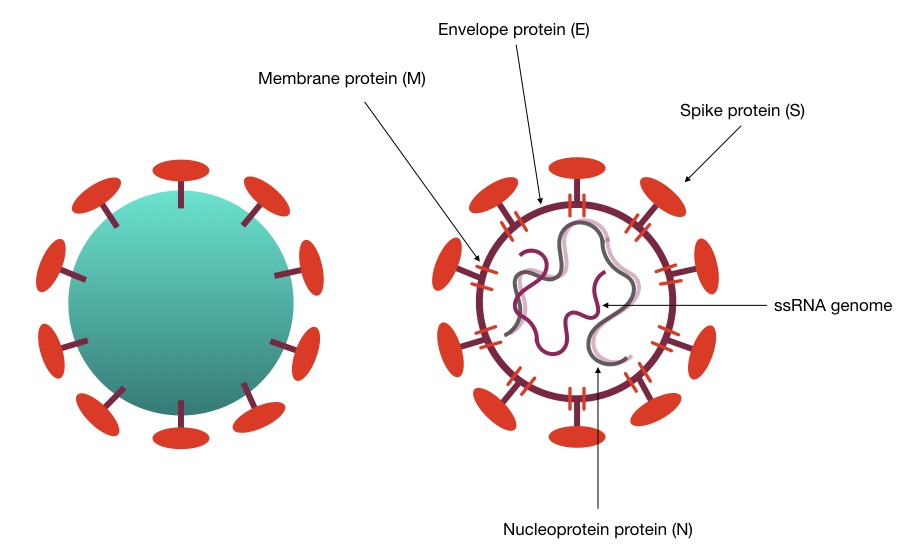
The HCoV-HKU1 or coronavirus HKU1 is also a kind of single-stranded RNA (Ribonucleic acid) virus having the same genes alike to the other species. The spike of the virus binds to the human cell on the specific receptor known as the N-acetyl-9-O-acetylneuraminic acid receptor. And then starts its life cycle in the host.
As it infects especially the humans it is categorized into the Betacoronavirus family. See the table below for various categories of nCoV.
Interestingly, the research indicates that the HKU1 in more similar to the mouse hepatitis virus. The complete genomic sequence of the HCoV-HKU1 is now available which is more different than other groups of coronavirus with only 32% of total GC content lower amount all strain of corona.
Genomic data of 22 HCoV-HKU1 revealed that the genome size of it is approximately ~30Mb with replicase, spike, nucleocapsid, envelope, and membrane genes majorly. To know more about the genomic features of coronavirus, read our previous article: Coronavirus: Genome, structure, function and testing.
“HCoV-HKU1 is not cultivable to date.”
Coronavirus HKU1 PCR:
The quantitative Polymerase chain reaction technique (qPCR) is widely used in the detection and quantification of the various strains of coronavirus. The Real-time PCR, a quantitative version of conventional PCR, used to do so.
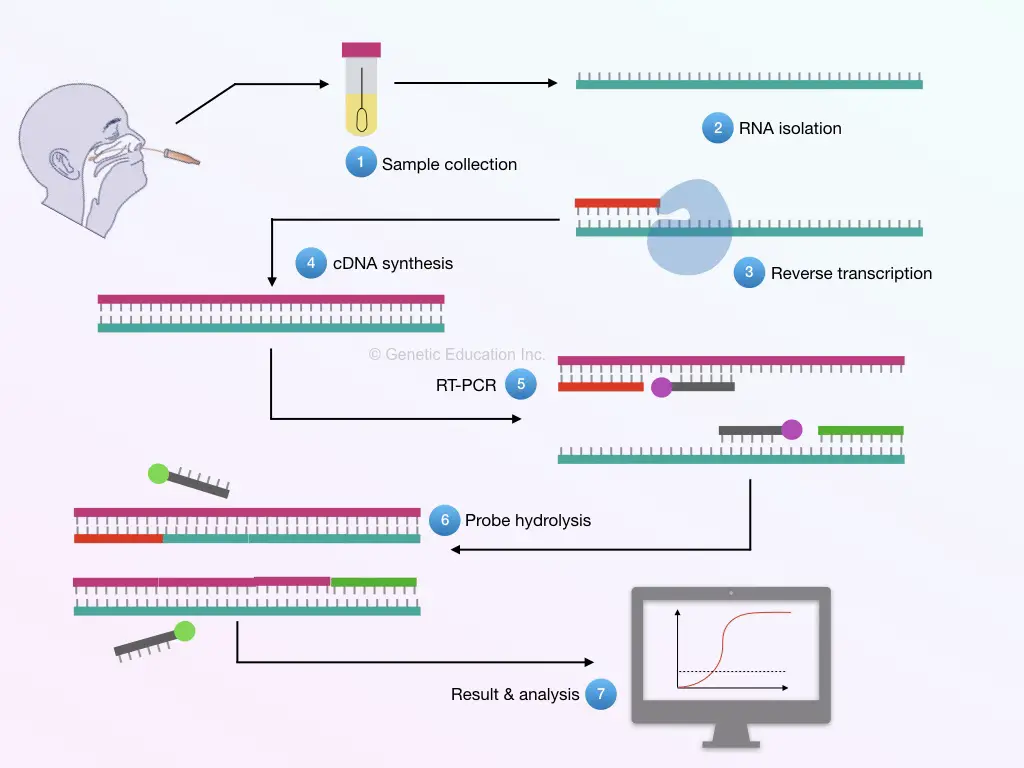
Here in the RT-PCR testing method, the sequence of viral RNA is selected to amplify using a set of primers. Positive amplification indicates the presence of the viral strain in the sample.
The RT-PCR detection method is used to detect the HCoV-HKU1 as well, using the pol (RdRp) gene and N- gene sequence.
The present method is similar to the SARS-CoV-2 RT-PCR method in which nasal swab, throat-swab, sputum or nasopharyngeal aspirates are taken for testing.
In the procedure, first, RNA is extracted from the sample and quantified for further preceding.
In the next step, the viral RNA is reverse transcribed into the cDNA and amplified using a set of primers and probes. The probe-hydrolysis increase the fluorescence signal which is detected through the detector.
Usually, as we said above, the primers are designed based on the sequence information of the RdRp and N-gene sequences. The reason to choose only these two sequences is that first, both genes are commonly found in all coronavirus strains, and second, to serve the purpose of ‘control’ in the reaction.
The RT-PCR (Real-time PCR) machine measures every template amplified in the log phase of amplification. The amplicon’s size of both the gene is rough ~400bp to 500bp. Moreover, microarray and antibody tests are also used to detect the HKU1 strain.
Related article: Strategies to Prevent Transmission of COVID-19 (Coronavirus).
Conclusion:
More and more new strains of coronavirus are evolving. Apart from the SARS-CoV-2, MERS-CoV, SARS-CoV, HCoV-229E, HCoV-OC43, HCoV-NL63 and HCoV-HKU1 are other strains which infect humans and other mammals as well.
China, USA, UK, Spain, Italy, and other developing countries like India and Pakistan are now facing serious challenges due to the coronavirus outbreaks. We don’t have any effective medication, therapy or vaccines, at least for now. The only way to stay safe is to stay at home and social distancing.
The RT-PCR based testing method is rapid, accurate, and effective, still high cost and limited reagent and kit availabilities are the issues countries are facing in testing.
Sources:
- Woo PC, Lau SK, Yip CC, Huang Y, Yuen KY. More and More Coronaviruses: Human Coronavirus HKU1. Viruses. 2009;1(1):57‐71.
- Bruning AHL, Aatola H, Toivola H, et al. Rapid detection and monitoring of human coronavirus infections. New Microbes New Infect. 2018;24:52‐55. Published 2018 May 9.