“Genetic testing practiced for knowing or identifying a defective gene, DNA, or chromosome during the pregnancy is referred to as pregnancy genetic testing.”
A healthy child is every couple’s dream, right!
During pregnancy, if women eat healthy food, live a healthy life and follow some instructions, a healthy baby can be born.
However, in some conditions, following only healthy practice is not enough, for instance, in the case of the genetic carrier.
If one of the parents is a carrier for some kind of genetic disorder, the baby might be at risk of a genetic disorder.
Hence genetic testing during pregnancy must be required, not for all but in some special cases.
Using the state of the art genetic technologies genetic testing often known as a DNA test or gene test or chromosomes test is done.
A gene is a functional unit of DNA, located on chromosomes. Any aberrations/ abnormality or variation in a DNA sequence or chromosome can be identified using the genetic testing.
In a simple language, we can say, those alterations might be
- deletion or insertion of some sequences
- Deletion of the entire coding region
- Translocation of chromosomal fragments
- Alteration in chromosome number
- Deletion of some of the important portion of the chromosome
- A single base change in the DNA sequence
- Uncontrolled expression of genes
These are some of the possible types of genetic abnormalities that occur in a baby during pregnancy in which the majority of cases are congenital.
The congenital genetic abnormality is a type of genetic condition that occurs by birth.
Notably, not all conditions are congenital, for instance, some non-inherited cancer occurs in any stage of life due to the influence of the external environment.
Ok now coming to the point,
As we indicated above, some conditions are inherited and some are not. In the present article, we will talk about the pregnancy genetic testing and in which condition it is required. We will also explain to you the exact process of how genetic testing for pregnancy is practiced so that you can understand it properly.
The content of the article is,
Key Topics:
What is pregnancy genetic testing?
Commonly known as prenatal genetic testing, the pregnancy genetic testing is practiced to find out genetic alterations of a fetus if any, using advanced genetic methods.
DNA of us functions to encode a protein, I mean any kind of protein in our body is formed only from a DNA that DNA are genes consisting of 3% of the total genome.
Moreover, the genome of us also regulates the expression of genes that portion of our genome is non-coding.
Approximately 21,000 genes are identified to date. Alteration is DNA (known as a mutation) that causes serious problems in which some are inherited and some are not.
The mutated genes passing on to offspring in one of the ways enlisted in the table:
| Type of inheritance | Condition | Examples |
| Autosomal dominant | A single copy of an autosomal mutant gene is responsible for the occurrence of the disease. | Huntington’s disease and Neurofibromatosis type 1 |
| Autosomal recessive | Two copies of an autosomal mutant gene are responsible for the occurrence of the disease | Cystic fibrosis and sickle cell anaemia |
| X- linked dominant | A single copy of the X-linked gene is responsible for the occurrence of the disease. | Fragile x syndrome and haemophilia |
| X-linked recessive | Two copies of the X-linked gene are responsible for the occurrence of the disease. | Duchenne muscular dystrophy and Fabry disease |
| Y-linked inheritance | The Y-linked gene is responsible for the occurrence of the disease in males. | Y-linked infertility |
As we know during the formation of an embryo, 23 chromosomes from the sperm and 23 chromosomes from the egg constituted the genetic makeup of the fetus.
Along with the chromosomes, a mutated gene inherited to the fetus in any of the ways explained in the table above.
Furthermore, some chromosomal aberrations occur randomly, without any known cause, for example, the common types of trisomy- 13, 18 or 21 happens due to the imbalance of chromosome distribution during germ cell division.
Although it is non-inherited, whether the fetus is suffering from a genetic abnormality or can not be predicted unless genetic testing is done.
And that is why genetic testing is important during pregnancy. But don’t worry, not all pregnant women require genetic testing. Sit calmly I will explain to you in which cases pregnancy genetic testing is needed?
When pregnancy genetic testing is required?
Here I am enlisting several conditions in which genetic testing must require.
Maternal age over 35:
The maternal age is one of the important factors in the occurrence of random mutation to the fetus.
Scientific literature suggests that the pregnancies of women over the age of 35 are at the highest risk of genetic abnormalities especially the trisomies.
With the progression of maternal age, the chance of trisomy increases, though the event is totally random.
Trisomy 21, trisomy 13 and trisomy 18 are the common numerical chromosomal aberrations reported globally.
If you are above the age of 35, the chromosome test or genetic testing is mandatory for you, however, the doctor’s recommendation and genetic counselor’s advice will require before that.
Positive screening test:
The doctor commonly advises ultrasound and some basic tests during pregnancy. If the primary screening test is positive, genetic testing must be required.
For example, if the triple marker or PAPPA with AFP results are positives with the indication of positive NT test during the ultrasound, the possibility of down syndrome is strong.
Immediately, the doctor referrers genetic testing.
Previous child with genetic abnormality:
If the pregnant women had a genetically abnormal previous child, genetic testing during their second pregnancy is strongly required.
However, there is less chance that the second child will suffer from genetic abnormality until the condition is inherited.
Environmental factors also play an important role in congenital abnormalities besides genetic factors.
Mother’s exposure to mutagens, teratogens, toxins, infections, and UV light are other factors that cause birth defects.
In addition to this, as we said earlier, due to the uneven distribution of chromosomes, birth defects may happen.
Hence the chance for the second pregnancy for any birth defect is very less, still, genetic testing is highly advisable in these cases, for a safer side.
The only case is the inherited genetic condition!
Serious advice– none of the parents are responsible for congenital problems, it randomly occurs in fetus cells therefore don’t blame each other or yourself for that.
Family history of genetic disorder:
Recessive genetic conditions are more dangerous than the dominant one, why?
Because it runs silently in the family and no one knows until it appears dominantly.
In your family, any of your sibling or cousin ever have a genetic disorder (inherited), it might be possible that it may present in your case.
Or if any of your family members is a carrier for any genetic disorder, you should think about genetic testing.
First, visit a genetic counselor, he or she will ask you several questions to rectify your genetic hereditary.
And if a genetic counselor finds any problem, he or she will suggest you for carrier test,
If both of you are a carrier for a particular genetic disorder, there is a 50% chance that your child may have the same condition.
Previous stillborn:
In case of severe developmental and physical abnormalities, stillbirth happens and genetic factors have an immense role in it.
Therefore, if you have a previous history of stillbirth with severe developmental abnormalities you should have to go for pregnancy genetic testing.
Two or more miscarriages:
Two or more consecutive miscarriages are the indication of something not normal with your pregnancy condition.
Some gene mutations and chromosomal aberrations are involved in continuous miscarriages.
Even, some chromosomal abnormality of the fetus also causes miscarriages in either case, during the early stage of your pregnancy you should have genetic testing done.
Genital infections:
Again, if a female was previously diagnosed or currently have any type of genital infection, there is a chance for fetal abnormalities.
If you have a previous history of genital infections, genetic testing is necessarily required.
Note: Before going for it, please take your doctor’s advice. Do as he says.
Types of genetic test:
Not only DNA but chromosomal analysis, as well as an epigenetic profile, is nowadays considered as a genetic test as well. And it should be done because from the DNA test, a chromosomal abnormality can not be diagnosed.
Similarly, by chromosome testing, a gene or DNA mutation can not be identified. Hence either test with or without epigenetic profiling (in some cases) required.
Process of Genetic testing:
Sample collection:
Every test starts with the sample collection. However, unlike the DNA fingerprinting or DNA profiling, blood, hair or saliva sample can not be used here. Here we are dealing with the fetus, a live fetus.
Thus fetus tissue or any biological specimen from the fetus is used for testing. Generally, amniotic fluid or chorionic villi are taken for DNA testing.
Chorionic villus sampling:
A small portion of chorionic or placenta tissue is taken by the gynecologist using the sharp long needle.
Generally, the chorionic villi sample can be collected between 10 to 12 weeks of pregnancy. Then the sample is sent for genetic testing.
Amniotic fluid:
The amniotic fluid is rich with the fetus cells, which can be collected and used for genetic testing.
Unlike chorionic villi sampling, the amniocentesis is done between 15 to 20 weeks of gestation. Using a long-fine needle, amniotic fluid is collected from the mother’s abdomen.
Note: As per my experience, if the women are at 20th or near the 20th week of pregnancy, the amniocentesis is not recommended because of the high risk of pregnancy loss associated with the pregnancy.
The sample is sent to the genetics laboratory in a collection media or saline under strict stringent conditions.
Genetic testing:
Once the sample is received, it is processed for either DNA testing or chromosomal testing.
DNA testing:
For DNA testing, first of all, the DNA is extracted from the sample.
Depending upon what is indicated by the doctor, the DNA test practices using PCR, DNA sequencing or DNA microarray.
For a single gene disorder like sickle cell anemia and thalassemia, PCR is the best option.
Using the PCR, inherited conditions like autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant or X-linked recessive can be diagnosed.
For complex genetic disorders or in conditions where more than two genes are involved, DNA sequencing or DNA microarray is used for pregnancy genetic testing.
Nonetheless, the microarray can only identify known mutations. In the case of some unknown mutations, only DNA sequencing is recommended.
Note: Major deletions, duplications and translocations can not be identified using DNA testing.
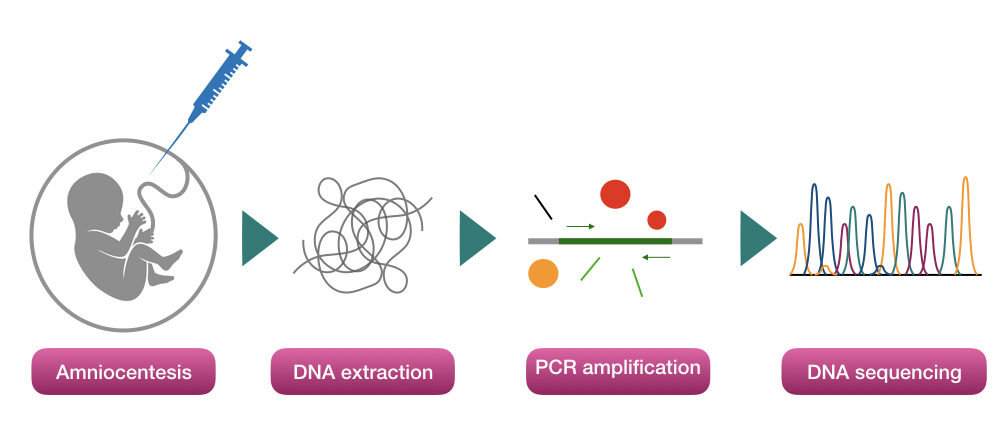
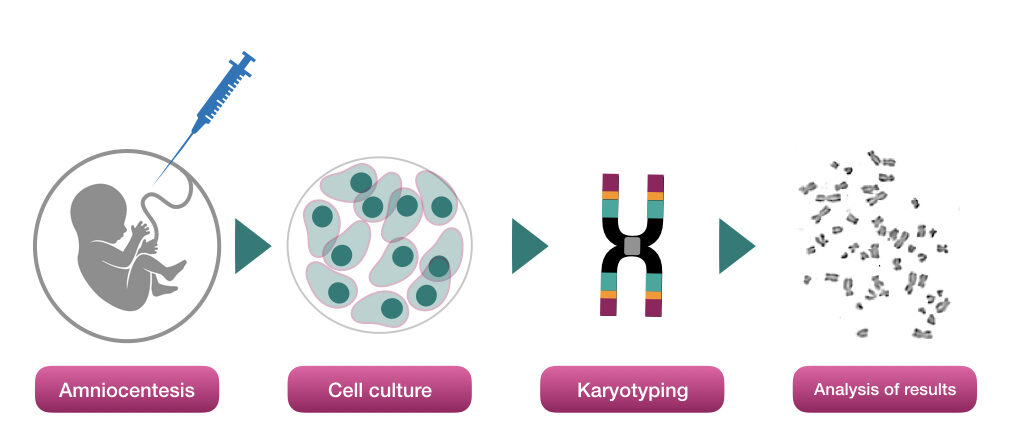
Chromosomal test:
Unlike the DNA testing, the chromosomal analysis is a totally different procedure. The sample must be cultured within 24 hours of collection, in the very first step of the chromosome testing.
It is also known as karyotyping or cytogenetic analysis.
The cells are arrested at metaphase for getting chromosome spread. The harvested chromosomes are now stained or banding is performed for identifying numerical as well as structural chromosomal abnormalities.
Trisomy 13, trisomy 18 and trisomy 21 are diagnosed using the conventional karyotyping method (a chromosomal test).
Notwithstanding, the chromosome testing is not powerful enough to rectify intermediate or minor deletion, duplication or translocations of chromosomes.
For that, another type of cytogenetic test is performed known as FISH-fluorescence in situ hybridization.
The FISH is more powerful, sensitive and trusted than the karyotyping.
Read more karyotyping: A Karyotyping Protocol For Peripheral Blood Lymphocyte Culture.
Cell-free DNA testing:
Cell-free DNA testing is sophisticated and futuristic genetic testing becoming popular nowadays.
A non-invasive prenatal genetic testing method- cell-free fetal DNA is quite a revolutionary approach.
Here, the free DNA fragments present in the maternal blood are isolated and used for genetic testing. Thus it is safer than amniocentesis.
Read more on the present topic here: cell-free DNA testing.
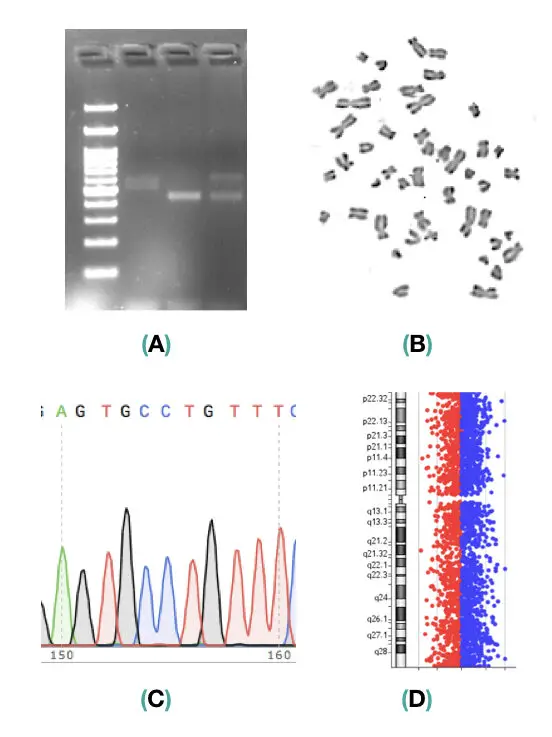
Results and interpretation:
Interpreting and analyzing the results of a genetic test is also a challenging task, required a lot of experience and expertise. Computation software is also needed for doing the same. We are not discussing the results part here because it is a very deep topic.
But some of the results of DNA test, chromosome test, DNA sequencing, and DNA microarray are looks like this, see the image below,
Benefits and risk:
I had read other literature available under the present topic, but unfortunately, not satisfactory enough to justify the topic, only used “benefits and risks of pregnancy genetic testing” as a keyword stuffing.
Anyway, let me tell you what exactly are some benefits and risks associated with DNA testing.
Among all the diagnosis methods available now, genetic testing, especially DNA testing is one of the most accurate and trusted methods.
The genetic testing method is incredibly accurate and reproducible. Based on the results of it one can make decisions to continue the pregnancy or not.
It is above the screening methods, the results of the first trimester and second-trimester screening test are not trusted enough to make a decision.
Take a look at the accuracy of the screening tests here:
| Marker | Probability of down syndrome |
| Maternal age | 95% |
| NT (nuchal translucency) Nuchal fold measurement test | 45 to 50% |
| Combination of PAPP-A, beta- hCG, AFP | 94% |
| Absence of nasal bone | 73% |
| Pyelectasis | 25% |
| Combination of All markers | 97% |
Genetic testing is the final confirmatory test must be performed to validate the screening results.
Besides this, in case of any genetic defects, preventive and management steps can be taken early.
In the case of Down syndrome and severe developmental disabilities one can take a decision to terminate the pregnancy, however, the decision is of pregnant women, solely.
As it is one of the most reliable methods, it helps in making a decision if required.
Nonetheless, besides benefits, several risks and limitations are also there with genetic testing.
One of the major risks for the pregnancy genetic testing is of pregnancy loss or miscarriage.
The chance of miscarriage is associated with amniocentesis and chorionic villi sampling. However, the reported cases are very few.
The present method is invasive, the female has to bear the pain.
Notably, the cell-free DNA is one of the non-invasive options, still, the method is not more reliable and trusted.
The cell-free fetal DNA test can be utilized as a screening method, for now, because it is not standardized yet.
Also, due to the contamination of maternal cells, the chance of false-positive results is extremely high in it.
Anxiety and conflict of emotions are associated with positive results. Which is also a drawback of the present technique.
My opinion:
I had worked in a prenatal genetic laboratory in the past, believe me, it is a very tough task to handle the patient as well as the sample.
We have to deal with the one time very low sample, even the extracted DNA quantity is very less in the case of amniotic fluid and after that, we can’t ask for another sample.
So, it is tougher.
Another important point related to the pregnancy genetic testing is the emotional trauma of a patient is always associated with their pregnancy, especially for the female.
And trust me, it is even very difficult to deal with them and make them understand, although, some females are very supportive in terms of testing as well as spreading the knowledge.
For now, curable options for the inherited genetic conditions are very less, still, gene therapy can be one.
In gene therapy, the faulty or mutant gene is replaced by a healthy one, but it is not as easy as we are talking.
So many risks and ethical issues are involved in it. Further, the success rate of gene therapy is very less and it is not ready for use now.
Always trust your doctor, we know he is not a god but his expertise and suggestions are valuable if he suggests for aborting a child, think on it, however, the decision is of the pregnant woman.
As per my experience and knowledge, genetic testing is one of the trusted methods, even, in the forensic science DNA testing is valuable evidence used for the identification of criminals. Hence it is an unmatched option for now, at least.
Although it is also true that not all the conditions related to pregnancy can be diagnosed using either DNA test or chromosome test.
Conclusion:
Not all the pregnancy required genetic testing, however, in the case of the above-mentioned conditions one should think about it. The testing procedure is tedious and costly but the results are more accurate and trustworthy.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for the latest blogs, articles and updates, and never miss the latest product or an exclusive offer.




Great content! Super high-quality! Keep it up! 🙂