“Y DNA and Mitochondrial DNA tests are used for ancestry patrilineage and matrilineage tracing, respectively. Learn about the differences between yDNA and mtDNA in this article.”
Ancestry genetic testing has been used to biologically trace someone’s ancestors. Three distinct markers— nuclear DNA, mitochondrial DNA and Y DNA are commonly used for this test.
Each marker is distinct, serving a unique purpose in a common process. Mitochondrial DNA and Y DNA, both exhibiting uniparental inheritance, play crucial roles in ancestry genetic testing.
In this article, I will explain the differences between yDNA and mtDNA and how their testing differs.
Stay tuned.
Related article: 8 Reasons Why Is Mitochondrial DNA Inherited Maternally?
Disclaimer: The content presented herein has been compiled from reputable, peer-reviewed sources and is presented in an easy-to-understand manner for better comprehension. A comprehensive list of sources is provided after the article for reference.
Key Topics:
Y DNA vs mitochondrial DNA
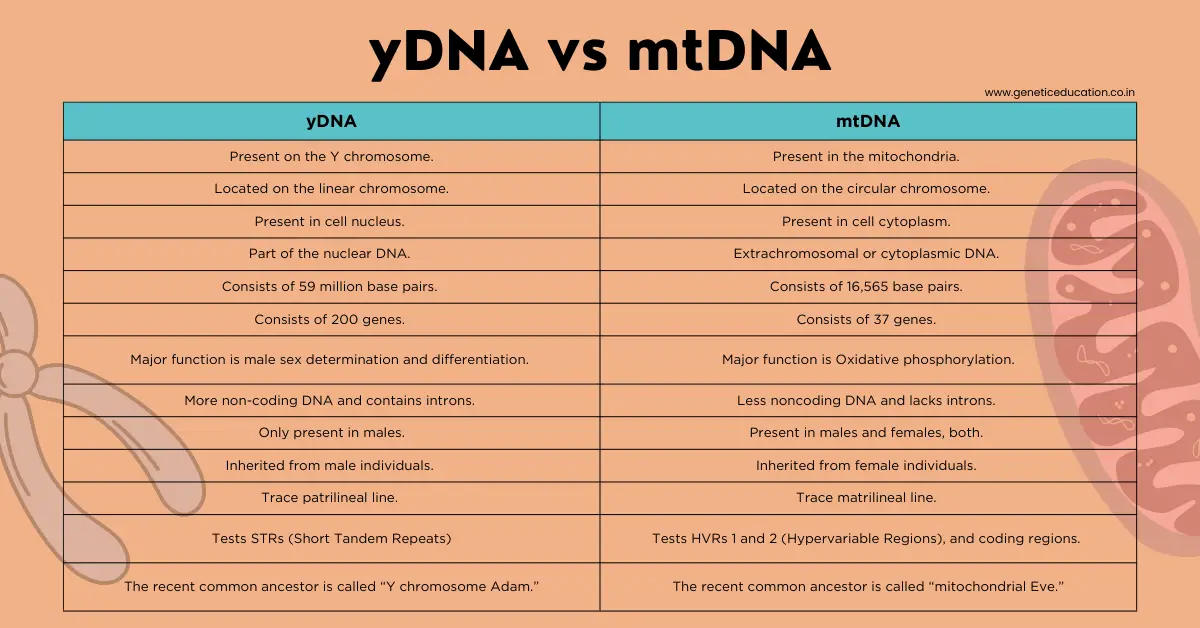
yDNA is located on the Y chromosome whereas the mtDNA is situated in the mitochondria— a cell’s powerhouse which produces energy.
Y chromosome is a type of human sex chromosome and located in the cell nucleus. So yDNA is nuclear DNA, whereas mtDNA is cytoplasmic or extrachromosomal DNA.
The yDNA is located on the linear chromosome and consists of 59 million base pairs, contrary the mtDNA is located on the circular chromosome and consists of 16,569 base pairs.
yDNA contains a total of 200 genes and 72 known protein-coding genes. On the other hand, the mDNA contains 37 genes. Y-linked genes have an exclusive function in male sex determination and differentiation, whereas the mt-linked genes have an exclusive function in oxidative phosphorylation.
A major part of the yDNA is noncoding and contains introns while the major part of the mtDNA is coding and lacks introns.
The y-linked genes produce the monocistronic mRNA, meaning, each protein product from each mRNA while the mtDNA genes produce the polycistronic mRNA, meaning, many proteins from a single mRNA.
yDNA is particularly present in mammals, conversely, the mtDNA is present in animals and plants.
Note:
yDNA is inherited from males while mtDNA is inherited from females, therefore, these genetic markers hold a promising application in ancestry genetic testing.
Related article: Mitochondrial DNA vs Nuclear DNA- Differences and Similarities.
Disease linked to yDNA and mtDNA
Mutations in yDNA and mtDNA can also cause serious health-related complications. Here is the list of various diseases or conditions associated with yDNA and mtDNA.
Diseases associated with the yDNA:
| Genetic Disorder/Condition | Inheritance Pattern | Brief Description |
| Klinefelter Syndrome | Non-Mendelian | Extra X chromosome in males (XXY), leads to infertility |
| Y Chromosome Deletions (infertility) | Mendelian | Deletions or mutations on the Y chromosome |
| Azoospermia | Mendelian | Absence of sperm in semen, linked to Y chromosome issues |
| Swyer Syndrome | Non-Mendelian | XY individuals with female physical characteristics |
Diseases associated with mtDNA:
| Genetic Disorder/Condition | Inheritance Pattern | Brief Description |
| Mitochondrial Myopathies | Maternal | Muscle disorders due to mutations in mtDNA |
| Leber’s Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) | Maternal | Vision loss caused by mutations in mtDNA |
| Mitochondrial Encephalopathy | Maternal | Neurological disorders resulting from mtDNA mutations |
| Kearns-Sayre Syndrome | Maternal | Progressive external ophthalmoplegia and other symptoms |
| Leigh Syndrome | Maternal | Neurodegenerative disorder affecting the central nervous system |
Now let’s talk about some of the differences between yDNA and mtDNA tests.
yDNA vs mtDNA tests
First, the yDNA is inherited from male individuals and present in male individuals, whereas the mtDNA is inherited from female individuals and present in males and females both.
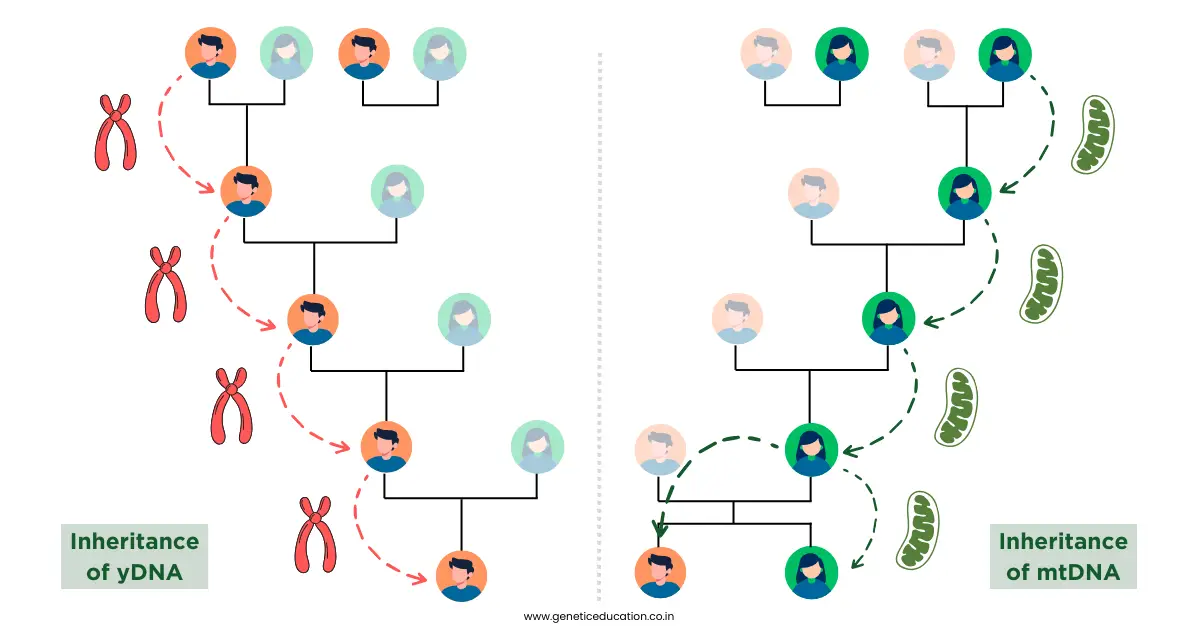
The yDNA test exclusively studies the Y chromosomal DNA and helps establish a patrilineal line. Contrary, the mtDNA test exclusively studies the mitochondrial DNA and helps establish a matrilineal line.
yDNA, as it is only present in males, is used to identify the male individuals from the sample or population. On the other hand, although the mtDNA is inherited from the maternal side, as it is present in both males and females, it can’t distinguish male and female individuals from the sample or population.
Thus, the yDNA test can be used for sex determination and identification, while the mtDNA test can not be used for it.
At a technical level, short tandem repeats (STRs) present on the Y chromosome have been utilized for the yDNA test, whereas HVR1 (Hypervariable Region 1), HVR2 (Hypervariable Region 2) and even coding regions have been utilized in the mtDNA test.
Note that mtDNA lacks STRs and VNTRs (Variable Number of Tandem Repeats).
yDNA vs mtDNA test results:
The yDNA test results provide exclusive and accurate information regarding the male descendent of the family whereas the mtDNA has a high mutation rate and doesn’t provide as accurate information as the yDNA test for female descendants.
In forensic studies, the yDNA test tells us if the sample or evidence belongs to a male or not, whereas, the mtDNA doesn’t provide such gander-related information.
Oftentimes, it is difficult to isolate the yDNA from the older samples, as the nuclear DNA degrades over time. Contrary, the mitochondrial DNA can easily be isolated due to the high copy number.
This is also one reason, why is mtDNA typing used in forensic science and ancient DNA studies.
The yDNA test can trace back to the prehistoric father, ‘Y chromosome Adam’ (the most recent common ancestor of all males) whereas the mtDNA test can trace back to the prehistoric mother, ‘mitochondrial DNA Eve’ (the most recent common ancestor of all females).
Summary:
| yDNA | mtDNA |
| Present on the Y chromosome. | Present in the mitochondria. |
| Located on the linear chromosome. | Located on the circular chromosome. |
| Present in cell nucleus. | Present in cell cytoplasm. |
| Part of the nuclear DNA. | Extrachromosomal or cytoplasmic DNA. |
| Consists of 59 million base pairs. | Consists of 16,565 base pairs. |
| Consists of 200 genes. | Consists of 37 genes. |
| Major function is male sex determination and differentiation. | Major function is Oxidative phosphorylation. |
| More non-coding DNA and contains introns. | Less noncoding DNA and lacks introns. |
| Only present in males. | Present in males and females, both. |
| Inherited from male individuals. | Inherited from female individuals. |
| Trace patrilineal line. | Trace matrilineal line. |
| Tests STRs (Short Tandem Repeats) | Tests HVRs 1 and 2 (Hypervariable Regions), and coding regions. |
| The recent common ancestor is called “Y chromosome Adam.” | The recent common ancestor is called “mitochondrial Eve.” |
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, both yDNA and mtDNA tests are integral to ancestry genetic testing, tracing paternal and maternal lineages, respectively.
While yDNA is challenging to isolate from aged samples, it uniquely provides information on maleness traits and matrilineal tracing, making it advantageous over mtDNA. Both tests are essential for comprehensive ancestry tracing.
Share this article with friends and bookmark the page for future reference.
Sources:
Quintana-Murci L, Fellous M. The Human Y Chromosome: The Biological Role of a “Functional Wasteland”. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2001;1(1):18-24. doi: 10.1155/S1110724301000080.
Habbane M, Montoya J, Rhouda T, Sbaoui Y, Radallah D, Emperador S. Human Mitochondrial DNA: Particularities and Diseases. Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 1;9(10):1364. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101364.


Hey, your website is seriously impressive! I’m thoroughly enjoying the informative content and the relaxed design—it’s like the most welcoming playground ever. Big kudos for the dedication! Let’s connect soon and brainstorm some seriously awesome ideas.
I needed to thank you for this excellent read!! I
definitely loved every bit of it. I have got you bookmarked to
check out new things you post…
Thank you paul