“mRNA is a messenger RNA, present in the cell cytoplasm and translates into a functional protein (amino acid sequence). However, it’s entirely different from DNA. Here are some of the important properties of mRNA.”
DNA and RNA, as nucleic acids are two important components of our cells. Without which we are nothing; in fact, we even can’t survive. DNA is something well-explored, established and studied thoroughly, conversely, RNA is mysterious.
RNA is amazing! Less-studied, many types and very important. Specifically, mRNA is very important for gene expression studies. Gene expression is defined as the amount of protein a cell produces from a gene.
So after removing all the non-coding elements, the coding sequence carrying mRNA forms the protein, and thus by studying the mRNA- the amount of mRNA, the amount of protein can be estimated.
If you are in diagnostics, you know the importance of gene expression studies, but to understand it more keenly, it’s important to understand the mRNA. In this article, I will explain 10 unique properties of the mRNA which no other RNA or even DNA has.
Want to know what those are? Let’s get into the article.
Key Topics:
10 Unique Properties of mRNA
A Type of nucleic acid
Much like DNA, mRNA– a type of RNA is also a kind of nucleic acid. It’s ribonucleic acid. Its structure consists of sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous bases, however, it contains Uracil, instead of Thymine.
Nitrogenous bases in the mRNA are Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil. Notedly, as it carries the message to form the protein, the name mRNA is given.
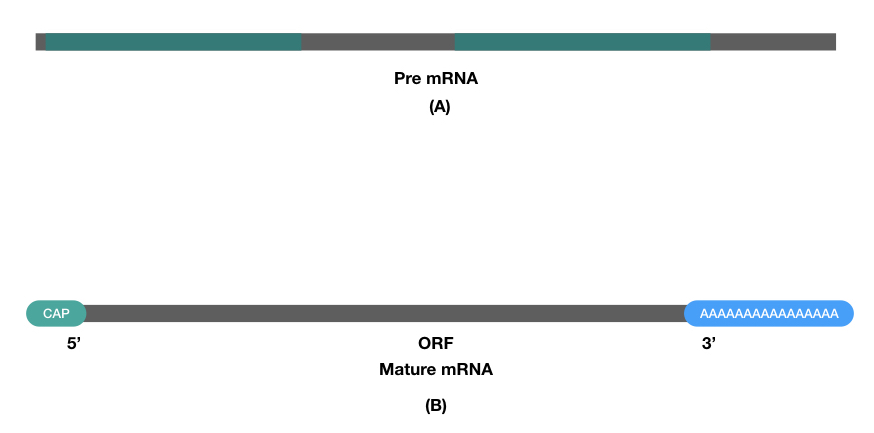
Single-Standard
The very first unique property of the mRNA is that it’s single-stranded. Unlike DNA, which is double-stranded in nature, RNA is– in general, single-stranded. The single-stranded RNA lacks hydrogen bonds and thus can’t associate with another strand.
The single-stranded nature of the mRNA provides a ready-to-utilize template site for enzymes and factors to initiate translation. Polymerase finds a unique site on the single strand of mRNA, settles there and starts translation adding the amino acids.
Fragile
mRNA is, unlike DNA, very fragile. Meaning, it breaks very easily. The denaturation temperature for DNA is around 94°C. Contrary, the mRNA is very fragile and can be easily broken at room temperature, even.
mRNA can be broken only by gentle heating. It starts degrading even at room temperature (37°C).
Shorter in length
The most common nucleic acid- DNA is very long but the RNA isn’t. In fact, in simple language, we can say that RNAs are present in parts. In fact, the microRNA, siRNA, and shRNAs are very short.
While the mRNA and tRNAs are a bit longer than the shorter RNAs. Although the estimated length of mRNA varies from cell to cell it’s very smaller in size than the DNA. Keep in mind that every gene has differential lengthened mRNA which also varies between tissues.
So the exact estimation of mRNA length isn’t possible, but it is much smaller than the DNA.
Low abundance
Yet another crucial property of mRNA is its low abundance nature. See, DNA is much longer, some DNA sequences are coding, some are non-coding and the rest are pseudogenes. Unfortunately, a very small percentage of DNA can encode protein.
Henceforth, a very small amount of mRNA is transcribed from the DNA. Studies suggest that the mRNA has a very low abundance.
Unique poly-A tail
The most crucial property of the mRNA is a long poly-A tail. As the mRNA is highly unstable, to make it more stable and further processable, the process called ‘RNA processing’ adds a poly-A tail to the 3’ end of the mRNA.
Once the mRNA is formed, during the post-transcriptional modification– RNA processing phase, adenylation leads to adding adenine nucleotides to the one end (3’-OH) end of the mRNA and makes it stable.
Note that the poly-A tail is like the authentication ticket for mRNA but doesn’t take part in the process of translation.
Capping
5’-P capping is yet another important property of the mRNA. During the RNA processing, the guanine nucleotides are added to the 5’ end of the mRNA by 5’ to 5’ phosphate linkage and eventually form a cap-like structure on the mRNA.
The main function of the cap is for performing cap-dependent protein synthesis. However, other important functions a cap performs are preventing the mRNA from exonuclease degradation, helping in splicing, recruiting translation enzymes and helping in nuclear transfer.
We can consider this as another factor in the two-factor authentication for the mRNA.
Highly variable
mRNA is an important molecule for life on earth. Because it contains the actual information/message to form a protein. As each cell forms different proteins in a different amount, the amount of mRNA varies between cells and tissues.
In fact, no organisms have the same amount of mRNA. Studies suggest that the highly unstable and fragile nature has a direct effect on the amount of mRNA. In disease conditions, the cell’s mRNA concentration abnormally varies.
Less stable
Another critical property of the mDNA is its less stable nature. Extreme heat, temperature, radiation, abnormal condition or any external stimuli are some factors that directly affect the stability of the mRNA.
In fact, the mRNA should be processed as soon as possible after isolation, as it readily starts degrading at room temperature. Studies suggest that to process the mRNA, for gene expression studies and analysis, mRNA stabilizers are added prior to use.
Nuclear mediated transport
One of the unique properties of the mRNA is that it transports to the cytoplasm, at the ribosome to manufacture the amino acid chain. Once the mature mRNA is prepared– with poly-A tail and cap, in a series of protein-mediated reactions it is transported to the cell cytoplasm.
Protein called nuclear export proteins and a process called nuclear-mediated transportation, the mRNA travels to the cell cytoplasm via nuclear pores. At the ribosome- in the cytoplasm, it synthesizes new proteins using the tRNA.
Related article: RNA: Structure, Types and Function.
Wrapping up:
mRNA is unique in nature, in all senses, then DNA and other RNAs, however, the sole function of the mRNA is to craft an excellent protein. Gene to gene the length and concentration of the mRNA vary.
The mRNA is formed as per the requirement of the cell, sometime, when the mechanism is abrupt, the up or down-regulation of mRNA results in a disease condition. I hope you like this article.
Please share it and read our other articles.


