“A carrier genetic screening test is used to know if a person carries a faulty gene copy for a disease or not. Explore the concept of carrier genetic screening, and why it is for other related information.”
A DNA or genetic test tells us many things regarding one’s health. The study of DNA, genes or chromosomes unveils the genetic status of an individual. Inherited genetic diseases can be uncovered by a genetic test.
Becoming a parent is an exciting journey. However, they should have to go for a genetic test to know the genetic and carrier status of their baby. A carrier genetic screening helps parents make informed decisions and assures their newborn’s health.
Do you want to know what the carrier screening test is and why it is performed? What do the positive and negative carrier screening results mean? This article covered it all. In this article, we will understand the significance of carrier screening.
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
What is a carrier genetic screening test?
The carrier genetic screening test often known as a carrier screening or just a carrier test is a genetic or DNA test that determines if the baby can carry a faulty gene copy or not.
Carrier genetic screening is particularly significant for recessive genetic disorders. For example, Sickle cell anemia or Thalassemia.
“Carrier” in layman’s means, “carry something.” Here, it means, the carrier of a genetic disease, a person who carries a faulty gene copy. It shows the likelihood of getting a genetic disease condition.
Therefore, testing is crucial. It’s noteworthy that carrier screening differs from genetic testing, revealing the inheritance of a mutant gene allele without necessarily affecting the person’s overall health.
Let me explain these things comprehensively. Genetic compatibility is a kind of carrier screening test performed on parents. Now, this is first, important to understand.
GCT shows genetic compatibility between parents. If either or both parents carry a faulty gene copy it can be inherited to their offspring. GCT provides that information.
Anyone can go for carrier genetic screening tests “in general” not only parents. Even, a growing embryo can be tested to know if it carries any faulty gene copy or not.
Related article: Cancer Genetic Testing- What Is It & How It’s Done?
How does it work?
Understand the basic concept first!
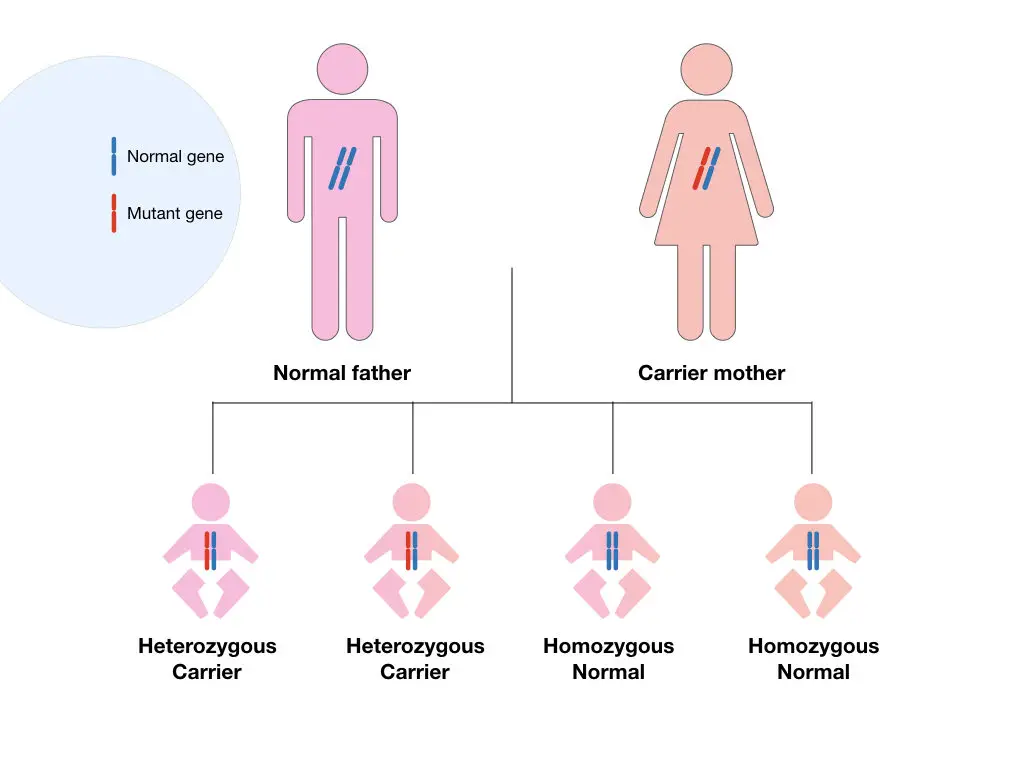
We have two alleles (or copies) for a gene as we have chromosomes in pairs. For example– the beta-globin gene is located on chromosome 11, meaning two copies of beta-globin genes we have, one located on one chromosome 11 while the other located on the other chromosome 11.
We get each copy from our parents and will pass it on to our offspring. If any of the gene copies is mutated, it will be inherited in the same manner and increase the likelihood of getting the disease.
However, here is a small catch!
Carrier screening tests are only advised for the genetic test category called recessive genetic disorders. In this condition, the individual only shows symptoms when they carry both the mutant gene copies, otherwise, will remain normal without any disease symptoms.
Related article: Pregnancy Genetic Testing- What, When and Why
What is the carrier genetic screening test for?
Now, let’s understand why someone has to go for it! what are the benefits or carrier screening?
Parents’ genetic status
The very first benefit of getting the carrier genetic screening is that it allows parents to know whether they are suffering from any recessive genetic condition or not. Or the likelihood of inheriting the allele to their offspring.
The fate of the fetus
It will tell us if the fetus carries a single or both copies of the mutant gene allele or not thereby telling us if it will show disease symptoms or will remain healthy.
Early intervention
Identifying the carrier status allows for proactive health planning. For certain conditions, early intervention can make a significant difference in managing or treating the disorder.
Informed family planning
Carrier screening simply means the likelihood of passing on the genetic disorders from parents to their children. This knowledge can guide family planning. Parents can make an informed decision about continuing the pregnancy or not if the fetus is affected by a complicated and incurable genetic condition.
Reducing population risk
Carrier screening can be especially beneficial for populations with a higher incidence of certain genetic disorders. It allows for the identification of carriers, reducing the risk of two carriers having a child with the disorder.
Reproductive choice
Carrier screening is particularly helpful to both the carrier parents having a higher risk of inheriting the disease. They can opt-in for subsidiary reproductive techniques like IVF or pre-implantation procedures that can reduce the chances of autosomal recessive conditions for the disease by artificial means.
Besides, carrier screening also helps prepare families emotionally and economically in case a fetus is suffering from the disease. These are some of the benefits of carrier genetic screening tests.
Read more: How is the Genetic Testing for Breast Cancer Performed?
Results of carrier screening
For individuals, it is crucial to understand the results of carrier screening. It can be either positive or negative carrier screening results.
Negative results:
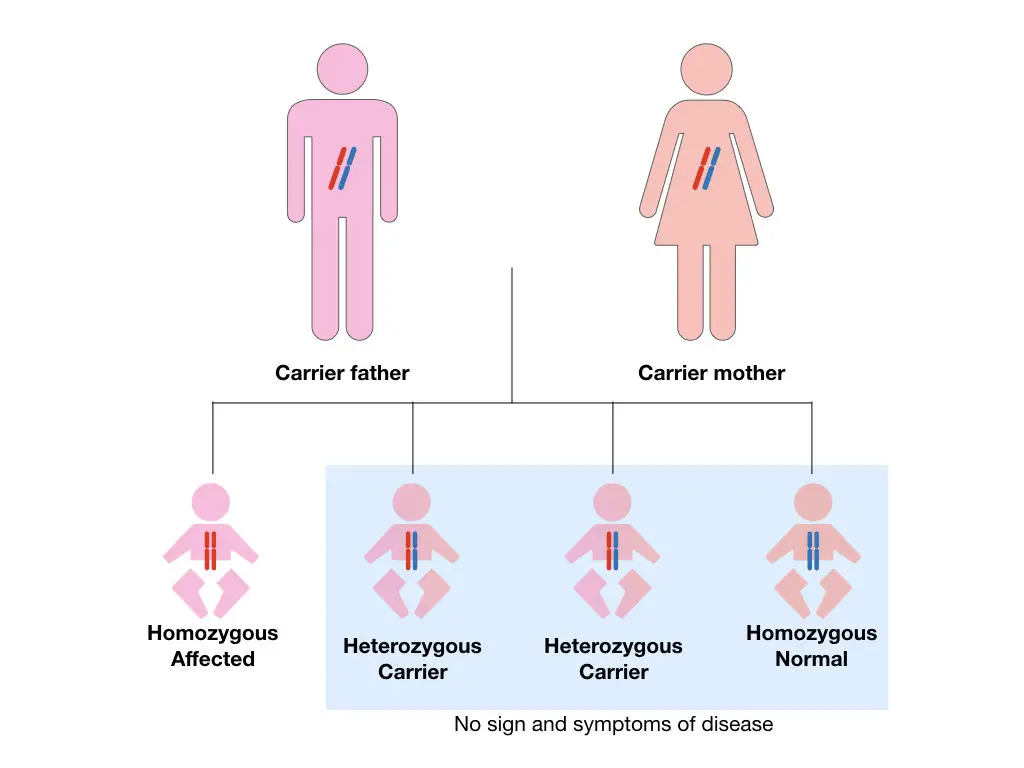
For a single-carrier parent, the chances that the baby will carry the mutant gene is 50% only. Meaning out of 4 offspring two individuals will be a carrier. A negative carrier screening result suggests that no mutations associated with the tested genetic disorders were found in the individual being screened.
The person or the fetus is absolutely normal for the tested recessive condition.
Positive Results:
A positive carrier screening result indicates that an individual carries one copy of a gene mutation associated with a particular genetic disorder. This means they are carriers but typically do not show symptoms of the disorder.
If both parents are carriers, the chances of normal, carrier and affected progenies are 25%, 50% and 25%, respectively.
Is it risky?
Now, in case of the positive results, you wonder about the consequences. Let me answer the question. Carrier condition is not risky or doesn’t carry a likelihood of acquiring the disease symptoms.
However, it shows that the carrier may contribute to spreading the mutant allele to his or her offspring. Individuals with the carrier condition or carrier gene can live a healthy life without any adverse consequences.
Read more: How does Home DNA Test Work?
When to go for it?
Now, you may have questions; does everyone go for it? If not, who can go for it?
Firstly, the present genetic test isn’t for everyone. However, if you don’t know if you or your parents have any genetic condition. You should definitely test for common genetic disorders.
It is required when
- Either of the parents has a recessive genetic condition.
- Previous, personal or family history of genetic disorders.
- The previous child is positive for the carrier test.
- Either of the parents belong to the high-risk population.
- Couples going for IVF or IUI.
List of carrier genetic tests:
| Genetic condition | Gene | Association |
| Cystic Fibrosis | CFTR | Affecting the respiratory, digestive, and reproductive systems |
| Thalassemia | HBB | A group of blood disorders characterized by abnormal hemoglobin production |
| Sickle Cell Anemia | HBB | It leads to abnormal hemoglobin and can result in anemia and other complications. |
| Congenital Deafness | GJB2 | Some forms of inherited deafness result from mutations in genes like GJB2 |
| Maple Syrup Urine Disorder | BCKDHA, BCKDHB, and DBT | An amino acid metabolism disorder. |
| Phenylketonuria | PAH | This metabolic disorder results from mutations in the PAH gene, leading to the inability to metabolize phenylalanine. |
| Tay-Sachs disease | HEXA | Accumulation of harmful substances in the brain. |
| Gaucher disease | GBA | Fatty substances accumulate in cells |
Wrapping up:
Carrier screening is an important genetic test for those covered in the high-risk population. However, the absence of mutations in the tested genes does not eliminate the possibility of being a carrier for other conditions.
Furthermore, it is also important to test other genes or DNA to know if the patient carries other genetic disorders. The process will remain the same as other DNA tests.
I trust you find this article informative. It is intended for informational purposes and for students seeking knowledge for a career screening test. However, decisions should not be solely based on this information for parents or patients. It is strongly advised to consult with your doctor for personalized guidance.