Approximately 10% of breast cancer are genetic, the genetic test for breast cancer is performed using techniques like a polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequencing or DNA Microarray.
Breast cancer is one of the most common types of carcinoma that occurs especially in the female, also happens in males too, rarely. Though the genetic basis of breast cancer isn’t understood fully! Some candidate genes are involved in it.
BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are two main candidate genes present in 90% of inherited breast cancer types. Other genes like NF1, P53, STK11, ATM, PTEN, CHEK2, PALB2 also have a role in it.
Gene mutations cause serious problems for a person, cancer is one of them. Techniques like a mammogram, MRI and physical examination are enough to diagnose breast cancer, genetic testing must be required in the case of familial breast or ovarian cancer.
State-of-the-art genetic testing facilities like a polymerase chain reaction, DNA sequencing and DNA microarray are good options to detect or examine the prognosis of hereditary breast cancer types.
It is also known as the BRCA genes testing as only two candidate genes are routinely screened to detect alterations.
The PCR and sequencing are amplification-based methods while DNA microarray is a method based on hybridization. Interestingly only the DNA sequencing technique is powerful enough to identify new variants or alleles or mutations.

In the present article, I will explain various techniques used for genetic testing for breast cancer. Who can go for the test and when the test is advised. Also, I will try to explain the results and outcome of the testing.
Related article: Breast cancer genetics: Genes, Mutations, Inheritance pattern, Testing and Diagnosis.
Key Topics:
What is a genetic test for breast cancer?
Comprehensively, the genetic test identifies alterations in the DNA, genes or chromosomes and identifies new mutations or alleles associated with the disease.
Various techniques are employed to study different types of alterations, for instance, a PCR or sequencing identifies gene mutations while karyotyping identifies chromosomal alterations.
Hereditary breast cancer is a kind of carcinoma that occurs by gene mutations of BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. This genetic test identifies alterations in the patients having a previous history of breast cancer in their family through various techniques.
A genetic test for cancer identifies,
- A gene associated with carcinoma.
- Alterations or mutations related to the conditions
- Origin of new allele if present, associated with the condition.
- The inheritance pattern of cancer.
- The inheritance pattern of genes associated with it.
- Association or spread of the tumor to other related persons.
“The Ashkenazi Jewish descent have 10 times more the risk of having hereditary breast cancer than others.”
How is the genetic test for breast cancer performed?
Genetic testing for breast cancer is only performed if advised by the geneticist or genetic counselor. It includes a screening of a gene or genes that have a role in developing breast cancer, especially in hereditary or familial breast cancer.
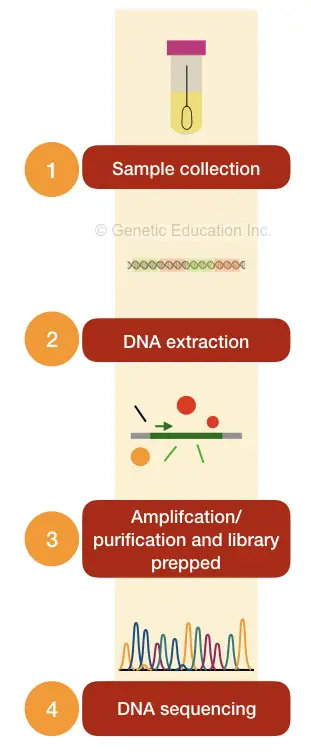
The procedure is similar much like the other DNA testing.
The expert collects a small portion of blood or saliva samples to test genes. Soon after, isolates genomic DNA and performs quality checks for DNA. The quality test includes checking the purity and quantity of the DNA to perform a particular test.
For gene expression studies RNA may also be extracted, although less preferred.
After that the expert processes samples for next-generation DNA sequencing in which the machine detects every nucleotide of two candidate genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 to detect sequence variations.
Sometimes other genes may also be associated with the condition that can also be encountered using DNA sequencing, but as the number of genes increases for sequencing, the cost increases. So doctors first advise to sequence only two candidate genes.
Once the machine completes nucleotide sequencing, the results are computationally analyzed to identify mutations. Sequenced genes are compared against the available data of a normal person in order to detect the abnormality in genes.
The examiner indicates variations if present as the possible reason for the occurrence of breast cancer.
In another technique- polymerase chain reaction; known mutations are screened using various pairs of primers in the thermocycler machine. The machine amplifies DNA using the primer set and on a gel- the agarose gel, the amplicons are run to know the results. The PCR technique is less preferred as only a few ‘known’ mutations can be screened.
Another technique known as DNA microarray-based on DNA hybridization can screen many mutations of breast cancer genes.
In this technique, millions of known probe sets for various alleles or mutations associated with breast cancer are immobilized on a slide. gDNA is employed to hybridize, the detector detects signals of hybridization and collects the results.
Many genes can be screened using the breast cancer microarray or BRCA microarray. Nonetheless, the present technique can’t identify new alleles.
The technique of genetic testing for breast cancer includes these steps:
- Collection of sample
- Isolation of DNA and quality check
- Processing of DNA for testing- PCR, DNA sequencing or DNA microarray
- Collecting the data and signal
- Processing of data and collecting the results
- Interpreting the results
Techniques used in breast cancer genetic testing:
BRCA1 and BRCA2 by MLPA assay:
Deletion or duplication- copy number variations in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 are also another concern for testing breast cancer. Copy number variation is when the number of copies of a gene changes.
When deletion or duplication of more than 1Kb happens, is categorized into the CNV and can be detected using the MLPA assay. A total of 81 CNVs for BRCA1 and 17 CNVs for BRCA2 are present and can be screened using the present method. However, the number of copies may vary in different populations.
For instance, a few copies of a gene in one population or large copies in another population, the reason for that is duplication or deletion effect. The copy number variations in the case of BRCA1 and BRCA2 are detected using the MLPA assay.
MLPA acronym as Multiplex Ligation- dependent Probe Amplification technique is based on the amplification in which CNV specific regions are amplified using the sets of probes.
Different probes for different CNVs are employed for amplification in a multiplex reaction and the final results are analyzed using the capillary gel electrophoresis.
Read more: Multiplex PCR.
Detection of SNPs by NGS:
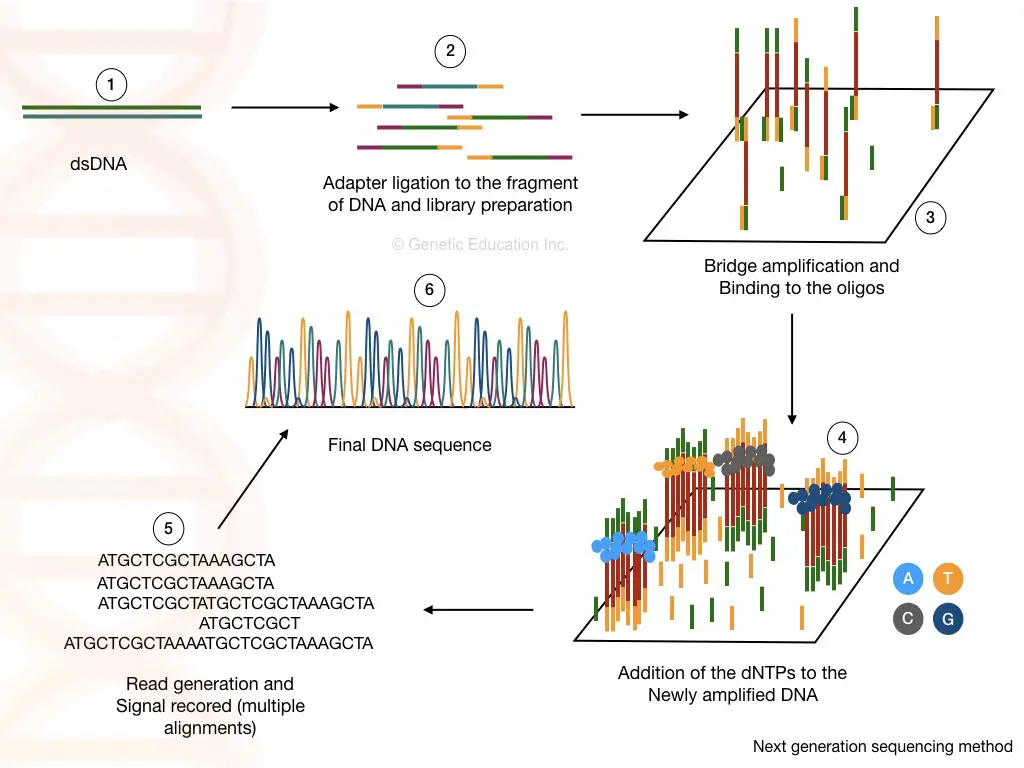
NGS- next-generation sequencing technology is high throughput, highly accurate and rapid technique to screen the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes to identify the single base or single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Known and unknown SNPs are detected using the NGS. In the process, the genomic DNA is isolated and amplified in the PCR and fragments of different lengths are generated to create the library.
The library is employed first for bridge amplification followed by sequencing of nucleotides. Every single nucleotide is sequenced and if a change occurs, the machine recognizes it.
Note that NGS can also detect other minor deletions and duplications too along with the single nucleotide polymorphism. It notes results in the form of various colored peaks.
HRD assay for detection of breast cancer:
The homologous recombination deficiency assay is used to detect DNA damage and genetic instability in the case of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. The role of both genes in homologous recombinants is known to us.
The HRD assay detects the amount of genetic instability or DNA damage occurs through external or internal stimuli which causes tumor. For instance, how much genetic instability arises due to platinum salts and PARP inhibitors.
Results of genetic testing for breast cancer:
The negative results:
Negative results don’t give relief to patients in the case of genetic testing. The true negative results indicate the tested gene mutations are not present in the person, though he or she may carry other gene mutations or alterations.
The negative results are hard to interpret, as it can’t give more idea about the condition of breast cancer.
Suppose if a person tested for only the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes and tested negative, it indicates that the mutations of the BRCA genes are not present in the person or in their family but may carry some other gene mutations.
In that case, other gene tests advised.
Conclusively, true negative indicates the same risk of getting breast cancer as the general population.
The positive results:
The positive results indicate the presence of mutant allele or mutations in a gene tested.
But here also,
The positive results don’t mean that the person may carry breast cancer. The positive results are helpful in predicting the likelihood of cancer if any of the family members has previously tested for the same.
Uncertain results:
The genetic test is not a standardized test to defect every type of hereditary breast cancer therefore uncertainty and ambiguity in results may occur. There are several conditions that strongly indicates uncertainty in results, are;
Even though mutant variants in the family, gene testing may show negative results (uncertainty). Any of the mutant alleles are present in the family of the patient, he or she carries cancer but gets a negative result.
In another scenario, some new mutations are obtained by genetic testing which is not reported previously. In those conditions, the results can’t be conclusive.
In which conditions a genetic test for breast cancer is advised?
Genetic testing is costlier techniques and other social, personal, ethical and emotional issues are associated with it and therefore not advised commonly to all. Doctor prefers genetic testing in cases enlisted below;
If a person undergoes testing has a previous history of hereditary breast cancer in their family.
Any of the patient’s family members having hereditary breast cancer.
Mutant alleles present in the family of the patient.
The patient above the age of 30.
Presence of breast cancer in patients above the age of 40.
Genetic testing, genetic counseling and breast cancer:
All the genetic tests should be performed if a doctor or genetic counselor gives advice for it. The process of genetic testing especially for breast cancer is uncertain because there are so many factors associated with it.
Therefore it is very important for a genetic counselor to do a risk assessment for the likelihood of getting hereditary breast cancer. Genetic tests are costlier and may cause mental and emotional issues for a person, only a genetic counselor helps you to understand the test, procedure, outcomes and other related things.
Conclusion:
Conclusively the genetic testing for breast cancer isn’t the only technique used to encounter all types of breast cancer. However, it plays a very important role in hereditary breast cancer. BRCA1 and BRCA2 are the two candidate genes in the present condition.
Nowadays many different assays and techniques are available to test the BRCA genes in various assays. The most common technique for genetic testing is DNA sequencing- more precise, accurate and fast.
Common FAQs:
Is genetic testing for breast cancer worth?
Genetic testing or the DNA test for breast cancer tell a patient if the condition is inherited or not. Their progenies have a 50% chance of carrying breast cancer mutations.
The post-treatment or chemotherapy DNA damage can also be determined through it. It also tells a patient of having a chance of getting breast cancer and one can eliminate the harmful allele from their family over a period of time.
Hence we can say the genetic testing is worth it in case of hereditary breast cancer.
What to do in case of positive results?
If you tested positive for breast cancer genetic testing, don’t panic. Contact your genetic counselor and ask them about it. The positive results don’t mean that you have or you may suffer from breast cancer.
It only indicates that you have a mutation or the harmful allele that likely causes breast cancer. In the case of positive results your chances of getting breast cancer increases in comparison with the normal population.
Note that it doesn’t mean you will suffer from it. It just shows the chance of predisposition of the tumor.
How long does it take to get the results of breast cancer genetic testing?
Testing genes is a long process and takes time. Patients have to wait for one or two weeks to collect the results.
At what age one should go for BRCA gene testing?
One can go for gene testing for BRCA after the age of 18, it is advisable to go for breast cancer genetic testing between the age of 20 and 30. Although at any age one can go for genetic testing.
In which conditions the genetic testing for breast cancer is advised?
Genetic testing for breast cancer is advised only if a patient has a previous history of breast cancer, familial ovarian or breast cancer, breast or ovarian cancer in close relatives and previous history of breast cancer.
How expensive is breast cancer or BRCA genetic testing?
Genetic testing is costlier compared to other tests. Various testing procedures starting from MLPA to next-generation sequencing are involved in the BRCA gene testing hence the cost may vary also.
In the USA the breast cancer genetic testing cost around $450 to $4000 and covered under the insurance as well.
How accurate is breast cancer genetic testing?
Genetic testing is 99.99% accurate.
—–End of the article—–
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for the latest blogs, articles and updates, and never miss the latest product or an exclusive offer.