“Gel-loading dye is often used during electrophoresis to monitor the migration. Learn about the loading dye and its types in this article.”
DNA is a colorless and odorless molecule. Thus, it can not be studied directly. So when we run the DNA in an agarose gel electrophoresis, it can’t be seen and hence can’t be monitored. Resultantly, DNA can overrun the gel.
And when we observe the gel under the UV-transilluminator, we see nothing! What’s the solution here? If we add a colored substance that can run ahead of our sample, we can easily monitor the migration, won’t we?
Loading dye, often known as tracking dye, does exactly the same function. It runs ahead of our DNA and helps us track the migration. In this article, I will explain the function, types and properties of a loading dye and how to prepare it.
In addition, I will also explain how you can use it effectively for better results. The present article is written with my years of experience in a molecular lab. I will give you my own recipe for making the loading dye at last.
Stay tuned.
Disclaimer: Information provided here is collected from peer-reviewed resources and re-presented in an understandable language. All the sources are enlisted at the end of the article.
Key Topics:
What is a loading dye?
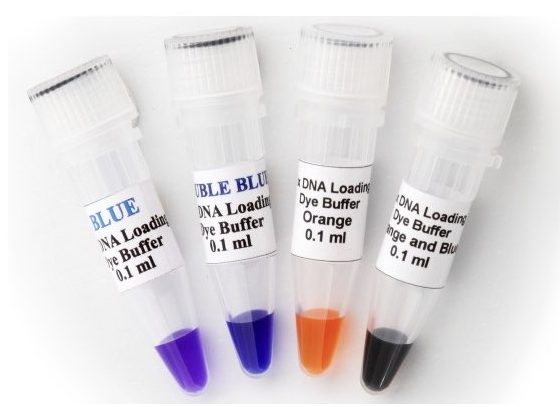
A loading dye, also known as tracking dye or sample loading dye is a dye-based solution added to the sample, prior to load. Bromophenol blue, Xylene Cyanol, Bromocresol Green, Orange G and Cresol Red are common and popular dyes used in electrophoresis.
Each dye has its own advantages and limitations and depending on that it is used in the experiment. The components used in a loading dye or the loading buffer provided help in migration tracking, densifying the DNA and estimating the migration distance.
Functions:
Tracking migration:
The very first and prime function of any gel loading dye is to track the migration. It’s a colored marker that can run alongside the nucleic acid sample. We can visualize it running in the chamber.
At a sufficient distance, we can remove the gel and observe it. Each dye has its own molecular weight and so its own migration rate. For example, BPB and Orange G migrate between 100-300 bp and 50 to 80 bp, respectively.
So the dye can be selected depending on our product size. BPB is used for usual PCR products between 300 to 1500 bp while Orange G can be used for restriction digestion.
We will discuss each dye in a separate section.
Related article: How to Read and Understand Restriction Digestion Results?
Provides density:
Let me tell a short story first. During our master’s dissertation, we decided to prepare a loading dye in our lab, as we were running out of budget. So we prepared a BPB solution (not buffer) as per the indication given with the chemical.
When loading the sample using this BPB solution, immediately it came out of the wells and diffused. That problem was new to us at that time. Our guide knew it but decided, “Let them play.”
We came to know that we had to add something that could hold the sample in a well and prevent diffusion. Adding Glycerol or Ficoll can settle down our sample DNA or RNA at the bottom of the gel well.
Put simply, Glycerol densifies the sample and makes it heavier enough and prevents floating out. Usually, 2.5% Ficoll or Glycerol should be added to the dye solution.
Estimation of migration distance:
For experiments like multiplex PCR and restriction digestion in which we need to separate multiple fragments in a single lane, monitoring sufficient migration becomes crucial.
Using the gel loading dye we can estimate sufficient migration of sample fragments and understand if they are sufficiently separated or not.
Other functions:
Besides, if Tris and EDTA are used in the loading buffer (which is usually provided in a kit), they maintain the pH of the sample and protect it from nuclease degradation.
These are a few important functions of the tracking dye, however, an ideal dye should have the following properties to use in the gel electrophoresis.
Properties of a loading dye:
- The dye should not interfere with the results to improve the effectiveness and quality of the results. For example, BPB is a dark blue dye, if it runs along with the DNA fragment and overlaps it, it makes interpretation difficult.
- The dye used as a tracking dye should have enough contrasting color. It should not mix with the color of a fluorescent dye used for monitoring purposes.
- The components of a loading dye or buffer should not interact with either sample nucleic acid, agarose gel or even gel running buffer. Such interaction may negatively impact the integrity of DNA or RNA and overall results.
- The loading dye should be temperature stable. Oftentimes, current increases the temperature of a gel. In such a condition, the loading dye should remain stable.
- It should not diffuse, degrade or break down during the run and remain stable. High stability provides a uniform migration pattern.
- The loading dye should have a uniform banding pattern.
- Most importantly, it should be non-toxic and safe to use.
- It should work independently and should not alter the pH or buffering capacity of the running buffer.
- It should have minimal UV absorbance so that it can’t interfere with the analysis part.
- Lastly, the loading dye should be affordable and easy to use.
Related article: TAE vs TBE buffer for Agarose Gel Electrophoresis.
Types of loading dye:
Bromophenol blue, Xylene Cyanol, Orange G and Cresol Red are the four most popular and common loading dyes. Here I am explaining each loading dye in detail.
| Bromophenol blue | Xylene Cyanol | Orange G | Cresol Red | |
| Chemical name | 3′,3′′,5′,5′′-Tetrabromophenolsulfophthalein sodium salt | sodium 4-{(Z)-[3-methyl-4-(ethylamino)phenyl][3-methyl-4-(ethylimino)cyclohexa-2,5-dien-1-ylidene]methyl}-3-sulfobenzene-1-sulfonate. | 1-phenylazo-2-naphthol-6,8-disulfonic acid disodium salt | o-cresolsulfonephthalein |
| Chemical formula | C19H9Br4NaO5S | C25H27N2NaO6S2 | C16H10N2Na2O7S2 | C21H18O5S |
| Molecular weight | 691.94 | 538.6 | 452.37 | 382.43 |
| Color | Blue | Cyan | Orange | Red |
| Banding size | 100 to 300 bp | 4000 to 5000 bp | 50 to 80 bp | 400 to 500 bp |
| Toxicity | Safe | Toxic | Toxic | Safe |
*The banding size is determined on a 1% agarose gel.
How to select a loading dye for gel electrophoresis:
The more the options, the more the confusion! You may wonder, which option to select.
Ideally, for our routine PCR in which our product would be between 200 to 1200 bp, the BPB dye can be used. However, to improve the effectiveness, a combination of two dyes, for example– BPB and Orange G or Xylene Cyanol can be used.
Such a combination can also help better separation of smaller fragments. In addition, BPB can also be used for DNA sequencing and genomic DNA electrophoresis.
For restriction digestion with smaller fragment sizes, orange G is recommended.
I’d like to inform you that currently, there are ready-to-use mastermix available in the market, and these come pre-loaded with the loading dye. For example– A dye-added PCR mastermix from TaKaRa.
You can use them as well.
Loading dye recipe:
There are so many compositions available on the Internet. Here I am giving you my own recipe for 10X, 6X and 1X loading dye preparation.
10X loading dye:
- 0.42 % (W/V) Bromophenol blue powder
- 25 % Ficoll
- 0.42% (W/V) Xylene cyanol FF (optional)
This is your 10X DNA loading dye composition. Add distilled water as per your requirement.
For example, if you are preparing 100 ml BPB dye, add 0.42 gm BPB powder, 25 ml Ficoll and 0.42 gm Xylene cyanol FF or Orange G (option). Make the final volume up to 10 ml with distilled water.
Note that some recipes add Tris and EDTA optional to this combination but as per my experience, both are not required as Tris and EDTA are already present in the running buffer.
6X loading dye:
The 6X loading dye combination is the most popular and commercially available. To make 6X from the 10X, we can use the formula N1V1 = N2V2 or simply, do the direct calculation.
To make a 6X loading dye add 6 ml composition of stock loading dye (10X) to 4 ml buffer or distilled water.
1X loading dye:
To make 1X loading dye add 1 ml from the stock (10X) loading dye to 9 ml buffer or distilled water.
How do we use a loading dye?
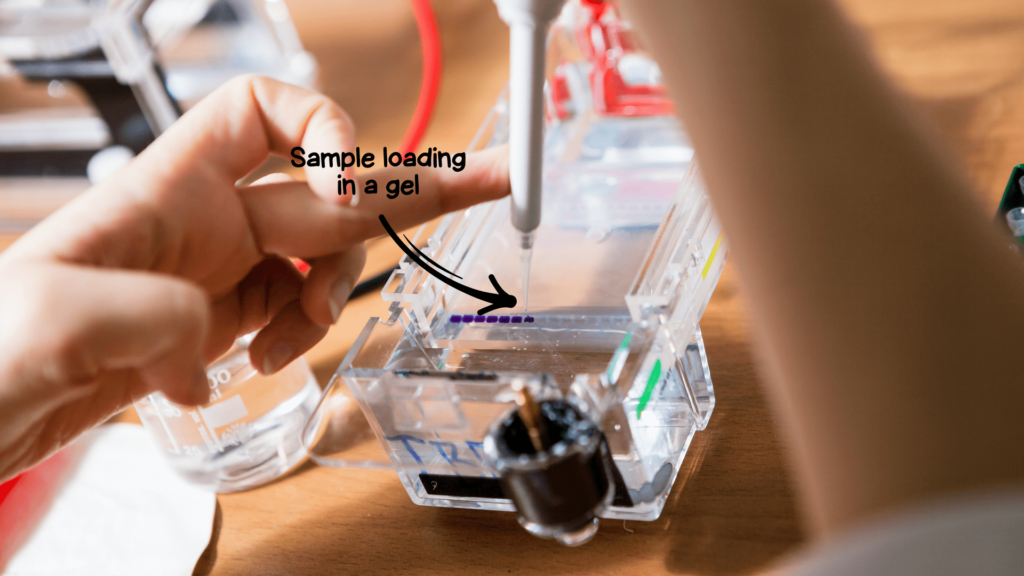
- Approximately 10μl sample is added to a gel well. For that 3μl loading dye is added to a 7μl DNA sample.
- On a parafilm, drop 3μl BPB dye– 5 samples 5 drops, 6 samples 6 drops, etc.
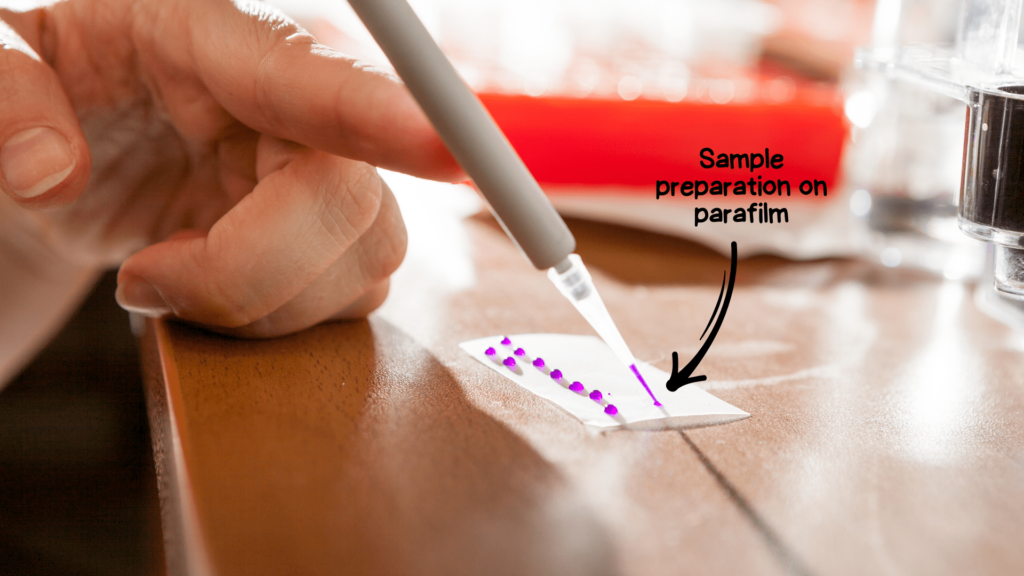

- Now take a 7μl sample and mix it with the 3μl drop of the dye.
- Set the pipette at 10μl, collect the mixture and load it into the gel.
- This technique is time-consuming, error and contamination-prone.
- To make things more comfortable, you can use my method. Roughly add 8 to 10μl BPB dye directly into the PCR tube, mix well and load 10μl. This technique is more convenient but has two major limitations.
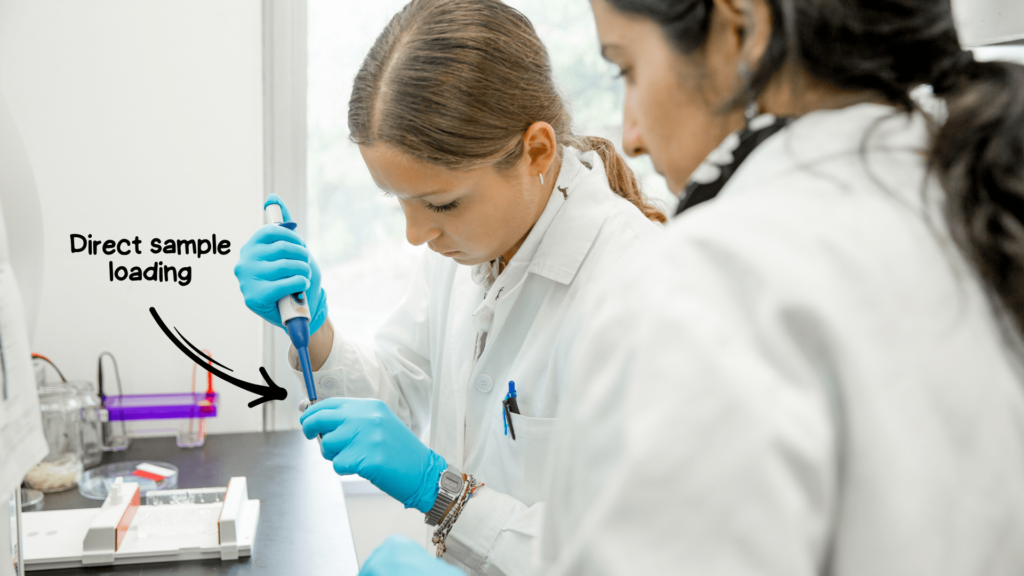

- If we have to use the products for downstream applications like sequencing or restriction digestion, avoid direct use of dye or ready-to-use dye-based master mix.
- This technique utilizes more reagents and cost.
Note:
3μl DNA and 1 to 1.5μl DNA ladder is added to 7μl and 9 to 8.5μl BPB loading dye, respectively for gel electrophoresis.
Wrapping up:
Tracking nucleic acid migration is so crucial during gel electrophoresis, it can produce many problems, queries and questions, otherwise. Bromophenol blue is by far the most popular and convenient option.
For cost-cutting, you can prepare the loading dye in your lab and that’s sufficient for so many experiments. Give it a try, it’s easy! I hope you like this article. Share and let me know if you have any questions.
Sources:
Lee PY, Costumbrado J, Hsu CY, Kim YH. Agarose gel electrophoresis for the separation of DNA fragments. J Vis Exp. 2012 Apr 20;(62):3923. doi: 10.3791/3923.


great work…can you also plzz discuss about western blotting.