“The full form of the most common nucleic acid on earth- DNA is Deoxyribonucleic Acid. The function of DNA is to store and transfer genetic information and help organisms to survive on earth. Here I am enlisting 10 types of DNA abbreviations and their full names.”
DNA and RNA are two types of nucleic acid, however, DNA is the most common. It is located in a cell, packed on a chromosome or sometimes present freely in the cytoplasm. Nitrogenous bases, sugar and phosphate are three components of DNA.
Structurally, hydrogen bonds join two nucleotides from opposite strands while phosphodiester bonds join two adjacent nucleotides on the same strand. All the DNA is located on 23 pairs of a chromosome.
nDNA, mtDNA, cpDNA, pDNA, eDNA, cfDNA, ctDNA, rDNA, rcDNA and cccDNA are common terminologies used to explain various types of DNA. Here I am explaining each type of DNA, their full form and function in this article.
Key Topics:
Full form of 10 different types of DNA:
nDNA:
The full form of nDNA is nuclear DNA or nuclear deoxyribose nucleic acid.
The nDNA is found in the nucleus of a cell. It’s also known as the genome and contains a huge portion of the cell’s nucleic acid. Nuclear DNA helps express, inherit and store biological information.
All the nuclear DNA is located on 23 pairs of chromosomes. It contains a total of 23,000 known genes that encode different proteins. A huge cohort of non-coding nuclear DNA helps regulate gene expression.
mtDNA:
The full form of mtDNA is mitochondrial DNA or mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid.
Mitochondrial DNA is small, circular or linear, non-nuclear and membrane-bounded DNA present in the powerhouse of a cell, mitochondria. The mitochondrial genome contains a few genes, and regulatory and synthesis proteins.
It has its own synthesis machinery and can synthesize its own DNA and form protein too. Human mtDNA carries some crucial genes that when mutated cause serious abnormalities. Cytoplasmic DNA and organelle DNA are two common and alternative names for mtDNA.
cpDNA:
The full name of cpDNA is chloroplast DNA or chloroplast deoxyribose nucleic acid.
Chloroplast DNA is present in plants and other chloroplast-containing organisms. Akin to mtDNA, the cpDNA is also non-nuclear, circular or linear and membrane-bound DNA. The genome of chloroplast has a few genes and synthesis machinery.
Again like mtDNA, it can synthesize its own DNA, can encode a few proteins too and is also known as cytoplasmic or organelle DNA.
Read our article on organelle DNA, you can get more information on this topic: Organelle DNA- Mitochondrial and Chloroplast DNA.
pDNA:
The full name of pDNA is plasmid DNA.
Plasmid DNA or pDNA is circular bacterial DNA present in the cytoplasm. The plasmid contains its own genome, free from the bacterial chromosome and carries some important genes like antibiotic-resistant genes which helps the bacteria to survive.
A bacterium contains more than one plasmid in its cytoplasm because each plasmid exhibits a different function. Some common bacterial plasmids are F-plasmid, col-plasmid, v-plasmid, d-plasmid and r-plasmid.
Interestingly, the plasmid can be edited and used for gene transfer experiments in genetic engineering. To know more about plasmid DNA, read this article: Plasmid DNA- Structure, Function, Isolation And Applications.
rDNA:
The full name of rDNA is recombinant DNA.
In genetic engineering, rRNA or recombinant DNA is an artificially synthesized DNA prepared by the joining of two different DNA, gene segments or nucleotide sequences.
Recombinant DNA is used for producing recombinant proteins, altering gene function, restoring a gene function, creating artificial mutagenesis and studying sequence alterations. Hence, it is applicable in plant research, GMO studies, gene therapy and other fields of genetic engineering.
To know more about rRNA read this article: Definition of Recombinant DNA (rDNA).
cfDNA:
The full name of cfDNA is cell-free DNA or cell-free fetal DNA.
cfDNA is a term used in the prenatal genetic field. DNA testing by cfDNA is a non-invasive method but is less effective. In this technique instead of precious amniotic fluid, directly, the fetal DNA is tested for screening any genetic abnormality.
Studies show that fetal DNA, to some extent, circulates into the mother’s blood. Scientists isolated this DNA and used it for testing. The amount of cfDNA obtained is very less. To learn more on this topic you can read this article: Cell-Free DNA Test- What is it & How to do it?
eDNA:
The full name of eDNA is environmental DNA.
The DNA obtained from any environmental sample and used for DNA testing is known as eDNA or environmental DNA. The eDNA may be mitochondrial or nuclear DNA shredded by any organism in the environment.
Sources of eDNA are feces, urine, hair, skin shred, water (pond, sea or river), soil or any natural sources. eDNA is used for identification, metabarcoding, metagenomic analysis or phylogenetic analysis.
To know more you can read this article: What Is Environmental DNA?
Related articles:
- What is Metagenomics?-Definition, Steps, Process and Applications.
- What is a Phylogenetic Tree and How to Construct it?
- Importance of Molecular Phylogeny
rcDNA:
The full name of rcDNA is relaxed circular DNA.
rcDNA is a specialized form of a natural type of DNA found in viruses like HBV (Hepatitis B virus). It’s a partially double-stranded circular DNA but with a discontinuous positive and complete negative strand.
Such forms help the viral DNA to stabilize, convert into cccDNA and better replicate. To know more about the present topic you can read our previous article: What is rcDNA?- rcDNA vs cccDNA.
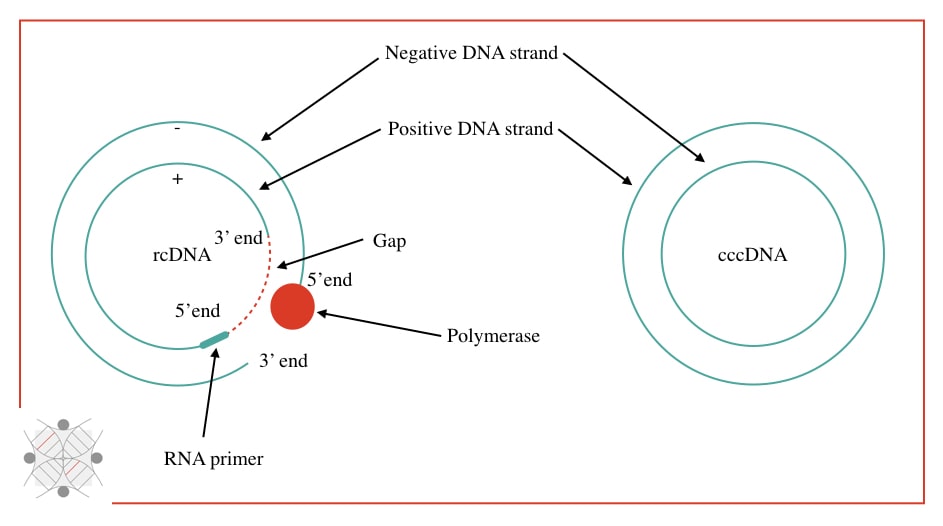
cccDNA:
The full name of cccDNA is covalently closed circular DNA.
cccDNA is a double-stranded DNA covalently closed end to end. The 5’ end of one strand is bound with the 3’ end and the 3’ end of another strand is bound with the 5’ end. It does not contain any gap or discontinuity.
It is a temporary form of the DNA that forms during the intermediate step ahead or replication in some viruses like HBV. cccDNA lacks supercoiling.
ctDNA:
The full name of ctDNA is circulating tumor DNA.
Circulating tumor DNA is fragments of DNA that are circulating in the blood. This DNA is released from cancer or tumor cells and freely floats into the blood. ctDNA is an important cancer marker and helps scientists to understand cancer.
I just read about ctDNA while researching this article. So I am planning to write one dedicated article on this topic later.
Wrapping up:
DNA is an amazing and mysterious entity as I always said in many of my articles. As we explore more, we get much more information. And indeed it raises more questions. This article is entirely different, I just have enlisted the full names and a brief introduction of a few types of DNA.
This article will let you understand some unknown types of DNA and encourage you to learn about it and add more knowledge to this community. Hope you like it. Do share with your friends.



