“Over the past few years, environmental DNA has become a popular subject of discussion in the scientific community. Discover what eDNA is and how scientists utilize it for biodiversity and ecology studies, in this article.”
Do you know, a single liter of seawater contains billions of DNA fragments making it possible to identify thousands of species through eDNA analysis? That’s pretty insane, Isn’t It?
Environmental DNA, eDNA for short, is a technique to study DNA obtained from environmental samples like– soil, water or seawater. The concept is based on the fact that organisms shed or leave behind their DNA or biological material containing DNA in nature.
Scientists collect these samples, isolate DNA and perform various experiments to identify, study and find the origin of a DNA fragment. eDNA studies, like microbial studies, are gaining recognition in recent years and constantly evolving at a rapid pace.
The present techniques have been used in the environment, ecology and conservative studies and thus, proved a valuable tool in various fields. However, the core element of the technique relies on molecular genetic techniques such as DNA extraction, PCR and DNA sequencing.
In this article, I will explain what environmental DNA is and how it is beneficial in various fields of science. I will also explain the sample collection and processing, limitations and future endeavors.
Related article: 15 mind-blowing facts about microbes revealed by Metagenomics.
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
What is Environmental DNA?
eDNA or environmental DNA is a mixture of different DNA fragments of various organisms. It is obtained from samples like– soil, snow, and water. Instead of collecting samples from organisms, invasively, eDNA sampling helps study DNA non-invasively.
The concept demonstrates that when organisms perform various activities in their surroundings, they leave behind DNA fragments or biological material. Such samples are rich sources of DNA.
For example,
- When fish, animals or birds are involved in serious fights.
- When animals or birds rub their back or body with stones or a tree.
- When animals urinate or leave behind faeces samples.
- When they bathe in water.
- When they even move from one to another place.
In all these situations dead tissues, cells, mucus, skin or any other biological material are left behind, which is a direct-reach source of DNA. Scientists collect such samples, extract DNA and analyze it.
eDNA, indeed, is a mixture of genomic/nuclear DNA and extracellular (mitochondrial or chloroplast) DNA. It detects species at any stage of life, sex or kingdom. Even dead organisms can also be studied from the samples.
Interestingly, it gives us an idea about the habitat of species. And also, what concentration of biological diversity a particular environment or ecosystem possesses. This technique is so powerful that it enables scientists to identify all the organisms including the prokaryotes if present in the sample.
Henceforth, eDNA sampling and analysis is a valuable tool to study a plethora of tiny, rare and unknown organisms, if they visited the habitat once or many times. Metagenomic analysis is one such related technique that studies microorganisms in their natural ecosystem.
The eDNA analysis also helps to study extinct organisms and their genetic characteristics if present in the sample.
Definition:
Environmental DNA or eDNA is a mixture of DNA fragments shed or left behind by various organisms in their natural habitat and collected from the samples like soil, water, snow or air.
Step and Process:
The process of typical eDNA analysis comprises steps like sample collection, DNA isolation, DNA processing and DNA analysis.
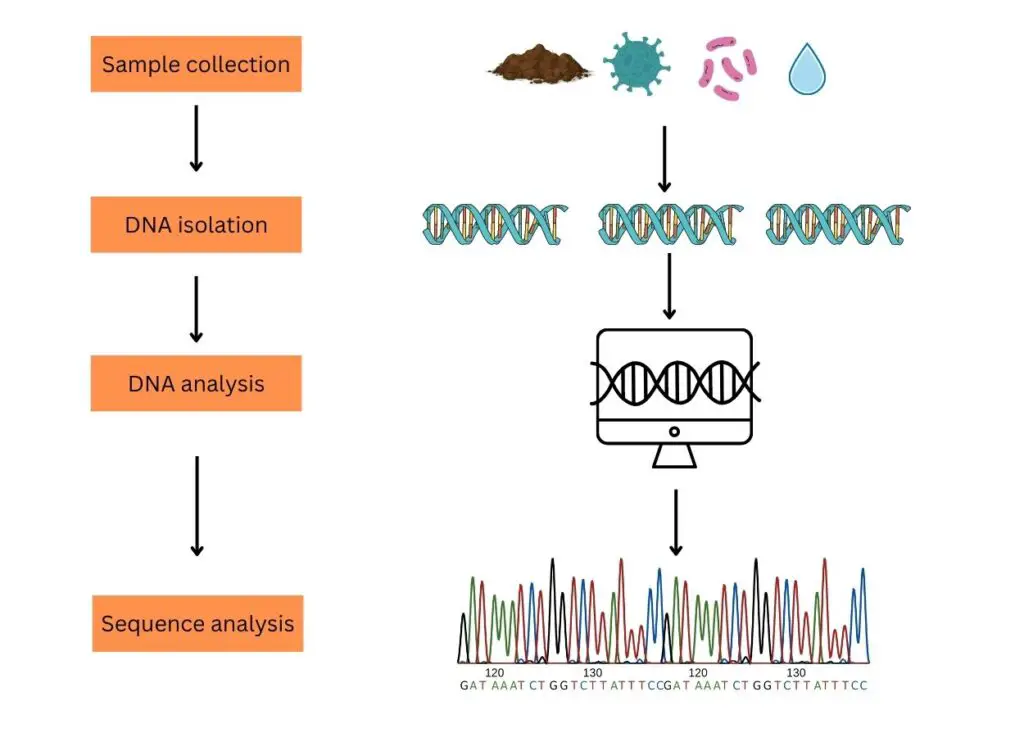
Sample collection:
Sampling for eDNA analysis can be classified into two broad categories. Environmental samples (soil, water, seawater, mud, air and decomposed biological materials) and biological samples (stool, urine, dead skin, mucous, semen or sperm, saliva, eggs, blood, secretion, root, fruit, pollen, leaves, etc).
DNA is prone to degradation. Endogenous nucleases (a class of enzymes that degrades nucleic acid) start degrading DNA soon after cell death. In addition, after releasing in the environment, cells rupture and release fluid in the environment which grows microorganisms.
The effect of exogenous nucleases (by microorganisms) also starts degrading DNA. Note that microorganisms use DNA as a nutrient and use it to repair their own DNA. These two events cause DNA loss.
DNA depurination and hydrolysis are two common causes of DNA degradation in aquatic samples (samples obtained from any water). Furthermore, oxidation and UV radiation can also cause DNA degradation. So to avoid DNA loss these practices should be followed.
- Collect samples in a sterile and clean container, bottle or tube.
- Quickly dry the water sample or place it in the solution containing alcohol.
- Freeze the sample immediately to prevent nuclease activities.
- Do not expose the sample to direct sunlight to prevent UV damage.
- Follow strict environmental sample collection guidelines.
DNA isolation:
Based on the sample type, the DNA isolation technique has been selected. Usually, a ready-to-use eDNA isolation kit is recommended to get good results. Good quality and quantity DNA extraction should be the aim of DNA isolation.
Bead-beating used for metagenomic studies is also used for eDNA isolation from the soil or water samples. After isolation, the quality and quantity of the DNA should be checked before sending it for analysis.
eDNA Processing (PCR and sequencing):
Single-species analysis and multi-species analysis are two strategies to study eDNA samples. In a single-species analysis, only a single set of primers is used to amplify the DNA. A set of primers is designed from the species we want to study and allows for PCR amplification.
In the multi-species analysis or to study thousands of DNA present in the sample, NGS- next-generation sequencing is used. Here, the fragments are amplified and sequenced using the universal set of primers.
eDNA analysis:
Now each sequenced fragment is aligned with the reference sequence database one after another using computational software and a final list of species is generated based on DNA sequence similarities and differences. It also gives us an idea about the organisms present in the environment (from the site of the sample collection).
This process is usually known as the metabarcoding of environmental samples.
Advantages of eDNA:
High sensitivity: The eDNA analysis is sensitive enough to detect low-abundance or low-detection rate species.
Non-invasive: No organism handling, capturing or distribution is required. Thus, it is less stressful for animals and other organisms, and a safer and non-painful sample collection option.
Cheap: The present technique is cheaper than the conventional environmental sampling technique as it requires the least field work or equipment.
Time-saving: eDNA sampling and analysis is a fast and rapid method that gives us results within a day or two.
Universal: The present technique is universally accepted in the study of ecosystems, wildlife conservation and other fields.
Safer: The present technique is relatively safer as it does not rely on cell culture or harvesting.
Technically strong: The analysis is performed at the molecular level. Hence, NGS or PCR-based analyses are so accurate, and precise that give it a strong technical background.
Disadvantages of eDNA
DNA degradation: DNA is subjected to degradation by nuclease activities, resulting in limited persistence in different environments. This poses a challenge in comparative sample studies between different samples. Note that the rate of DNA degradation is influenced by abiotic and biotic factors.
Small fragments: Smaller fragment sizes or inadequate or partially fragmented DNA poses additional challenges as many sequences are highly similar between organisms.
Maternal inheritance: Mitochondrial DNA-based analysis can not allow the identification of hybrid organisms.
False positive results: DNA analysis has higher chances of false positive results when dealing with closely related species.
Challenges in data analysis: eDNA analysis, metabarcoding and metagenomics generate a huge amount of data. It’s difficult to handle, store, process and interpret such a huge amount of data.
Lack of standardization: The field of environmental DNA testing is still growing. Meaning, standard protocols and data for comparative analysis have not yet been fully established. Consequently, differences in results can occur between studies.
Applications of eDNA:
From biodiversity studies to tracking animal migration, eDNA has many lucrative applications in various fields of science. Let us see some of the amazing applications.
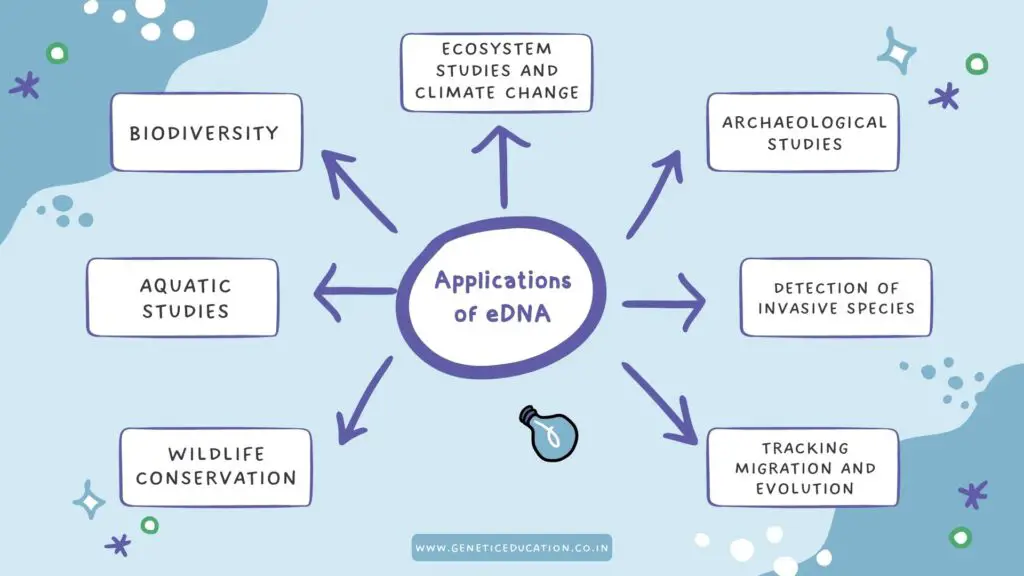
Biodiversity studies:
The very primitive application of eDNA was in studying the biodiversity of various ecosystems in which various species of organisms (plants, animals, fishes, birds, microorganisms, etc) have been identified.
A study published in Trends in Ecology and Evolution (2014) by Kristine Bohman et al. (2014) demonstrated that the eDNA can be used for monitoring and assessing biodiversity for rare and elusive species from freshwater and terrestrial habitat.
Aquatic studies:
eDNA studies are popularly used in aquatic studies, monitoring, conservation and migration. It is used for the detection of common, popular, indigenous and invasive aquatic organisms.
A study published in Biology Letters by Ficetola et al 2008 showed the significance of eDNA over a traditional survey method. They collected water samples to study amphibian species’ DNA and concluded that the eDNA method is an effective tool for aquatic studies.
Archaeological studies:
The present technique is proved to be an amazing tool for archaeological studies. Ancient eDNA samples are studied to trace the migration and evolution events that occurred in various ecosystems.
A study published in Nature Communications Journal showed the significance of eDNA as a tool to study the migration pattern of fishes, birds and even animals across the river. Researchers collected samples from different sites in the Danube River, analyzed eDNA and postulated the migration pattern of fishes, birds and seasonal movement of animals along the river system (Deiner et al. 2016).
Another amazing study published in Molecular Ecology Journal showed the movement of the Pacific giant Salamander (threatened species) in the forest ecosystem. Researchers collected soil samples from various parts of the forest (the potential habitat of the Pacific giant Salamander).
They analyzed the eDNA collected from every soil sample and compared it across the entire landscape over time and were able to create the migration root of the Salamander (Goldberg et al. 2016).
Wildlife conservation:
Environmental DNA is also used for wildlife conservation programs and strategies. It is used to assess elusive and endangered species by looking into the rare DNA traces present in the eDNA samples. Not only that, it is also used to find out the abundance of any species in the environment.
Besides, it is also used for species and speciation studies, forensic analysis, pollution control and ecosystem studies.
Related article: Why Microbial Genetics Is The Future of Microbiology? Comparison and Applications.
Wrapping up:
eDNA analysis is gaining popularity and will continue ruling microbiology, ecology and wildlife fields in upcoming years due to its accuracy, speed and automation. However, scientists have to look after some limitations.
Environmental DNA is a significantly important tool for ecology studies, right now. But tools like metagenomics makes it possible to use it in microbial studies as well. I hope you like this introductory article on eDNA. I will add more value in this vault timely.
Sources:
Deiner, Kristy et al.` Environmental DNA reveals that rivers are conveyer belts of biodiversity information.” Nature communications vol. 7 12544. 30 Aug. 2016.
Janosik, A.M., Johnston, C.E. Environmental DNA as an effective tool for detection of imperiled fishes. Environ Biol Fish 98, 1889–1893 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10641-015-0405-5.
Deiner, K., Bik, H. M., Mächler, E., Seymour, M., Lacoursière‐Roussel, A., Altermatt, F., Creer, S., Bista, I., Lodge, D. M., Vere, N., Pfrender, M. E., & Bernatchez, L. (2017). Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Molecular Ecology, 26(21), 5872–5895.
Goldberg, C. S., Turner, C. R., Deiner, K., Klymus, K. E., Thomsen, P. F., Murphy, M. A., … & Taberlet, P. (2016). Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Molecular Ecology, 25(7), 1424-1435.
Thomsen, Philip Francis et al. “Monitoring endangered freshwater biodiversity using environmental DNA.” Molecular ecology vol. 21,11 (2012): 2565-73.
Bohmann, Kristine et al. “Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring.” Trends in ecology & evolution vol. 29,6 (2014): 358-67.
Ficetola, Gentile Francesco et al. “Species detection using environmental DNA from water samples.” Biology Letters vol. 4,4 (2008): 423-5.



