“Molecular phylogeny is a science to construct a phylogenetic tree by using the nucleic acid sequence information.”
Phylogeny, a branch of genetics and/or evolutionary science, has a specialization in representing relatedness and differences between species and organisms using various parameters.
A computational software-based analysis creates a tree-like view with branches and sub-branches, just like the tree and determines how closely and distantly organisms are related.
However, molecular phylogeny relies on the information of relatedness of gene or DNA sequence between organisms. Techniques like genetic mapping and DNA sequencing are used here. Note that, It not only used DNA but also RNA and protein sequence to construct a phylogenetic tree.
Once the sequence information of various genomes is collected, based on the sequence similarity, organisms are arranged on a phylogenetic tree by computation software.
The present technique is considered one of the accurate phylogeny techniques to construct a tree and classify organisms by their relatedness. But do you know? The molecular phylogeny also provides other valuable information besides classification only.
In the present article, I am explaining the importance of molecular phylogeny and which crucial information it provides. But before that, if you wish to learn more about various types of phylo-trees and how to construct them, you can read our previous article too.
What is a phylogenetic tree and how to construct it?
Key Topics:
Importance of molecular phylogeny
At a molecular level, the phylogeny gives us information about,
- How genes and genomes evolved
- Genetic variations between species
- The evolutionary distance between species
- History of life ib earth
- Classifying protein and genes
- Determination of species and speciation
What is a Phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree, often known as “a tree life” shows the evolutionary relationship between organisms.
Let us understand each point one by one.
How genes and genome evolved:
We know that life on earth evolved from single-cell prokaryotes having a simple but well-organized genome. Over the course of evolution and under the influence of new natural forces genomic changes lead to new combinations of genes.
Natural forces such as mutations, transposition and interaction with the environment are common factors causing change at a genetic level. Genes evolved as per the requirements and for the survival of organisms.
Genetic and evolutionary analysis of a gene depicts that it has several conserved domains since evolution and it is present in almost all organisms which conclude that genes are evolved. However, the presence of the conserved domain ensures proper functionality of a gene.
With this, periodically, the genome acquired new DNA sequences to maintain, strengthen and regulate newly produced genes and their expression. By this means, the genome also evolved.
Genetic variations between and among species
Classification is defined as organizing organisms depending upon their genetic composition. One of the pivotal pieces of information the tree of life provides is the genetic polymorphism between and among species.
It accurately finds and measures the variations by sequencing. This information facilitates the classification of species or organisms. Closely related and distantly related organisms are located near and far, respectively on a tree.
The evolutionary distance between species:
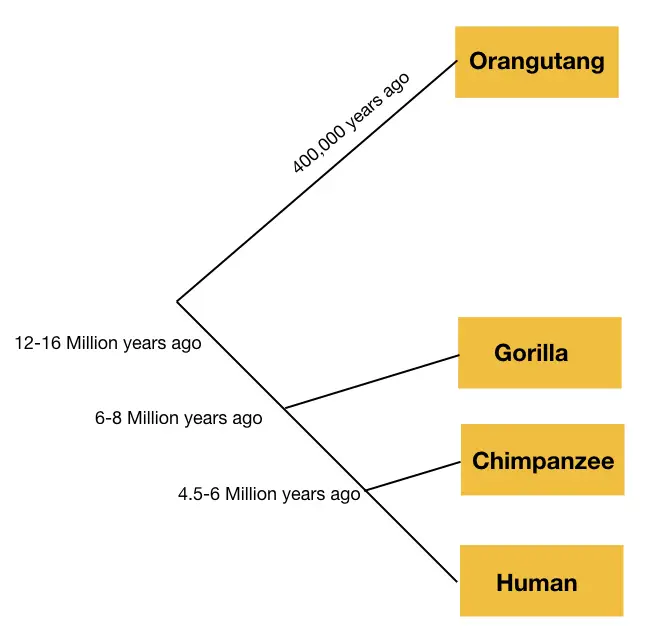
The present technique also provides information regarding the distance between species, accurately. Depending upon the location of each organism on a tree, the distance between them can be calculated using the computation software.
Meaning, it gives us data regarding the lineage or common ancestor of two organisms and when they separated on the course of evolution. Take a look at some data here:
| Organism | Organism | Divergence time |
| Human | Chimp | 4 to 6 million years ago |
| Human | Other mammals | 85 million years ago |
| Human | Fruit Flies | 782.7 million years ago |
| Human | Gorilla | 6 to 8 million years ago |
The above data clearly shows that chimpanzees and gorillas are more closely related to Humans than other mammals and fruit flies.
History of life on earth:
We, humans, are close relatives of Monkeys because we are close enough on the phylogeny hence we have more similar DNA. Such a relationship between organisms can only be established by reading the phylogenetic tree back.
The phylogeny research is based on sequence variation, when we look back we can get information of parental organisms or from where the organisms evolved.
As it also states the distance and percent of relatedness or difference, this meaningful information helps study the history of life on earth.
The phylogeny shows that the prokaryotes were the first inhabitants of the earth and have been present since 3.5 to 3.8 billion years ago on the earth.
Classifying proteins and genes:
Molecular phylogeny not just classifies organisms but also proteins and genes. Sequencing provides the data on relatedness based on that the computer software generates the hierarchy.
This particular method also helps organize genes and proteins by looking into their history, relatedness with other domains; presence on the phylogenetic tree, sequence variations and presence of conserved domains.
Species and speciations:
Speciation is a process by which new species on earth evolve. As aforementioned, desired changes in a genome ultimately evolve new species and consequently create a new branch on a tree.
For instance, we separated from chimpanzees around 6 million years ago. And since then our genome evolved constantly by creating new genes, allelic combinations and genetic variation.
This shows that we and chimps were similar 6million years ago (genetically) but speciation led us to become modern humans.
Origin of pathogens:
Another important consideration of molecular phylogeny is to study and thereby manage the outbreak of pathogenic disease. We can find and study the lineage and evolutionary relation of the pathogenic microbe, track them on the tree as well as the mode of transmission too.
The study eventually helps construct a path of infection or mode of transmission during the outbreak. In addition, investigations of the ancestor pathogen also provide information regarding how often the pathogen gets mutated thereby the frequency of origin of new strains in nature. It provides predictive data and a time frame of epidemiology.
Read more: Genetic Mutations- Definition, Types, Causes and Examples.
Wrapping up:
A phylogenetic tree is an important tool for understanding life on earth, variations among genomes, how life evolved, the distance between organisms and how variations occur.
Techniques like molecular phylogeny broaden our knowledge on genes, genomes and variations within. The predictive modeling based on the tree data can accurately predict the life of organisms and when they will go extinct. Also, it can predict how often and when variation occurs in a gene or genome or an organism.
Sources:
Read more on this topic (External link). Why is phylogenetics important?- ebi.ac.uk.
