“The low expressive MAOA gene variant is associated with extreme aggression and anger and, therefore, referred to as the Warrior gene. It is also involved in criminality and antisocial behavior.“
Behavioral genetics studies behavior, behavioral traits or psychological phenotypes using genetics. It raised contention among scientists because such traits can’t be studied only by genetics.
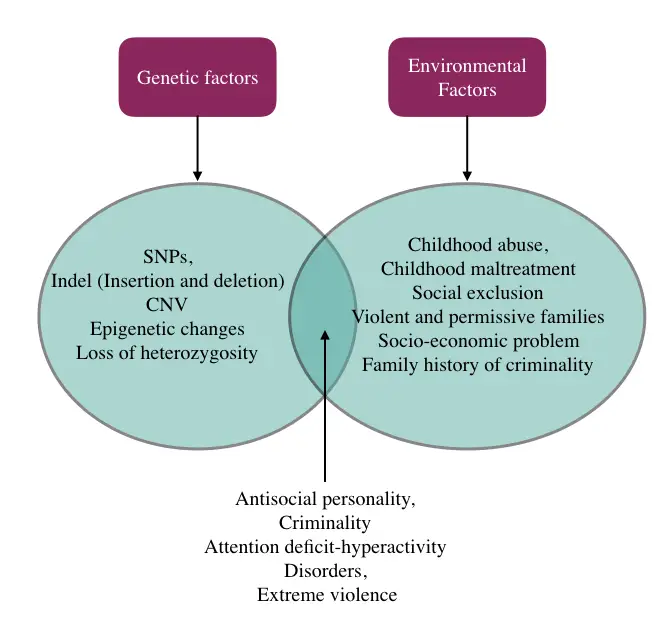
Several examples suggest that some behavioral traits are genetics while some are not. Studies suggest that even though genes govern traits but how it expresses fully depends on an individual’s surrounding environment.
Meaning, that behavioral traits occur through the complex interaction between genes and the environment. Monoamine Oxidase A gene abbreviated as MAOA is one such gene that regulates a specific type of behavior and is important in criminal study.
In the present article, we will study the genetics of the MAOA gene and why it is known as the Warrior gene.
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
What is a Warrior gene?
The MAOA gene that encodes Monoamine Oxidase A enzyme is often known as the Warrior gene because the abnormal variant of the MAOA gene leads to extreme aggression. Biologically, the gene is involved in the neurotransmitter breakdown.
Why is it known as the warrior gene?
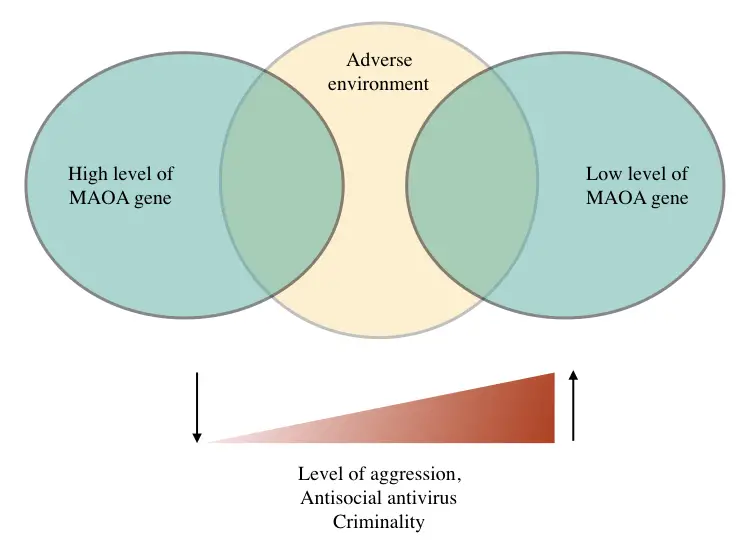
Various studies suggest that due to mutations in the MAOA gene, a low expressive allele of the MAOA causes hyper aggression and anger in people (only when it comes across negative environments like childhood abuse and maltreatment).
How common is the warrior gene?
The normal form of the MAOA (warrior gene), located on the X chromosome is present in both males and females, however, the variant that causes hyper aggression is present in around ~30% of the population.
What is MAOA?
MAOA, short for Monoamine Oxidase A gene, encodes an important mitochondrial enzyme. It is located on chromosome X between X: 43.65 to X: 43.75, cytologically at Xp11.3. The approximate size of the gene is 90.6Mb. It encodes a 527 amino acid protein whose size is 59.6KDa is the Monoamine oxidase A gene (GeneCard, 2022).
Function:
The specific function of the enzyme encoded by the MAOA gene is to break down the neurotransmitters, hence it works in serotonin, dopamine, epinephrine and nor-epinephrine pathways.
Genetics of MAOA gene:
Brunner et al. (1993) reported for the first time the involvement of the MAOA gene in impulsive and aggressive behavior. Their finding suggested that occurring of a Single Nucleotide Polymorphism within the MAOA gene reduces its expression.
The low-expressive MAOA variant upon finding a negative environment such as childhood abuse, childhood malnutrition and social exclusion, results in the development of aggressive and impulsive traits.
In addition, Brunner et al. (1993) further explained that the MAOA-L variant also increases the likelihood of acquiring such antisocial traits in normal populations as we.
Huang et al. (2015) in their article entitled, “Advances in Biomarkers of Major Depressive Disorders” explained how the low transcriptional activity of the MAOA gene causes abnormal behavior, especially in MDD (Major depressive disorders).
They explained that the VNTRs (Variable Numbers of Tandem Repeats) located one after another repetitively have a significant impact on the transcriptional activity of the gene.
The number of VNTR located within the promoter region of the MAOA gene when changed produces a low expressive MAOA-L allele which is directly linked with the MDD.
Studies on the MAOA, ‘Warrior gene’ manifest that it causes hyper aggression and anger, abnormal traits like antisocial behavior, extreme violent crime and criminality (Tielbeek et al. 2017; Rutter, 1997).
In 1996, Brunner and coworkers published a review on the MAOA gene suggesting why such psychological traits are more common among males than females? As the females have two X chromosomes, the healthy MAOA allele masks the effect of the mutant allele in the 46, XX females.
Complications:
Mutations, altered gene expression of MAOA gene and interaction with various extrinsic factors produce various psychological traits some of them are,
- Antisocial behavior
- Antisocial personality
- Borderline mental retardation and autism
- Hyper aggression
- Extreme anger
- Bipolar disorders
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorders
- Major depressive disorders
- Criminality
Various studies on various groups of criminals suggest that the MAOT mutant variant is extremely common among criminals, specifically those who are involved in brutal crimes, repeated extreme violence, homicide, attempts to homicide, assault, and manslaughter.
Read more: Influence of Gene-Environment Interaction on life.
Wrapping up:
MAOA is one of the candidate genes involved in extreme criminality. However, it doesn’t follow any specific inheritance pattern. The magnitude of the governing trait depends on the individual’s past history of maltreatment, abuse or childhood depression.
Tools like genome-wide association studies allow researchers to investigate warrior genes within the context of known SPNs. The cohort of SNPs reported in patients shows the involvement of mutant alleles in trait development. Furthermore, it also suggests the likelihood of getting the same traits in the normal population as well.
Sources:
- Huang TL, Lin CC. Advances in biomarkers of major depressive disorder. Adv Clin Chem. 2015;68:177-204. doi:10.1016/bs.acc.2014.11.003.
- Brunner HG, Nelen M, Breakefield XO, Ropers HH, van Oost BA. Abnormal behavior associated with a point mutation in the structural gene for monoamine oxidase A. Science. 1993;262(5133):578-580. doi:10.1126/science.8211186.
- Brunner HG. MAOA deficiency and abnormal behaviour: perspectives on an association. Ciba Found Symp. 1996;194:155-167. doi:10.1002/9780470514825.ch9.
- Li D, Zhao H, Kranzler HR, Oslin D, Anton RF, Farrer LA, Gelernter J. Association of COL25A1 with comorbid antisocial personality disorder and substance dependence. Biol Psychiatry. 2012 Apr 15;71(8):733-40. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.12.011. Epub 2012 Jan 31. PMID: 22297151; PMCID: PMC3548659.
- Tielbeek JJ, Johansson A, Polderman TJC, et al. Genome-Wide Association Studies of a Broad Spectrum of Antisocial Behavior [published correction appears in JAMA Psychiatry. 2018 Mar 1;75(3):303]. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(12):1242-1250. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3069.
- Rutter, M., Giller, H. & Hagell, A. 1998, Antisocial Behavior by Young People, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
- MAOA- GeneCard.