“Want to become a cytogeneticist? Choosing your path into the field of cytogenetics? An expert’s guide, knowledge and career wisdom are shared in this article.”
Cytogenetics is a ‘kinda’ traditional approach in the field of genetics. Chromosomal studies are the prime focus here. However, the field has evolved, and techniques such as FISH and microarray have developed, later on.
This approach is collectively known as molecular cytogenetics, which is although technically different from conventional cytogenetics, the objectives are the same– to find out chromosomal alterations.
Techniques like FISH or microarray power up our strength to study chromosomal alterations like deletions and duplication that can’t be studied using the conventional approach.
Still, cytogenetics (the conventional way!) is the most popular, most demanding and high-paying field, even in 2024! I’m a trained geneticist and have substantial experience and expertise in the field of cytogenetics and molecular cytogenetics.
Here, I’m sharing my experience and guide to becoming a cytogeneticist in 2024. The present article would be a clear path for those who want to pursue their career in this field.
We will indeed be talking about what a cytogeneticist is, what they do, career options, salary and so many things from a cytogeneticist’s perspective.
Stay tuned.
Read more: 50 Ways You Can Be a Geneticist Today.
Key Topics:
What is a cytogeneticist?
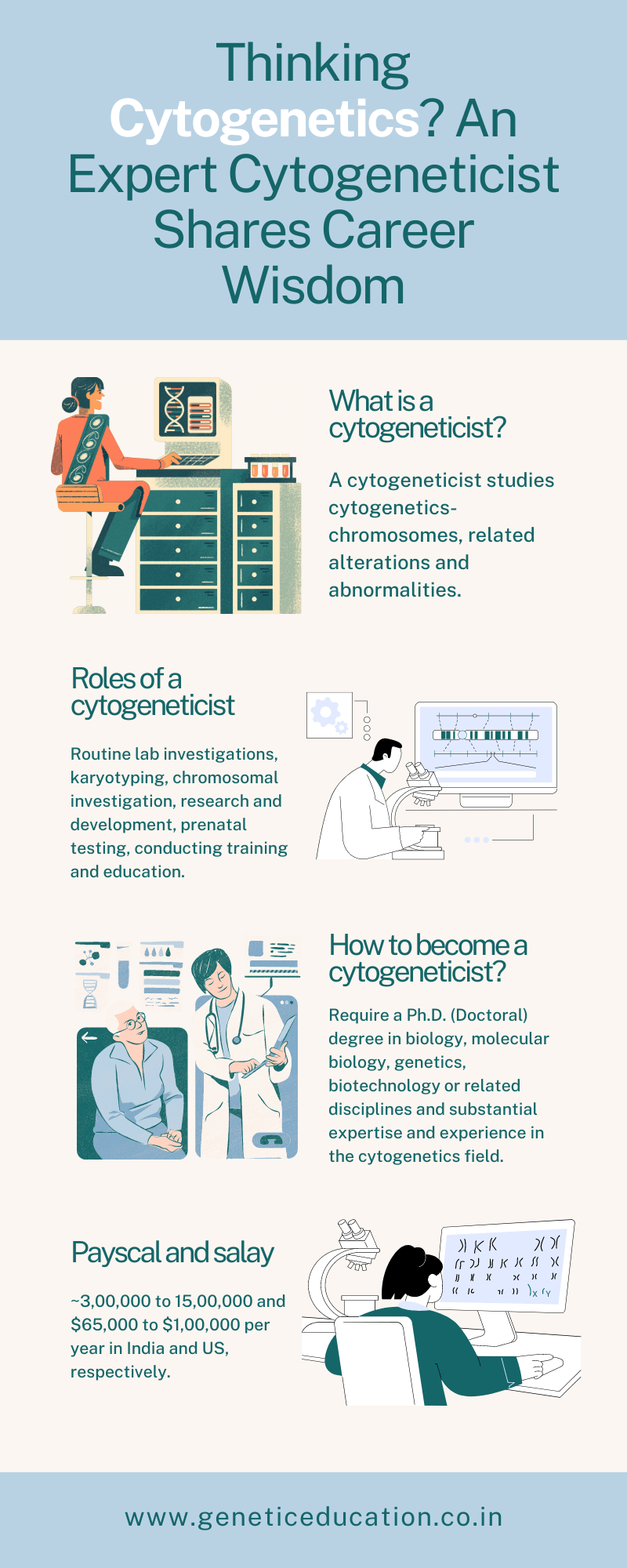
A cytogeneticist studies cytogenetics- chromosomes, related alterations and abnormalities. They work in the setup of cytogenetics, which is indeed a different setup than the molecular one!
“Cyto” means “cytology” or “related to cells”, and “geneticist” means “someone who studies genetics.” So cytogeneticist means, “who studies the genetics of a cell.” Here, we are talking about chromosomes because the first thing that scientists have noticed in a lab as genetic material is the chromosomes.
So broadly, cytogenetics is a field of studying chromosomes. Thus, the one who studies them is known as a cytogeneticist. The present field is still a specialized field because one has to rely on the expertise of a cytogeneticist to understand the results.
What do cytogeneticists do?
The chromosomal study is a prime function of a cytogeneticist. In addition to that, they have to perform other functions as well. Here is the list of roles for a cytogeneticist in a lab.
Routine lab investigations:
The first, and very crucial function of a cytogeneticist is to perform routine lab investigations, like– assessment of chemical preparation, sterility standards and safety. They ensure that everything is working as per the SOP and standard procedure or not.
They also follow up if all the instruments are working properly or not. Cytogenetic success highly relies on how you manage the lab (chemical preparation, sterility standards and safety).
Karyotyping:
Wet lab work is the responsibility of a cytogenetic technician but a cytogeneticist should have to perform karyotyping in some crucial cases. For example- in the case of a prenatal sample. So the very next responsibility is to perform wet lab work– cell culture, harvesting, microscopy and FISH.
Read more: Karyotyping: Definition, Steps, Procedure and Applications.
Chromosomal investigations:
The second most important part after routine lab investigation, is to perform chromosomal investigations. Now, this part is a dedicated job of a cytogeneticist as only he or she has the expertise and experience to understand the structural and numerical chromosomal alterations.
In addition, they also need to investigate slides and validate the results of previous tests. They finally deliver results to the reporting section.
Prenatal testing:
Prenatal samples (amniotic fluid or chorionic villi) are so important that repeat collection can’t be ordered. It’s a cytogeneticist’s role to see if prenatal samples are transported, stored and processed under adequate conditions, or not. If needed they have to handle the sample and process it.
Genetic counseling:
In addition to performing wet and dry lab work, the cytogeneticist also has to educate the patient as well. They have to communicate the findings to the patient or their family and explain to them the consequences of the chromosomal abnormality if any.
Research and development:
A cytogeneticist studies and explores new conditions related to chromosomes. They work to understand these conditions and find ways to identify them through research. By doing this, they can create new tests and methods.
Additionally, they investigate any changes they discover and attempt to connect them to known diseases or abnormalities. The goal is to enhance the quality of testing facilities by developing improved tests and techniques through ongoing research.
Additional roles:
Besides all of these major roles, they have to educate lab personnel, and trainees, conduct training sessions, educate students, encourage and motivate their technicians and manage the whole cytogenetic lab.
How to become a cytogeneticist?
To become a cytogeneticist, one has to hold a doctoral degree in the field of life science and gain substantial experience working in a cytogenetic lab. However, a PhD in genetics or related inter-discipline is highly recommended.
Educational background:
Bachelor’s and master’s degrees in biology, molecular biology, genetics, microbiology or related discipline and PhD (doctoral) degree in the same field.
Expertise:
To become a cytogeneticist, one has to have expertise in karyotyping, cell culture and microscopy. They also know how to prepare and understand chromosomal plates.
Experience:
One important criterion for becoming a cytogeneticist is to gain experience in chromosomal investigations from a reputed lab or scientist. He or she should independently understand and interpret chromosomes and report results.
Certifications and accreditations:
As such no additional certification or accreditations are required, however, several countries require additional certifications for practicing as a cytogeneticist. Note that PC-PNDT is mandatory for prenatal samples in India.
What are the career options for a cytogeneticist?
Here are some of the career options for a cytogeneticist.
Clinical Cytogeneticist:
Work in a clinical laboratory, analyzing patient samples to diagnose and detect chromosomal abnormalities. This may involve performing karyotyping, FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization), and other molecular cytogenetic techniques.
Onco-Cytogeneticist:
Focus on studying chromosomal abnormalities associated with cancer. Onco-cytogeneticists play a crucial role in identifying genetic factors (particularly chromosomal abnormalities) influencing cancer development and progression.
Prenatal cytogeneticist:
Focus majorly on the prenatal samples, their testing, validation and finding abnormalities. They have to deal with congenital malformations and thus have a crucial role in this setup.
Laboratory Manager/Director:
Take on leadership roles in cytogenetics laboratories, look after operations, quality control, and personnel. Laboratory managers/directors may also be involved in implementing new technologies and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards.
Plant cytogeneticist:
Work in the agriculture and horticulture industries as a plant cytogeneticist. They look after research in this field to understand various ploidies and abnormalities in plants.
Animal cytogeneticist:
Work in animal husbandry or veterinary field to study animal chromosomes and abnormalities.
Pharma industry:
Cytogeneticists also achieve their careers in the pharmaceutical industry. They work to find out cytotoxicity and adverse effects of medicines or therapies on chromosomes.
Genetic counselor:
A cytogeneticist can also work as a genetic counselor as well. As a genetic counselor, they educate the patient or parents regarding the genetic condition or chromosomal abnormality.
Cytogeneticist pay scale and salary
Cytogeneticist pay scale and salary vary from country to country. In India, freshers may earn 25,000 to 40,000 per month depending on their highest level of degree and experience. An experienced cytogeneticist with a doctoral degree can earn from 80,000 to 1,25,000 per month.
However, the salary may depend on the highest level of degree the candidate holds, experience and expertise, and operations that the candidate can conduct. Some literature suggests that in the US, the average salary of a cytogeneticist is between $65,000 and $1,00,000 per year which means ~$5,500 to $8,500 per month.
Read more: 10 Common Lab Techniques to Work in a Genetic Lab.
Wrapping up:
Cytogenetics is an evergreen field. The reason behind that is that every genetic lab should need a cytogeneticist. Chromosomal investigations will never go outdated and thus, they will remain in the game for a longer time.
So we can say, that a cytogeneticist’s future is bright and will remain bright. I hope this article helped you and made you understand the significance of a cytogeneticist in a clinical setup.
In conclusion, with a cytogenetics degree, you can achieve your career in the clinical field, healthcare, hospitals, research, educational institutes, and even in agriculture.


