“The X chromosome is a classic characteristic of females while the Y chromosome is a classic characteristic of males, more often than not. Here is the comparison between two sex chromosomes X vs Y chromosome.”
Among 23 pairs of human chromosomes, a dedicated pair is of sex chromosomes. Two X chromosomes in females while one X and one Y chromosome in males. Each chromosome comprises traits for each gender- for example, Y-linked traits for maleness and vice versa.
However, in addition to the fact that sex chromosomes have a profound role in not only sex determination but also in sex differentiation, they govern other traits too. Specifically speaking about the X chromosome, it has many other genotypes for traits like mental and cognitive development.
On the other side, Y is yet, we can say a mystery for us. We don’t know more about it besides its role in maleness. But we know both, though belong to the category of sex chromosomes, are different.
Some differences are known to students and even to common science people, although some are not. There are several technical aspects only experts know about, regarding the differences between both. So what are those?
In this piece of content, I will explain to you some of the major differences between the X and Y chromosome. I will also explain how both are different at the molecular level and also discuss some other unknown areas about these two.
Stay tuned.
Related article: Explaining the Y chromosome: Definition, Structure and Function
Key Topics:
Differences between X vs Y chromosomes
Firstly, let’s start with some of the common differences between the X and Y chromosome.
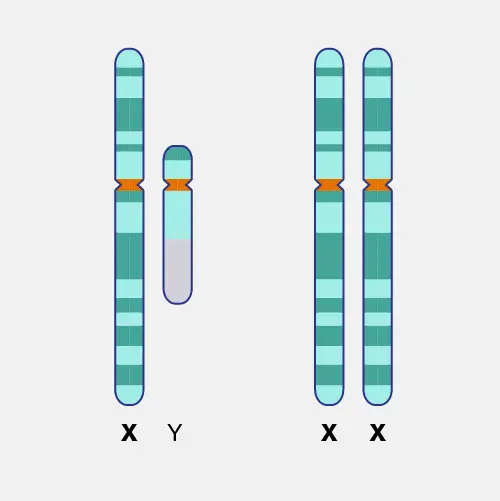
Structure:
Structurally, the X chromosome is metacentric, contains a centromere exactly in the middle of the chromosome, and contains 4 chromatids and other usual chromosome structural elements. Contrary, the Y chromosome is acrocentric, contains a centromere at the end towards the p arm and contains only 2 chromatids with other usual chromosomal structural elements.
Size:
The X chromosome is larger in size compared to the Y, and contains 155 million bp. It covers approx. 5% part of the human genome. Contrary, the Y chromosome is shorter and tiny. It contains 59 Million bp and covers around only 2% part of the entire genome.
Catch! The total No. of base pairs, the X chromosome carry is 156,040,895bp while the total No. of base pairs, the Y chromosome carry is 57, 225, 415bp.
No. of Genes:
From the structure and size comparison, it’s clear that the X chromosome contains way more functional genes than the Y chromosome. Let’s expand our knowledge a little more. As per the Medlineplus report, the X chromosome has 900 to 1400 genes while the Y chromosome has 70 to 200 genes.
As per the NCBI data, the specification of types of genes is here.
| Protein-coding genes | Non-coding genes | Pseudogenes | Total | |
| X chromosome | 874 | 494 | 879 | 2247 |
| Y chromosome | 73 | 122 | 400 | 595 |
From the data I have extracted some amazing statistics. 38% part of the X chromosome is coding while only 12.26% part of the Y chromosome is coding and contains protein-coding genes. Suckingly, the X chromosome contains only 21.98% part of non-coding DNA while the Y chromosome contains 76.22% part of non-coding DNA.
Present outcomes literally suggest that the X chromosome is genetically more active as it contains more genes and less non-coding part compared to the Y chromosome. Genes for X-linked muscular dystrophy, hemophilia and color blindness are located on the X chromosome while only the sex-determining region is located on the Y chromosome.
Function:
The above interpretations and comparisons suggest that the X chromosome is more functionally rich, henceforth, to support the fact, it contains vital genes for an individual. However, the Y chromosome contains genes that are only involved in the male sex determination, testicular development and development of male-secondary sex traits.
The presence of two X chromosomes helps develop female-specific traits while the presence of a Y chromosome helps develop male-specific traits.
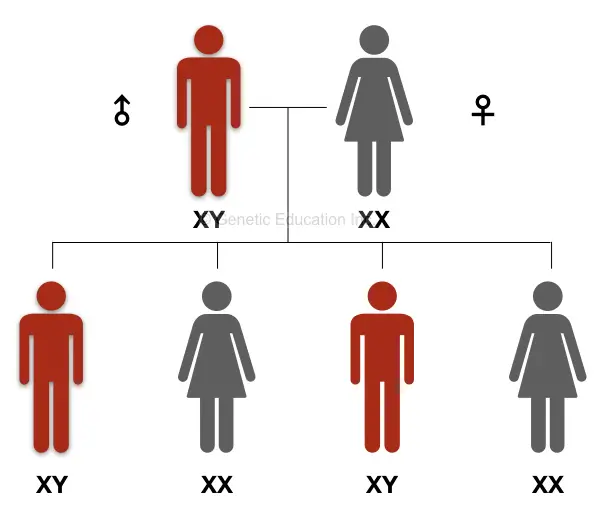
Inheritance:
The X chromosome follows an X-linked inheritance in which the X chromosome can be inherited into either male or female progenies. Noteworthy, the Y chromosome though doesn’t have any specific inheritance pattern but is only inherited into male progenies only.
Inheritance is a complex thing to understand so go through the examples given below.
Euchromatin and heterochromatin
As the X chromosome contains a large number of genes, it contains more euchromatin-rich chromatins than the Y chromosome. Likewise, the Y chromosome contains a huge part of the heterochromatin (non-coding) region than the X chromosome. Hence, the X chromosome is transcriptionally more active than the Y chromosome.
Notice
Do you know? In females, the entire X chromosome becomes transcriptionally inactive (converts to heterochromatin) to regulate gene expressions. We know it as ‘Barr body.’
These are some of the common differences between the X and Y chromosome, and enough for grade school students. Now, to know more let’s deep dive.
Epigenetics:
The epigenetics of X and Y chromosomes and Two X in the female and one X and one Y in the male is complex and different than we think. In males, both X and Y chromosomes are epigenetically active while in females, only a single X chromosome is epigenetically active.
Genetic abnormalities:
Klinefelter syndrome, Turner syndrome and triple X syndrome are several common chromosomal abnormalities associated with the X chromosome. Other associated genetic abnormalities are X-linked hemophilia, color blindness, albinism and muscular dystrophy.
Infertility due to mutations in the SRY and TDF regions is the only abnormality associated with the Y chromosome.
Similarities between X and Y chromosomes:
Both X and Y chromosomes belong to the category of human sex chromosomes or allosomes. Both contain DNA as genetic material. Sex chromosomes evolved from autosomes around 300 million years ago.
Related article: Difference Between Y DNA vs Mitochondrial DNA Test.
Wrapping up:
Human sex chromosomes are different in structure, function, shape, size and constituents. The X chromosome is large in size, contains more genes and a large number of genetic materials whilst the Y chromosome is small in size, contains fewer genes and genetic material.
However, each chromosome is equally important, X for both females and males while Y for males. Studies suggest that the X and Y chromosomes are separated from autosomes around 300 million years ago.