“PCR- the polymerase chain reaction is one of the most versatile and state of the art techniques used to amplify and quantify DNA.”
The PCR machine known as a thermocycler was discovered by Karry Mullis in 1983. The PCR machine amplifies or synthesizes DNA in vitro. The aim of doing artificial synthesis is to investigate the DNA sequence or a gene in order to find out mutations.
A specialized DNA polymerase known as the Taq DNA polymerase is used in the synthesis process which can even synthesize DNA at a higher temperature.
In the three different temperature governed steps, DNA denature, primer anneal and new DNA strand extends.
The function of the conventional ‘Karry Mullis type’ PCR is to only amplify the DNA, however, the recent advancement in it allows quantifying the nucleic acid either DNA or RNA as well.
The technique in which nucleic acid is quantified is known as real-time PCR or quantitative PCR. Note that real-time PCR is a version in which RNA is quantified using the reverse transcription mechanism.
Both PCR and qPCR are the type of thermocycler, though, the purpose, end product and results are different. In the present article, we are going to discuss some of the common differences between the PCR and the qPCR.
Key Topics:
PCR vs qPCR:
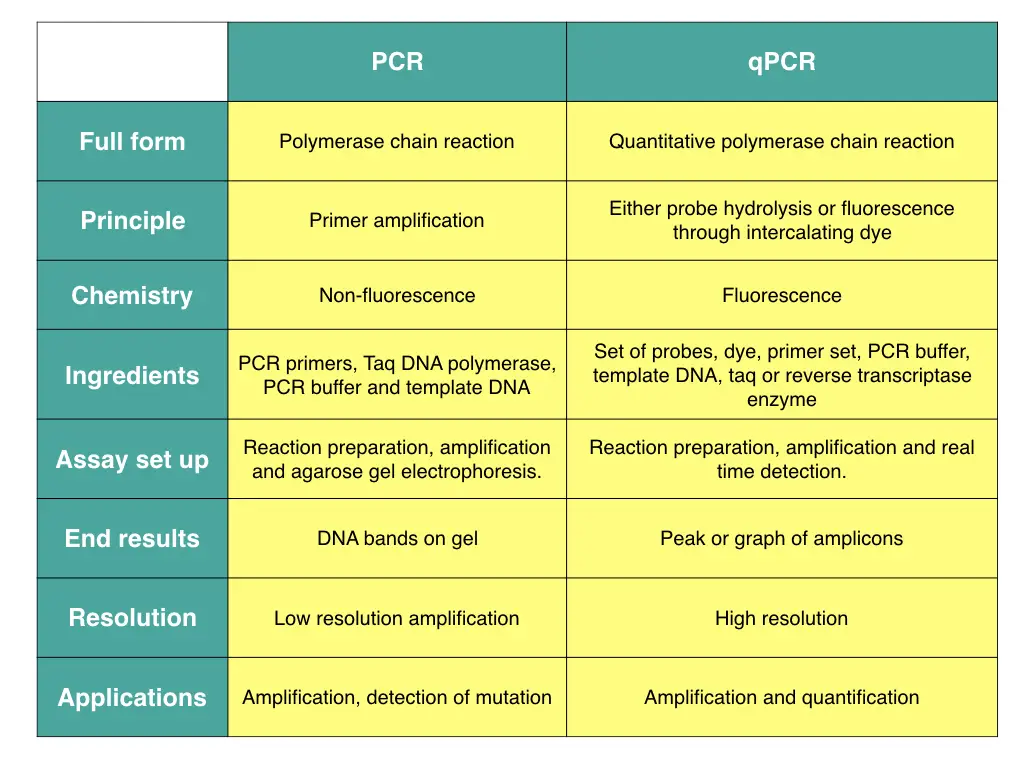
The conventional PCR can only amplify the DNA up to 2000 nucleotides precisely while the rtPCR or qPCR can amplify DNA as well as quantify the amount of DNA as well.
Quantification of nucleic acid measures how many DNA templates are present in the sample.
The PCR is based on the principle of DNA amplification by primer annealing using Different temperature zones. On the other side, the qPCR relies on the principle of the use of fluorescence probes or dyes that emit fluorescence during the amplification.
Only the set of PCR primers is used in the PCR reaction while the primer set as well as labeled probes are used in the real-time qPCR assay.
The primers practiced in the PCR are simple and non-labeled whilst the probes used in the qPCR are labeled with the quencher dye and reporter dye.
The PCR reaction completes in three steps; denaturation, annealing and extension, contrary; the q(rt)PCR besides these three steps, the quantification is done during the exponential phase of the amplification.
By using the conventional gel electrophoresis set up the results of PCR or PCR amplicons can be investigated. On the other side in the case of the qPCR, the results are recorded by the machine, based on the fluorescence emitted during the reaction.
Distinct DNA bands or amplicon bands are observed in a gel for agarose gel electrophoresis-based conventional PCR while peaks of the amplicon of different-sized fragments are observed during the qPCR.
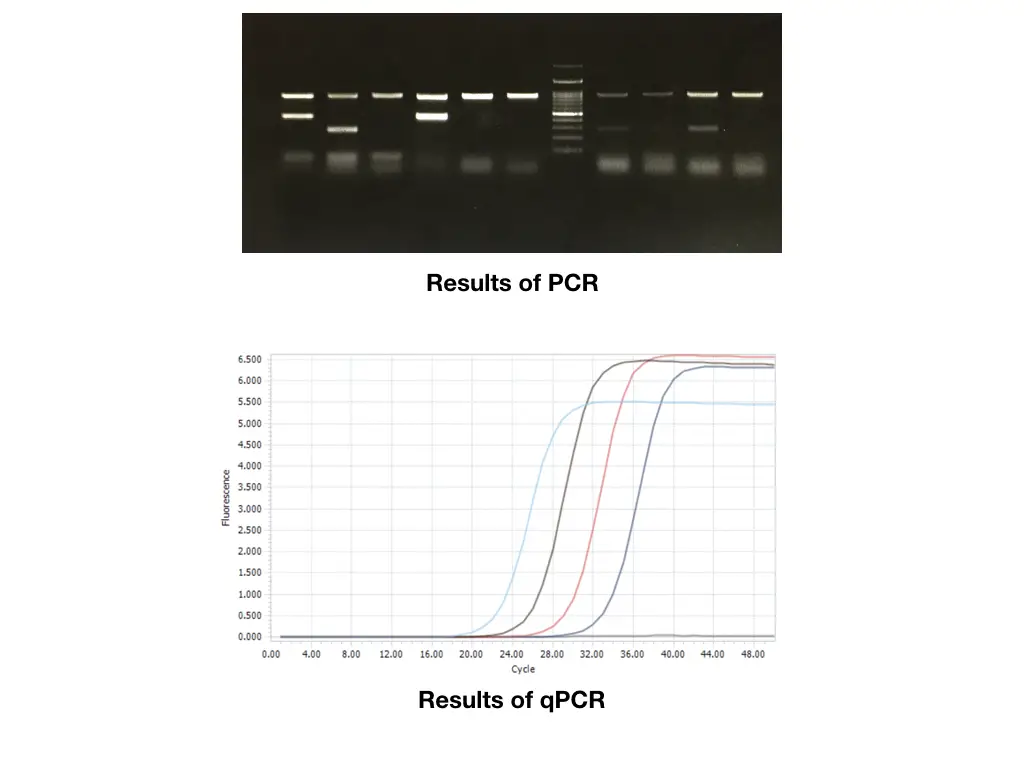
In the electrophoresis, under the influence of electrical current, the amplicon migrates towards the positive pole while in the RT(q)PCR when a dye is released or probe hydrolyzed, it emits fluorescence, the amount of fluorescence emitted is recorded and generated in the form of a peak. The peak indicates positive amplification.
Thus the results in PCR are obtained at the end of the reaction, while the results of qPCR are obtained during the reaction (exponential phase).
The conventional PCR technique is a low-resolution amplification technique whilst the qPCR or the rtPCR is the high-resolution quantitative amplification method.
Technically, the conventional PCR technique is a time-consuming method in which 3 to 4 hours are needed to prepare a reaction as well as to perform the PCR while the qPCR takes approximately 1 to 1.5 hours to complete.
Related article: How to prepare a PCR reaction?
Comparatively, high-end expertise is required to analyze and interpret the results of PCR on the agarose gel while less expertise is needed in qPCR.
The PCR technique is a qualitative technique contrary to the qPCR or the real-time PCR, which is a quantitative method.
Practically the PCR technique is used in the detection of mutation while the rtPCR technique is used to quantify the DNA, to detect the DNA strand, to identify the microbes and characterize the microbes.
It is also used in the quantification of ancient DNA samples as well.
The PCR technique is restricted and has low resolution while the qPCR is a high-resolution technique that relies on the principle of hydrolysis of probes.
The PCR is only applicable to detect mutations and to know the presence or absence of the allele. While the qPCR is used not only to amplify the gene but also to measure the amount of a gene.
qPCR is applicable in microbial identification and gene expression studies.
The standard variation of the qPCR known as the RT-PCR or reverse transcriptase PCR is used to study the gene expression. In the RT-PCR the RNA is first to reverse transcribed into DNA and then quantified.
The application of conventional PCR is limited only to detect some monogenic gene mutations, to amplify the template for DNA sequencing and microarray. On the other side, the qPCR or the rtPCR is used to study gene expression, microbial identification, food pathogen detection, detection and quantification of mutation and identification of alleles involved in various diseases.
Though both the techniques have so many differences, it has some similarities as well.
Similarities between PCR and qPCR:
Both methods are used to amplify or synthesize the DNA.
Both the techniques are based on the temperature-based amplification.
The machine used for both techniques is known as a thermocycler.
Both RNA and DNA can be amplified in PCR as well as qPCR however, to amplify the RNA a different type of DNA polymerase is used.
Conclusion:
Conclusively we can say that the PCR technique is a qualitative method to amplify the gene while the qPCR technique is a quantitative method to amplify as well as to measure the target gene.
Importantly, the qPCR, rtPCR and RT-PCR are widely used in microbial genetics and metagenomic studies to measure viral loads. The qPCR technique is more robust than the conventional one, nonetheless, one should learn the basic- conventional PCR and how to set up it.