“DNA extraction from a dried blood spot (DBS) is a non-invasive, simple and comparatively easy process. And also, a cost-effective way to obtain DNA for research, clinical diagnosis and forensic analysis. Here is the process of DNA isolation from dried blood spots.”
The most routine sample type for DNA isolation is blood. DNA isolation from blood is the common scheme in the research and diagnosis of genetic diseases. However, it is an invasive, expensive and logistically challenging technique. It also requires trained personnel and a specialized setup too.
In addition, it may spread infection and thus creates difficulties for large and population-based studies. The alternative method, we have right now, is dried blood spot sampling. A small spot of blood is collected on a filter paper, dried and allowed for nucleic acid isolation.
The present scheme is simple, safer and handy. However, the isolation of DNA from a DBS can be challenging. To use it effectively in various fields, a reliable and efficient protocol should be developed. Existing reviews have discussed protocols using magnetic beads and spin columns that require additional instrumentation, and are costly too.
In this article, I have explained the concept and importance of DBS DNA isolation and presented a simple and non-magnetic bead-based protocol that you can use. We also reviewed some crucial information and discussed the advantages and limitations.
Key Topics:
How to isolate DNA from dried blood spots?
Dried blood spot, abbreviated as BDS is a non-invasive and simple blood collection technique for DNA isolation. Good quality and quantity of DNA can be isolated by choosing the right paper for capturing blood spots and considering crucial extraction criteria and parameters.
The DBS sampling method has existed for the last 50 years and is popularly employed for newborn screening. Clinical and genetic analysis, drug monitoring and biobanking are other applications of DBS sampling apart from newborn screening.
The technique becomes so crucial when sampling is performed in remote places, transportation and storage conditions aren’t optimal and epidemics and pandemic studies are carried out.
Do you know?
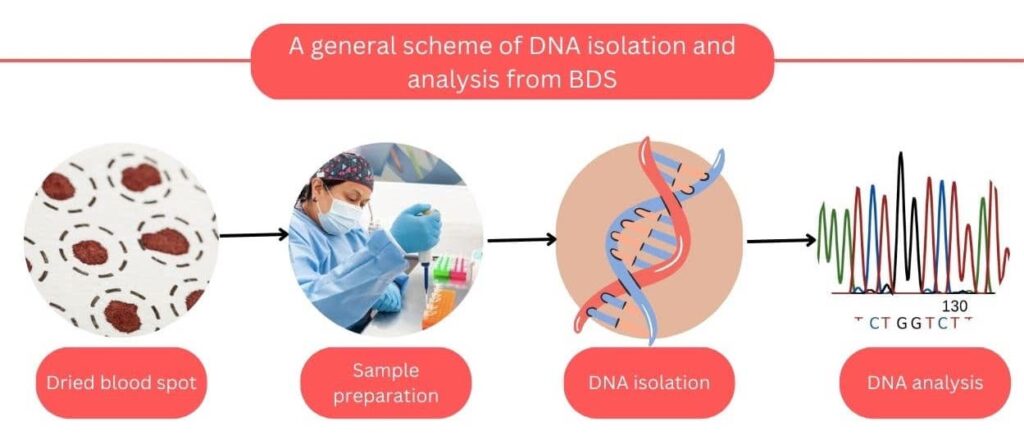
The common scheme includes sample collection, Pre-preparation, DNA isolation, purification and elution.
Sample collection:
A few drops of blood are drawn from the patient by pricking the finger or heel of a patient. Drops of blood are collected on a sterile, clean and cellulose-made filter paper. And allowed to air-dry at room samples. The paper is collected in a clean polythene bag and transported to the testing facility.
(How simple it is!)
Pre-preparation:
Unlike the conventional blood DNA isolation protocol, the pre-preparations for DBS DNA extraction are a bit different. A spot paper is carefully removed from a polythene bag, cut into small pieces using a scissor, and collected in a sterile (2ml) centrifuge tube.
Now approximately 50µL RBC lysis buffer is added to the tube and the sample is allowed for cell lysis. The cell lysis process will be discussed separately in the protocol section. After some time, the piece of paper is removed. Now, nucleic acid separation can be initiated.
DNA isolation:
After sample preparation, any protocol can be chosen for DNA extraction. Three commonly used protocols are spin-column DNA extraction, magnetic bead-based isolation and manual DNA extraction.
If you wish to know what are the differences between all three methods, you can read this article: Manual vs spin column and magnetic bead-based DNA extraction.
The manual scheme uses the same chemicals and centrifugation process as the blood DNA extraction protocol. Here, the DNA is precipitated using alcohol. Note that both ready-to-use kit-based methods are super easy and fast.
Purification:
Spin column or alcohol purification are two options to remove contaminants from DBS DNA. Two or three alcohol wash with ethanol is sufficient to purify the DNA. DNA pellets are air-dried.
Elution:
The DNA can be eluted in the dd/w, elution buffer, or TE buffer.
Manual DNA extraction protocol for DBS:
| Required chemicals | Required instruments |
| Lysis buffer, proteinase K, Ethanol, TE buffer, microcentrifuge tubes. | Centrifuge, dry bath. |
- Cut the DBS paper into small pieces and collect them in a clear 1.5ml centrifuge tube.
- Add lysis buffer or phosphate buffer (required amount) to the sample and 10µL proteinase K into the sample.
- The sample is mixed well and incubated at 55 to 60°C temperature for 20 to 25 minutes. Allow the sample to come at room temperature.
- Note: There are several protocol variations that perform the buffer + incubation and proteinase K + incubation steps separately.
- Centrifuge at low speed for 10 minutes.
- Additional step: you can use phenol: chloroform and isoamyl alcohol too in the protocol to improve the yield and purity.
- Now collect the supernatant without disturbing the pellets and transfer it into the new tube.
- Add the double volume of chilled alcohol and precipitate the DNA. For effective precipitation, invert the tube many times until visible threads of DNA appear.
- Perform centrifugation to settle DNA pellets at the bottom. Remove alcohol carefully. Now wash the sample twice with fresh alcohol.
- Remove the alcohol, air dry the pellets, and dissolve DNA in the TE buffer.
- Add 50 to 100 µL of TE buffer and dissolve the pellets.
- Perform DNA quality and quantity assessment.
- Store the DNA sample at -20°C until use.
Note: Sometimes, visible DNA threads can not appear, as the sample is very low, but that doesn’t mean it lacks DNA. You can still get DNA.
Spin-column DNA extraction protocol for DBS:
| Required chemicals | Required instruments |
| Lysis buffer, proteinase K, 70% Ethanol, elution buffer, microcentrifuge tubes, spin columns and a kit. | Centrifuge, heating block. |
- Cut the DBS paper into small pieces and collect them in a clear 1.5ml centrifuge tube.
- Add phosphate buffer or buffer provided by the manufacturer (ATL buffer in case of Qiagen blood mini kit) to the sample and incubate at 85°C for 10 mins.
- Spin it and add 10 µL proteinase K to the sample and incubate the sample at 56°C for 1 hr.
- Transfer the mixture to the spin column tube.
- Centrifuge the spin column tube and discard the flowthrough.
- Wash the sample with the washing buffer provided in the kit and centrifuge the sample.
- Remove the flowthrough and add a 100µL elution buffer.
- Place the sample for some time and collect the eluted DNA into a new sterile tube.
- Store the sample at -20°C after qualitative and quantitative analysis.
Note: This is just a brief overview of the overall protocol, it varies from kit manufacturer. Also, the buffer name and composition vary as well. Please carefully read the manufacturer’s protocol and guidelines to process the sample.
Magnetic bead-based DNA extraction protocol for DBS:
| Required chemicals | Required instruments |
| Lysis buffer, proteinase K, 70% Ethanol, elution buffer, microcentrifuge tubes, Magnetic beads | Centrifuge, Magnetic separator, heating block. |
- Cut the DBS paper into small pieces and collect them in a clear 1.5ml centrifuge tube.
- Add lysis buffer or phosphate buffer (required amount) to the sample and 10µL proteinase K into the sample.
- The sample is mixed well and incubated at 55 to 60°C temperature for 20 to 25 minutes. Allow the sample to come at room temperature.
- Now add 200 to 400µL magnetic beads to the sample and place it on the magnetic separator. It separates DNA from the rest of the samples.
- DNA remains bound with the beads, remove the supernatant and add 70% alcohol to the beads.
- Repeat the washing 2 times.
- Air dry the beads and re-suspend them in the TE buffer (100µL).
Kit recommendation for BDS
QIAamp DNA investigator kit:
This kit works on the principle of spin-column DNA extraction. It is used for isolating DNA from forensic and human samples. All the reagents are provided in the kit.
Xpress DNA DBS kit:
This kit uses a magnetic nanoparticle-based approach for DNA extraction. It can process samples from DBS, FTA and Guthrie cards. It can also be used for spot, clotted and aged blood samples too. All the reagents are supplied in the kit.
Dried blood spot DNA isolation kit by NORGEN:
The kit works on the principle of spin-column DNA isolation. Any blood spot can be processed within 30 minutes. The kit gives high pure and high-yield DNA.
Advantages of DBS DNA extraction:
One of the major advantages of the present technique is its non-invasive nature which is the main reason it can be widely applicable for collecting samples from infants, newborn babies and patients uncomfortable with conventional blood collection methods.
DBS minimizes the chances of infection for lab personnel. Traditional venous blood collection technique is highly contagious and accidentally spreads infection.
The DBS samples are easy to store and transport. A DNA extract can be stored for years at room temperature. This advantage is a great benefit in collecting and transporting samples from remote places.
Disadvantages of DBS DNA extraction:
Sample age, storage conditions, and amount of collected sample have a direct impact on the DNA yield and thus, the yield obtained by DBS is very low.
Also, it adds additional steps to the process which makes the overall process a bit complex and tedious.
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, DBS DNA extraction gives us flexibility and therefore is used for epidemic and population studies and large-scale sample analysis. Having the biggest benefits of its non-invasive nature, low DNA yield is the limitation of the present technique.
Nonetheless, it’s highly beneficial for newborn genetic studies. The sample protocols we have discussed so far can be used for the paper DNA extraction method too which is somewhat similar to the DBS.
Explore our protocol gallery which also includes the ready-to-use protocol for DNA extraction from dried blood spots and many other protocols. In case you wish to learn the basics of DNA isolation, I strongly recommend buying our ebook.