“Learn about the impact of two important evolutionary forces on the population. Discover some of the amazing differences between gene flow vs genetic drift in this article.”
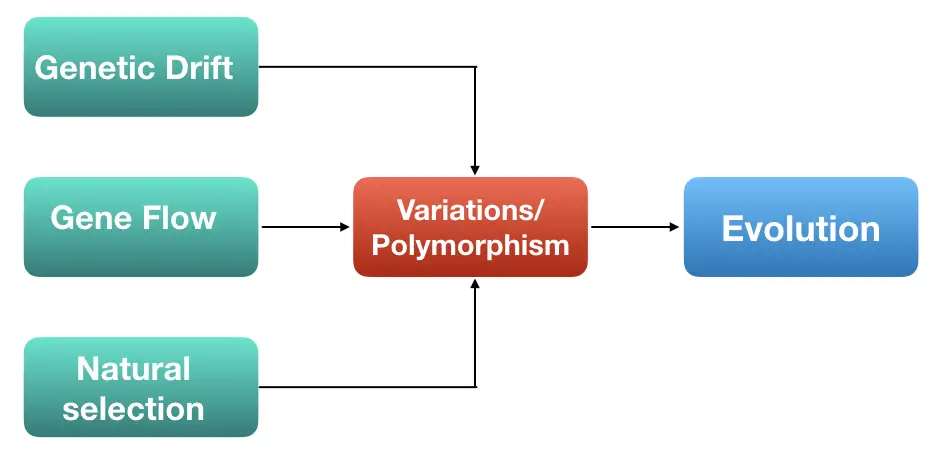
Have you ever wondered how evolution occurs? How do living things change over time and get new traits? Which forces work upon evolution? As per population genetics, important forces causing evolution are natural selection, genetic drift, gene flow and mutations.
Important article: What is a Gene?- Definition, Structure and Function.
Evolution has a direct impact on the population’s genetic composition and thereby overall fitness of the population. It creates diversity in any population, however, in large populations, it is less noticeable than in small populations.
Among these forces, gene flow and genetic drift are significantly important evolution factors. However, both have many differences and their own advantages and side effects for the population.
In this article, I will explain to you the concept of gene flow and genetic drift. Most importantly, we will discuss the differences between genetic drift and gene flow in a simple and understandable way.
I read tons of articles on this topic, but the majority are difficult for budding scientists. So I have prepared this amazing article in a very simple way so that from newbie budding scientists to researchers, everyone can understand it.
At Genetic Education Inc. we re-discover the knowledge in a layman. This article helps you to gain insight into how evolution and genetic diversity occur in any population and why it’s important for an individual.
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
What is Gene Flow?
Gene flow is an exchange of genetic material between two populations. Common ways gene occurs are migration, translocation, mating between two different populations and exchange of gametes.
For example, the great human migration between two continents, the transfer of pollen by animals, and winds of water to other locations and interbreeding between the animal species of two different regions.
Gene flow produces new genetic traits in the new population and produces genetic diversity. However, over the period, gene flow can make populations genetically similar.
Gene flow also helps to spread advantageous alleles in the population by introducing new genotypes.
Related article: What is Genotype?- Definition, Frequency and Methods.
What is Genetic Drift?
Genetic drift is an entirely different phenomenon in which allele frequency changes. An allele refers to the alternative forms of a gene. And the allelic frequency means the number of alleles in the population in percentage.
So genetic drift refers to an alteration in allelic frequency by chance or random events. This random error produces undesirable outcomes as a decrease or increase in certain alleles.
Notably, genetic drift shows a significant effect on smaller populations. Examples of genetic drift are natural calamities, disease outbreaks, etc.
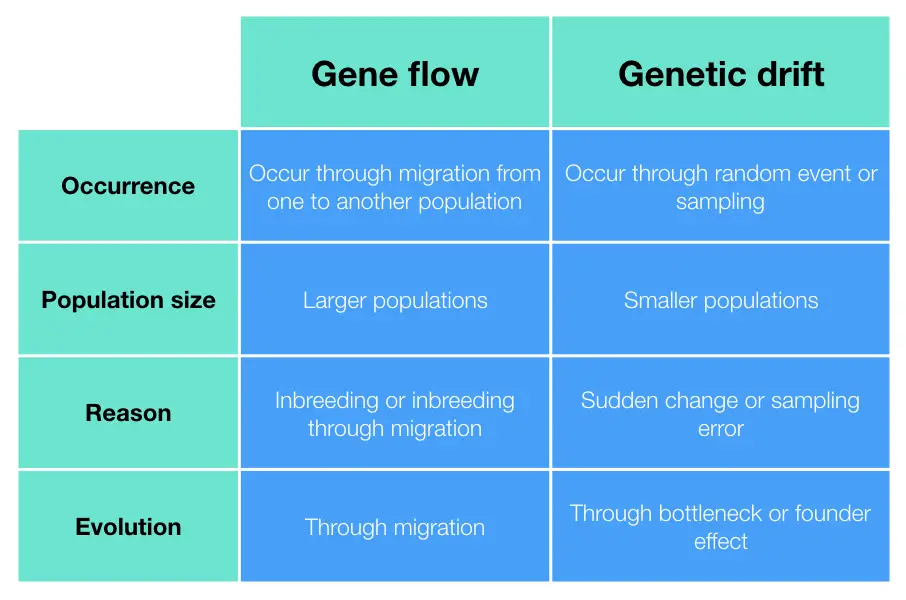
Differences between Gene flow vs Genetic Drift:
Definition:
Gene flow refers to the transfer of genetic material between two populations. For example, human migration between two continents or traveling between two countries.
Whereas, genetic drift refers to the random fluctuation in allelic frequency in the population. Examples of genetic drift are natural calamities or epidemics/pandemics.
Occurrence:
Gene flow occurs by migration, mating or movement of reproductive cells– egg or sperm between two populations. Genetic drift, on the other hand, occurs by chance or random events like–natural disasters, disease outbreaks or climate change.
Example:
Gene flow: Imagine animals migrate from one to another continent, where they mate with other animals of that population. Resultantly, they mix the genetic content and produce new traits. It leads to the transfer of genetic material between two populations.
Genetic drift: Imagine a few people in the population with green eyes. By chance, if individuals with green eyes have more children, the frequency of green-eyes governing gene changes suddenly.
Take another example. In India, a small group of the Sindhi population has a higher allelic frequency for Beta-thalassemia. It occurred by genetic drift in the past.
Thus, gene flow may produce new traits thereby diversity in the population while genetic drift causes a sudden increase or decrease in allelic frequency. However, genetic drift does not play any significant role in genetic diversity.
Gene flow may produce new allelic combinations and genotypes while genetic drift may cause loss of certain alleles or may fix some.
Population size:
Gene flow and genetic drift both can occur in any population size, however, genetic drift shows a strong effect in smaller sized-populations. take a look at the example of Sindhis (given above).
As gene flow mixes the genes, over a period, it produces a homogenizing effect and makes different populations genetically more similar. In large populations, it spreads advantageous alleles and reduces the effect of genetic drift.
Conversely, genetic drift doesn’t show such advantages. Notably, as it occurs within a small population, it has fewer chances for producing genetic diversity.
Read more: Role of Genetic Polymorphism in Human Evolution and Survival.
Summary:
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, gene flow is more advantageous than genetic drift for a population. In addition, gene flow increases genetic diversity in the population while gene flow reduces genetic diversity by random or chance events in the population.
I hope you understand the concept of gene flow vs genetic drift. I tried my best to simplify things. But the topic itself is very difficult to understand. In the future, we will write more content on this topic to make it better.

