“The new variant of SARS-CoV-2 named as “Delta” strain is infecting many countries throughout the world and will be a danger in upcoming times” – says Scientists.
The second wave of COVID-19 was outrageous, and did substantial damage, especially in India. After June 15th, a significant decrease in infectivity and mortality graph has been observed, however, we can’t put a full stop here!
Scientists have been predicting that the third wave- will hit in a few weeks, and will be more transmissible and contagious. The recently evolved Delta variant is now ruling the ground and will take charge to create more outrage in the forthcoming months, says research.
A lot of questions are being raised regarding the Delta virus & is continuously threatening people. Is the delta variant of COVID-19 is more dangerous? Is it more transmissible? Would it be more terrible? Would present vaccines protect against the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2?
And what actually is the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 of COVID-19? These are several common questions people keep asking on Google.
Organizations like WHO, CDC, ICMR and PHE have researched substantially and huge literature is now live, nonetheless, it is my moral responsibility, as a geneticist, to explain things, especially when genetics and genomics are involved.
This article will answer many of these questions satisfactorily but before that lets’ find out about the genome and genetics of SARS-CoV-2.
The genetic material of SARS-CoV-2 is RNA- ribonucleic acid, not so common in nature, eukaryotes have DNA as their genetic material, instead. The genome is made up of 6 to 11 ORF- open reading frames to encode protein.
The total genomic size of the family coronavirus is approximately 27 to 34Kb. Rep1a, Rep1b, spike protein, membrane protein, nucleoprotein and envelope protein are common proteins encoded by the coding regions of 11 ORFs.
Unlike eukaryotes, SARS-CoV-2 has reverse transcription machinery to form a protein and therefore scientists named it “retrovirus”. The RNA of SARS-CoV-2 first reverse transcribed into the DNA by reverse transcriptase enzyme and incorporated into the host genome. Using the host’s protein synthesis machinery it makes its own proteins.
Interaction of virus with the host cell and environment mutates the genome, some are helpful, some are not. The Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is a kind of mutation reported recently and will likely infect people faster and severely.
Let’s find out what the Delta mutation is!
Related article: Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)- Structure, Genome and Testing.
Key Topics:
What is a Delta Strain of SARS-CoV-2?
The Delta strain of SARS-CoV-2 is a mutation in a gene encoding the spike protein. Mostly are the “group of alterations” and are s type of substitution mutations.
The first case of the Delta variant was reported in India late in 2020, during the second wave. Technically, it’s a mutation or group of mutations in the genes encoding for the spike protein.
It’s a substitution mutation that occurs at two locations, commonly, at 478- substitution from Threonine to Arginine and at 452- substitution from Leucine to Arginine. Other mutations are also reported, notedly.
WHO recently adapted the Roman technique of nomenclature and named the B. 1. 617. 2 strain as the Delta variant.
The variant is now known as “variant of concern” classified in lineage B. 1. 617 and scientifically referred to as lineage B. 1. 6. 617. 2. In layman, it shows that this variant was originally evolved from the native variant B. 1. 617. The lineage was reported for the very first time in December 2020 in India.
Notedly, it evolved in India, though, is spreading faster in the UK. The penetration of the present variant is around ~60% more than the previous Alpha variant, said Public Health England (PHE).
WHO said, it’s a “variant of concern”, these are the top four reasons why.
- High capacity to neutralizing antibodies
- Less effectiveness of the vaccine
- Slower vaccination
- More severity and transmissibility of the variant
The ~90% of total COVID-19 cases are of the Delta variant, reported in the UK last week. Active cases are rising in almost 70 countries. India, Singapore, USA, Portugal, Belgium and Russia are now the hotspot for Delta variant cases. Here is the chart showing the percentage of cases in which the Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 is found.
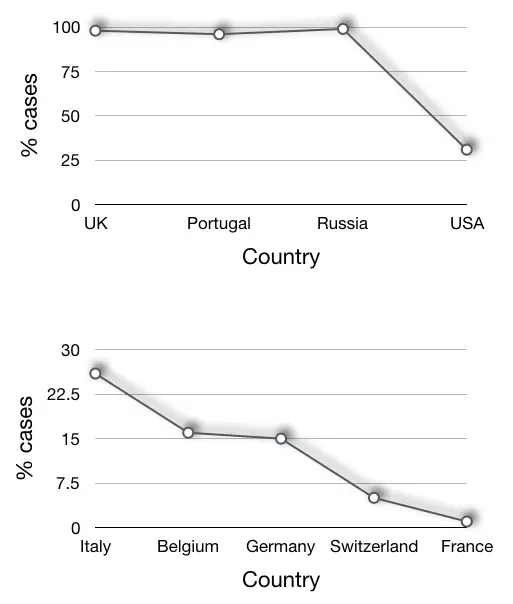
Studies show that the present variant is 50% to 60% more powerful and transmissible than the alpha and previous other variants. Furthermore, Public Health England said that the variant is infecting younger people between the age group of 12 to 20 faster than other age groups.
Mutations and classification:
The two most common substitution mutations are E484Q and L452R. The mutations are classified using the Nextstain Phylogenetic classification system. However, after observing increasing transmissibility, WHO classified the Delta mutations from “variant under investigation” to a “variant of concern”.
Among 13 common mutations of the strain B. 1.617. 2 (the Delta variant), several well-studied variations are explained here:
| Mutation | Protein | Amino acid | Contagious Ability |
| D614G | Spike protein | Substitution- Aspartic acid to Glycine | Highly transmissible |
| T478K | Spike protein | Substitution- Threonine to Lysine | |
| L452R | Spike protein | Substitution- Leucine to Arginine | |
| P681R | Spike protein | Proline to Arginine | Higher infectivity and transmissibility |
One of the above-listed mutations occurs in the “Furin Cleavage site” in the genome; this site is important for viruses to survive in the airway when infected.
(Source: Xia, S., Lan, Q., Su, S. et al. The role of the furin cleavage site in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated membrane fusion in the presence or absence of trypsin. Sig Transduct Target Ther 5, 92 (2020).)
Various strains of coronavirus and its names as per WHO, Pango lineage and Nextstrain clade are enlisted here:
| WHO name | Pango lineage | Nextstain clade |
| Alpha | B. 1. 1. 7 | 20I/S:501Y.V1 |
| Beta | B. 1. 351 | 20H/S:501Y.V2 |
| Gamma | P. 1 | 20J/S:501Y.V3 |
| Delta | B. 1. 617. 2 | 21A/S:487K |
| Epsilon | B. 1. 427/B. 1. 429 | 20C/S/452R |
| Zeta | P.2 | 20B/S.484K |
| Eta | B. 1. 525 | 20A/S484K |
| Theta | P. 3 | 20B/S:265C |
| Iota | B. 1. 526 | 20C/S:484K |
| Kappa | B. 1. 617. 1 | 21A/S:154K |
The mystery of double mutation and Delta plus:
I have enlisted several common mutations of the Delta variant, however recent studies show the presence of two mutations in one single Delta variant strain which are E484Q and L452R.
Both mutations are originally developed from two different strains and might be super infectious in the coming times. The first case of double mutation was reported from Maharashtra, India.
Researchers believe that the virus gathers information from its interaction with the host cell, and uses it to evolve and invade more aggressively. Recent findings show the evolution of yet another super strain having another mutation K417N.
Scientists named it as Delta Plus strain and believed it to be more transmissible than the Delta strain itself.
Related article: Strategies to Prevent Transmission of COVID-19 (Coronavirus).
Why is the delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 more transmissible?
To understand transmissibility, we need to understand how it invades. The spike protein present on the membrane interacts with the host cell surface receptors, usually is ACE2 receptors and gets in.
Adaptive immune systems get signals from receptor binding and release specific antibodies against it. Immunoglobulins- specialized proteins often said as antibodies bind to the spike proteins through antigen-binding sites.
The ABS (Antigen binding site) is a specialized structure on the “Ab” surface that interacts with the protein spike and guides the virus to the direction where antigen processing and cleaning occur.
Meaning, if an appropriate/ correct antibody is raised against the spike protein, the virus can’t do pathogenic invasion. The common receptor is ACE2 that interacts preliminarily with coronavirus.
Spike protein’s structure changes when mutations like alpha, delta or beta occur in the gene encoding spike. A newly formed crown-like mutated spike protein can’t be recognized by an ABS and henceforth immunoglobulin can’t process it.
Especially the 452- delta variant neutralized the antibodies raised against previous coronavirus strains and vaccination. So the present strain is supposed to be more transmissible. And contagious too.
“Delta variant is by far the most contagious with 97% faster transmissibility among all variants” – Tweeted on June 18 by Dr. Eric Ding.
What are the common symptoms of the Delta variant?
Similar to the previous coronavirus strains, Headaches, sore throat and runny nose are the three most common symptoms. Note that no different symptoms of this variant are reported to date, however, studies suggest that patients may feel funny “off” or a bad cold.
Common symptoms of the previous strains are cold, fever, cough, loss of taste and smell. Noteworthy, loss of taste & smell and fatigue isn’t commonly observed in variant Delta.
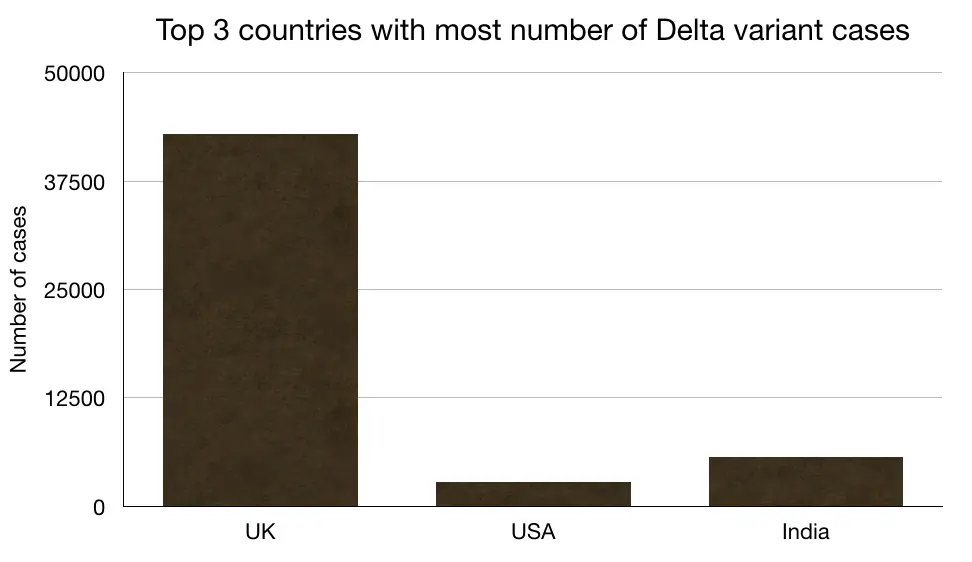
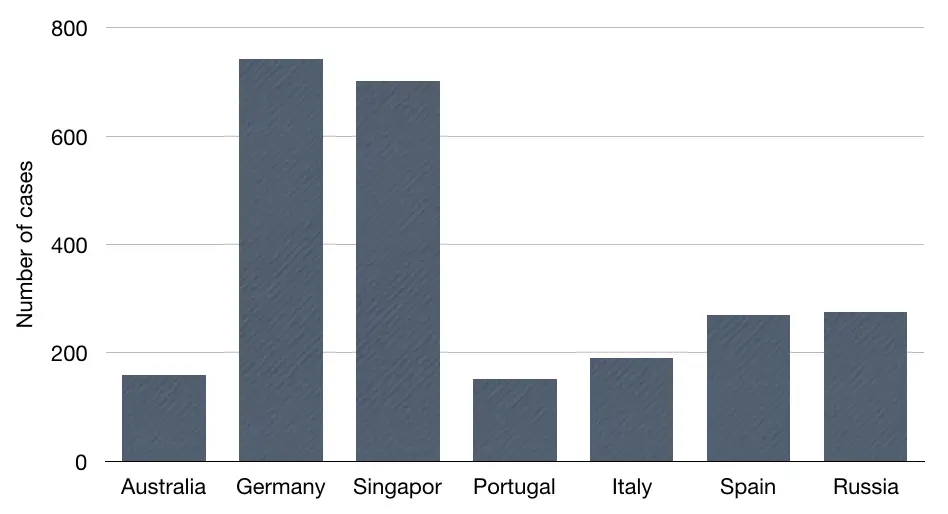
Risk factor and preventive measures:
The second wave is fading away. People want to go out to meet friends and do parties. Let me tell you that the risk isn’t lowered. The Delta variant is evolving faster and becoming stronger day by day.
People overlook symptoms of feeling cold and running nose as seasonal fever symptoms. If you have any of the symptoms reported above in this article, take doctor’s advice and do testing. If possible, sequence your sample to know if you have a Delta variant or not!
We never learn from other’s mistakes, not even from our own. We are thinking that everything is over!
Don’t risk your lives, things are yet not over. If we believe scientists then the third wave will hit the world, especially in countries where the Delta virus is reported, badly between September and October.
Avoid unnecessary outdoor activity. Do not gather, if required follow social distancing. Wear a mask and sterilize reusable masks frequently.
Get a vaccine, however, we don’t yet know which vaccine will work, but surely, you will be safe if vaccinated. It’s better to be immunized nonetheless be vulnerable without being vaccinated by having the second thought of fidelity of existing vaccines against Delta variants.
Studies suggest that the Bamlanivimab (Monoclonal antibody cocktail) is less active against the Delta strain. Among available 12 monoclonal antibody therapies, 5 fail to give protection against the Delta variant.
Read further: What is the Ct value of SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) RT-PCR?.
Are vaccines less effective against Delta strain?
Vaccines are now known to us. It’s a cocktail of inactive virus particles that induces a strong immune response against the pathogen. Various effective COVID vaccines are now available. Moreover, how it acts against the Delta variant isn’t known to us yet.
“Real-world data shows that the two doses of AstraZeneca vaccine are 92% effective against the Delta virus strain,” said PHE and AstraZeneca.
Courtesy to official circular: COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca effective against Delta variant.
But opposite the official statements, Dr Feigl Ding claimed that the AstraZeneca vaccine’s efficiency is 33% after the first dose and 60% after complete vaccination against the variant B. 6. 617. 2.
He also claimed that the effectiveness of the Pfizer vaccine against the Delta variant is 88% and 93% after the first and second dose, respectively (Link to both the tweet).
A mutant allele spreads faster when it is helpful to the organism and this is the case with the Delta variant too. The cluster of various mutations at the gene for spike proteins such as 452, 681 or 478 neutralizes weak antibodies.
Some reports suggest that several vaccines can’t help to escape infection, although studies need peer-reviewing. We aren’t reviewing the efficiency of vaccines available, but conclusively, studies suggest that some vaccines may not function to protect against the Delta variant.
One dose against two doses of vaccines:
60% and 92% success rate is reported after the first and second dose of vaccine, respectively against the Delta variant. While the Pfizer vaccine is 88% and 96% effective after the first and second dose of the vaccine, respectively.
However, other vaccine manufacturers have claimed to be effective, but did not provide real-world data. Proofs clarifying things that weak antibodies, raised after a single dose, neutralize faster than strong antibodies.
The Delta variant’s efficiency to invade strong immune responses raised after the second dose is becoming lesser. Still, people need to get vaccinated fast until new studies are published.
In their series of tweets between 14 to 21 June, Dr. Eric Ding has given significant information regarding the emergence of the Delta variant. You can read the tweets here: Dr Eric Ding’s tweets.
Read more: Coronavirus HKU1 (HCoV-HKU1) & HKU1-PCR.
Wrapping up:
To date, less published data are available on the Delta strain. As it was originally evolved in India, sequence data are yet very few. And therefore the best preventive option is to still stay at home, follow social distancing and wear a mask.
If you are worried about the vaccine, we need to wait a bit more, because as of now we don’t know whether present vaccines will work or not but definitely it will reduce the need for hospitalization. Studies and official sources of vaccine manufacturers also show that mRNA vaccines are more effective when given twice doses.
Data, information and statistics shown in the present article are taken from the various internet, news and article sources. Lack of peer-reviewed data limits the present article.
I am thankful to Mr. Debayan Baidya to review this article and give valuable suggestions.
If you wish to cross verify the data, here is the link of articles from where I got the information.
Sources:
Xia, S., Lan, Q., Su, S. et al. The role of the furin cleavage site in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-mediated membrane fusion in the presence or absence of trypsin. Sig Transduct Target Ther 5, 92 (2020).
The Delta variant is serious. Here’s why it’s on the rise– National Geography.
Delta variant begins to spread, threatening EU’s COVID progress. -Financial Times.
New symptoms of Delta COVID variant. – Times of India.
SARS-CoV-2 Delta variant. -Wikipedia.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for the latest blogs, articles and updates, and never miss the latest product or an exclusive offer.




