The paternity DNA testing is performed by isolating and examining the DNA samples collected from father, child and mother using the genetic techniques.
DNA can reveal one’s identity if he or she is biologically related to someone or not. DNA is a life molecule to us- made up of the three units viz a sugar, phosphate and nitrogen bases. This trio is collectively known as a nucleotide monomer.
A long chain of nucleotide monomers makes a DNA sequence. Around 3 billion bases are present in our genome. By the way, all the DNA in a cell is known as a genome.
Approximately 97% of our DNA is similar but only 3% of it is capable of making our unique identity.
Biologically or we can say genetically not every person is similar, not even monozygotic twins. You know the reason why? Read this article: Are monozygotic twins biologically identical?
So every individual has different sets of DNA or genes. But wait! If no person is genetically the same! Then how one’s biological, maternal or paternal relation can be established using the DNA test?
In the present article, we will answer this question and I will try to make you understand what a paternity DNA test is and how it is performed. Also, we will discuss some techniques used to do so.
Key Topics:
What a paternity DNA test is?
A paternity DNA test is a genetic test performed in order to establish a biological relationship between a child and an alleged father.
Every person has a unique DNA fingerprint and it’s his or her own identity. Even a fetus’s biological relation to his father can also be determined before its birth.
In a paternity DNA test, an alleged father’s DNA is matched against a particular child to make a match, which means, if father and child’s DNA got matched their relation can be established.
But as we said above, two people’s DNA is not the same! Then how it happens.
how one’s biological, maternal, or paternal relation can be established using the DNA test?
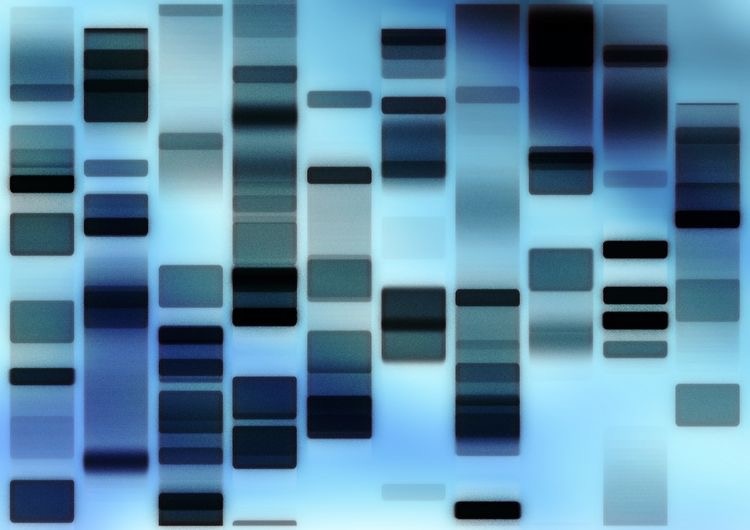
See, there are several regions in a genome that are highly repetitive, means occur one after another in a genome. See the image below,
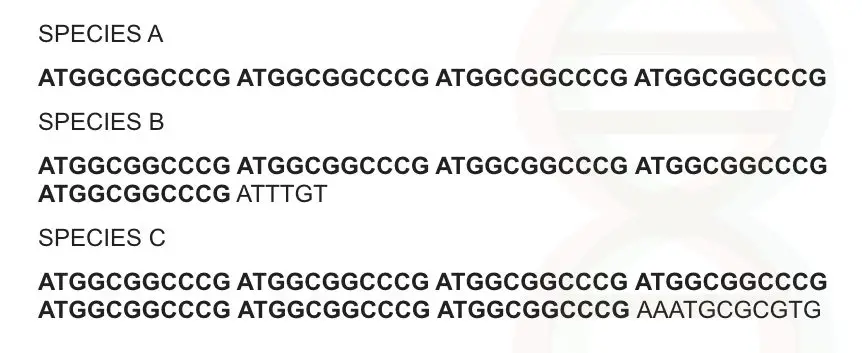
So the number of repeats of biologically related individuals is nearly the same. Thus almost the same DNA bands are observed. To make it more clear let us understand it properly.
The function unit of DNA is a gene and is located on chromosomes. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in a cell, one set comes from father and one from mother.
Thus one locus (a region we wish to study) inherited from father and one from mother.
If we analyze that particular locus we will get two DNA bands one matches with mother and one with father.
No make a DNA test for paternity possible as well as accurate, 10 or 15 or even 50 different loci or makers are taken and checked against the child DNA loci.
That is the whole mechanism, comprehensively.
Short history:
The first paternity test was not a DNA test, the blood type based paternal testing was introduced in the 1920s. However, the first HLA based DNA testing method was introduced in 1960 but the accuracy of it is only 80%.
The restriction digestion based RFLP method for DNA testing was introduced in 1980 while the PCR based detection method was introduced in the late 90s. To date, PCR is one of the most versatile, accurate, faster and reproducible methods used for paternity testing.
Now let’s see how to perform it.
How to perform a Paternity DNA test?
The process of paternity DNA test is completed in 4 steps; sample collection, DNA isolation, downstream processing and analyzing results.
Sample collection:
Every bodily cell (excluding the red blood cells) has DNA in it. We can use any cell type for performing the present test. However, buccal smear and blood are the common sources to do so.
Blood is collected in EDTA vial while a small amount of buccal samples is taken in a plain tube from inside a person’s cheek.
The buccal swab sample collection method is entirely non-invasive in which a plastic stick with cotton on top is taken and swabs inside the mouth gently.
While using a needle, a small amount of blood is drawn from a person.
To perform the paternity test at the prenatal stage, a technique known as amniocentesis is practiced to collect a fetus sample.
Usually, amniotic fluid or chorionic villi sample is taken in a plain tube or cell culture tube. To perform amniocentesis, a long sharp needle is inserted into a pregnant woman up to the fetus and a sample is drained.
After the sample collection, all the samples are sent to the DNA extraction lab. Notably, samples should be maintained properly. Store and transfer all the samples at 4°C.
DNA extraction or isolation:
Simply put, I can say, to perform a DNA test, we should have to isolate DNA from a cell or sample. It is very necessary that the isolated or extracted DNA must be of good quality. Also, the yield of DNA should be high enough to perform a test.
Various DNA extraction methods are used for different cell types. Usually, manual DNA extraction methods like PCI (Phenol, chloroform, and isoamyl alcohol) DNA extraction method and the proteinase K method are widely used.
If you wish to learn more on these methods read these articles:
- Phenol, chloroform and isoamyl alcohol DNA extraction method
- Proteinase K DNA extraction method
Two common methods are used for paternity DNA testing (in fact for any DNA testing); restriction fragment length polymorphism and PCR based amplification.
Polymerase chain reaction:
In the next step, an isolated DNA sample is processed for PCR- polymerase chain reaction to get copies of DNA (a few DNA aren’t visible enough to get results).
In a temperature-dependent biochemical reaction, the DNA sample is amplified in three different steps; denaturation, annealing, and extension.
We are not discussing the PCR here, it’s more technical. Anyway if you wish to learn about it, you can read our article on it: Polymerase chain reaction.
The PCR based paternity testing method relies on the use of STR and VNTR markers. The primers complementary to each STR or VNTR marker are used to anneal in PCR.
The STR (short tandem repeat) and VNTR (variable number of tandem repeat) are the regions in our genome that are highly variable and repetitive in nature. The number of every STR and VNTR region is different. Henceforth, by amplifying it we can distinguish the difference or similarities between individuals.
In the PCR based DNA testing, first in the denaturation step, DNA got separated at a higher temperature. In the annealing stage, the primers (specific to each VNTR or STR) got attached to its complementary sequence. And in the final extension stage, it expands.
Restriction fragment length polymorphism:
We know it as RFLP, is a traditional DNA fingerprinting or DNA testing method based on the use of restriction endonucleases.
The restriction endonucleases are enzymes (protein in nature, obviously!) that cut DNA in a pattern or at a specific location.
Every REase has a different cutting site (known as recognition site) at which it cuts.
Using a REase, genomic DNA of a child, father and mother are digested and incubated. Incubation facilitates proper digestion (cutting of DNA).
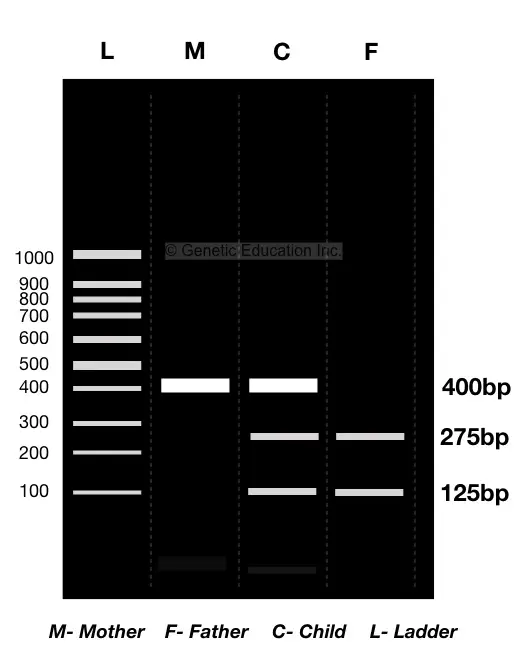
Digestion produces different DNA banding patterns for every DNA sample. You can see an example here:
For different DNA samples, different restriction digestion patterns are obtained, the reason behind it is the number of restriction sites!
As we said earlier in this section that every enzyme has a specific recognition or restriction site, the number of restriction sites is different in different organisms but nearly the same for biologically related ones.
Therefore, if a child is biologically related to the sample of the alleged father almost every band of their matches exactly.
After completion of restriction digestion, samples are run on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on agarose gel electrophoresis.
Analyzing the results:
Analyzing and interpreting the results of paternity DNA testing is entirely a different thing! It’s not like the computer will directly print the answer that someone is a child’s biological father or not.
An expert has to analyze each and every DNA bands in order to establish the relationship between the DNA samples. Also, he or she checks how many DNA bands or loci or markers are matching between the suspected child and alleged father, based on the results that are given.
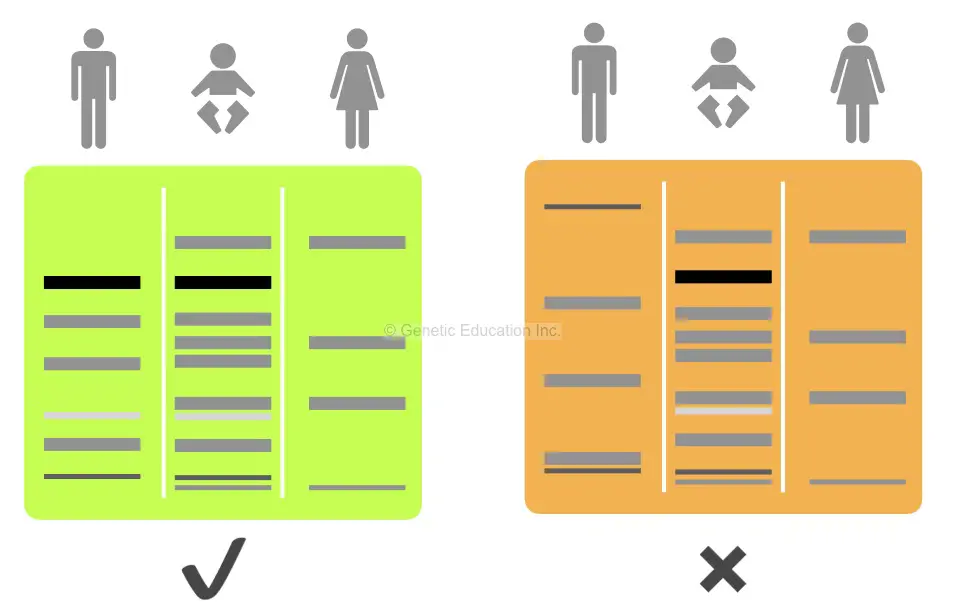
See the image below to understand the results.
In the image above, we have explained two different conditions, First is the exact match while the second one is not.
The reason behind that we already have explained. Every locus of a pair inherited from each parent that is one matches with mother and other matches with father.
The results are conclusive. If you have some basic science knowledge, you can understand which one is the exact match and which one is not.
So comprehensively, this is the whole process of paternity DNA testing.
Recent advancements:
Nowadays, robust and automated techniques are available to perform various DNA tests. Using the power of next-generation PCR technology and capillary electrophoresis, one can perform any DNA test easily.
Sample preparation, optimization, gel preparation and electrophoresis is not needed. Using a DNA extraction kit, high-quality DNA is obtained which is amplified and separated in a PCR and capillary electrophoresis machine directly.
The capillary electrophoresis is the latest version of a conventional gel electrophoresis method in which even a single base change between DNA samples can be detectable.
Yet another revolutionary finding has been made that enable the prenatal testing non-invasive. The technique is known as cell-free DNA testing.
A small amount of fetal DNA is present in a mother’s blood which can be isolated and used for DNA testing. The cell-free DNA testing offers accurate testing without risking the pregnancy. The technique is known as non-invasive prenatal DNA testing or non-invasive prenatal paternity DNA testing.
Paternity Index:
The paternity index or the combined paternity index is a statistical value used to measure the probability of success of a test (how accurate a test is!).
Usually, a 99% score is considered as most accurate while 0% is considered as no relationship in the CPI.
As per the US rules and regulations of paternity testing the minimum paternity index value is 99.0% for citizens and 99.5% for immigrants are decided.
Allelic frequencies of every locus or allele are considered in calculating the PI score. Simply put, 99 out of 100 markers should be matched.
Maternal DNA testing
The process of maternal DNA testing is almost similar to paternity DNA testing, however, the maternity DNA testing is yet more accurate than the other one, why so?
A set of non-nuclear DNA known as cytoplasmic DNA or mitochondrial DNA is only inherited from the maternal side. I repeat, “only a mother can pass on mitochondrial DNA to their baby”
By considering the marker from mtDNA the maternal side can be varied genetically.
Legal proceedings:
The paternity DNA is usually performed to get custody of a child and is a matter of the legal proceeding. It is considered as legal evidence for immigration purposes, giving custody of a child and for the social welfare benefits. But there are several rules for it.
The results or evidence of paternity DNA test should be performed under the concern of father, child and/or mother.
The test must be performed from the accredited body (of the country).
The indications of test results should be clear.
The person who has collected samples and performed a DNA test should not be related to any of the parties tested.
And of course, the results are conclusive only achieve 99% or above CPI.
The cost of a paternity DNA test:
Usually, we can say any DNA test is somewhat costlier. The test cost of the paternity DNA test varies between $300 to 600$.
The non-invasive method (a cell-free DNA testing method) is however costlier than the conventional one. The test cost of cell-free DNA testing or prenatal testing is between $1500 to $2500.
Now let’s check out some of the common questions asked for paternity DNA testing.
Related articles: Pregnancy Genetic Testing- What, When and Why.
Common FAQs:
When to use a paternity test?
The paternity test is performed to issue or give the rights and duties of a child to his father.
Also, it would be performed in the case when a child’s paternity is in doubt or not specified.
What are the other options for paternity DNA testing?
Besides a DNA test, several traditional and older methods used for paternity verification are ABO blood group typing, human leukocyte antigen testing and analysis of several protein markers.
The DNA testing method is the most accurate, faster and reliable method for paternity testing. Its accuracy is nearly 99%.
At which stage a paternity DNA test is performed?
DNA doesn’t change with age therefore at any age of a person’s life a paternity DNA test can be performed. Notably, nowadays it is also performed on pregnant women by taking its fetus sample directly.
Note: amniocentesis may risk pregnancy to abortion.
Who can’t be considered for the paternity DNA test?
A DNA test works on every one accurately except, “chimera”. Chimeric individuals are those who have two different sets of genomes. In chimeras, two different cell types with a different set of DNA and genes occur. Thus it may produce false-positive results. Chimeric conditions are very rare.
Conclusion:
The paternity genetic testing method is almost 99.0% accurate and widely used to solve claims of paternity in different countries, though, the rule sand regulations may vary.
To date, no other method is so accurate, like the DNA testing method. Various other testing kits are now available to know one’s family history and sibling history. Also your common ancestors can be encountered by a DNA test too.


