“Congenital disorders often referred to as the birth defects, occur by birth and due to genetic, developmental or environmental factors.”
Every couple wants a healthy baby. But unfortunately, not all are so lucky. Some babies suffer from the type of defects or abnormalities that are naturally present in them by birth.
These are either developmental, mental or physical abnormalities or problems that occur in a newborn due to unknown or known genetic factors.
Broadly, these types of abnormalities are categorized into “congenital disorders” or “birth defects”.
Every year there are thousands of kids born with congenital problems.
As per the WHO data, more than 3 lakh newborns die within a few weeks of birth due to heart defects, neural tube defects or Down syndrome, every year.
Simply put, congenital disorders occur before birth. Although there are so many factors that are responsible for congenital disorders, the genetic factors are so commonly responsible.
In most of the cases, the reason for the occurrence of birth defects is genetic or unknown. Heart defects, neural tube defects and cleft palate are common among them.
While most of the birth defects are non-treatable, some can be managed by several therapies and medications.
In the present article, We will explain to you what the birth defects or congenital anomalies are, the top 10 common congenital anomalies and how to detect it. Furthermore, we will also talk on related topics.
Key Topics:
What is a congenital disorder?
Congenital disorders are originated during the fetal developmental stage or might be inherited from parents to their offspring.
It is also known as birth defects, birth anomalies, congenital malformation or congenital metabolic disorders.
Many factors cause birth defects, such as,
- Chromosomal imbalance, gene defect or change in gene expression- genetic factors.
- Adverse environment
- Alcohol, smoking or drug consumption.
- Some accidents during pregnancy.
- Infections
Among all these, the genetic factor is one of the leading causes that results in abnormalities before birth.
Related article: Different type of Genetic Inheritances.
Cause of congenital disorders:
The random events occurring during the developmental stage known as the nondisjunction, leads to an imbalance of chromosomes. Here the number of chromosomes changes abnormally.
Down syndrome is the classic example of a chromosome imbalance in which three different 21 number of chromosomes are present in a baby. The child may suffer from serious developmental, cognitive, and mental problems.
Some disorders are recessively inherited! Means inherited from parents to their offspring but they don’t about that! For instance, the common metabolic disorder phenylketonuria or cystic fibrosis.
Recessively inherited genetic conditions are more commonly found in congenital problems because its signs and symptoms are not seen in parents.
Some birth defects occur by the influence of environmental factors on the genes of the fetus and are categorized into environmentally- influenced congenital malformations.
Comprehensively, the congenital disorders are
- Single-gene disorders
- Polygenic disorders
- Inherited disorders
- Non-inherited disorders
- other
Infections during pregnancy can also lead to some dangerous congenital problems.
Majorly the birth defects can be encountered through various techniques within the first three months of pregnancy. Some congenital problems are so harmful while others are not.
In the USA 20% of babies with congenital problems die before birth or immediately after birth.
In some conditions, using long term medications, treatment and several therapies, it can be managed.
Top 10 common congenital disorders:
- Cleft palate
- Down syndrome
- Heart defect
- Cystic fibrosis
- Cerebral palsy
- Sickle cell anemia
- Fragile X syndrome
- Phenylketonuria
- Thalassemia
- Glycogen storage disorder
Cleft palate
In the United States of America 1 in every 1,600 to 2,800 babies born with cleft palate, cleft lips or other lips abnormalities.
Though the cleft palate is a common congenital problem, it is not fully a genetic defect. Genes can be involved in the development of cleft palates, perhaps.
Genes such as TBX22, IRF6, PVRL1 could potentially be linked with the cleft palate or related problems, still, some other factors are also linked with it.
Down syndrome:
Yet another common congenital abnormality is the Down syndrome or the trisomy 21. The Down syndrome occurs completely due to the abnormal distribution of chromosomes
The triplet of chromosome 21 observed in the fetus. The baby may experience developmental and cognitive problems. During the meiosis cell division, an event called nondisjunction causes this type of condition.
Down syndrome is a non-inherited genetic defect. We have covered the whole article on it, you can read it here: Trisomy 21 (Down Syndrome): Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Pictures and Diagnosis.
Heat defects:
Problems in heart walls, tubes or vessels are considered in the heart defect.
Though heart defects are not completely genetic defects, Mutations in several genes play a crucial role in developing it.
Indeed, Trisomy 21 is one of the reasons for congenital heart defects. Scientists are trying to establish a genetic basis for congenital heart defects.
Cystic fibrosis:
Another common congenital problem is cystic fibrosis. Not so lethal, the cystic fibrosis occurs by the gene mutation which is inherited autosomal recessively.
The mutation in the CFTR gene (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductor regulator gene) causes serious respiratory-related problems.
The CF is not a lethal condition, further, mental and cognitive problems are also not observed in the patient. Babies with cystic fibrosis suffer from infertility in the future. Read more on a related topic: how is cystic fibrosis inherited?
Sickle cell anemia:
One of the common types of congenital blood disorders is sickle cell anemia. The sickle cell anemia is a kind of recessive autosomal genetic disorder that occurs by the single gene mutation in the HBB gene.
A person with the single mutant allele with the HBB remains totally normal (known as the carrier of the disease). When both, father and mother inherit single recessive alleles in the fetus, the fetus suffers from a severe type of non-curable anemia.
Related article: Sickle Cell Anaemia: Definition, Cause, Genetics, Trait, Symptoms and Diagnosis.
Thalassemia:
Yet another type of blood disorder that occurs from the birth is the thalassemia. Much like the sickle cell anemia, mutations in the beta-globin gene (HBB) results in thalassemia.
If a mutation occurs in the alpha chain of the globin gene, it is known as the alpha-thalassemia, and if mutations occur in the beta-globin gene, it is known as the beta-thalassemia.
The beta-thalassemia is more common than alpha-thalassemia. It is an autosomal recessive disorder that causes anemia.
When two mutant beta-globin chains are inherited in the fetus, it becomes thal-major, the patient suffers from the condition life long.
Cerebral palsy:
Cerebral palsy is a congenital motor disability that mainly affects someone’s ability to balance movement and posture. Usually, C palsy children have muscle weakness.
The genetic basis of the Cerebral Palsy is yet not established, however, research is ongoing on some candidate genes involved in it.
The CP is not a genetic condition and hence its inheritance pattern is unknown. Some of the common symptoms of it are; Speech difficulties, movement and walking problems, cognitive impairment, spinal and joint problems, Hearing and vision loss.
Phenylketonuria:
The phenylketonuria is a kind of congenital inborn error of metabolism that occurs in a baby by birth. The condition is genetic and inherited in families as an autosomal recessive pattern.
Amino acid phenylalanine can’t be metabolized properly which results in the accumulation of phenylalanine in the body. A higher level of it causes a musty odor and is secreted through urine or skin.
Delayed development, hyperactivity, intellectual disability and several neurological problems are commonly observed in the baby with PKU. PKU occurs by a mutation in the PAH gene.
Glycogen storage disorders:
Accumulation of glycogen due to mutations in some genes results in glycogen storage disorders. It is also a type of inherited congenital genetic condition.
Slow growth rate, low blood sugar, muscle weakness and other problems are generally seen. The present condition is polygenic in nature.
Diagnosis of congenital disorders:
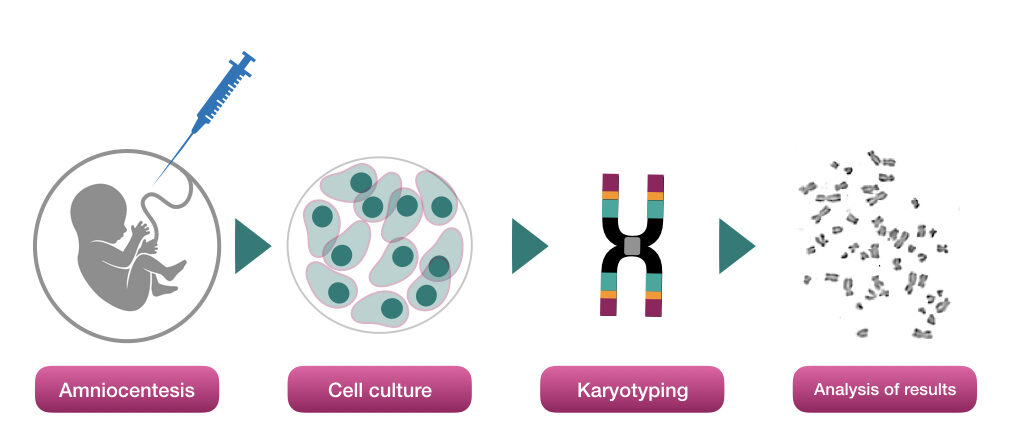
To screen a baby for encountering congenital problems, a doctor takes either amniotic fluid or the chorionic villi sample through the process of amniocentesis. Using the long needle, an expert takes a fetus sample and sends it for testing.
Chromosome defects:
For testing the chromosomal abnormalities or chromosomal problems the sample is processed through karyotyping in which the cells are cultured, harvested and metaphase chromosomes are investigated.
Chromosomal number or structural problems can be encountered using this technique. Read more: What is karyotyping?
To encounter minor chromosomal alteration, fluorescence in situ hybridization like techniques are used. Even smaller alterations are investigated by ArrayCGH or microarray.
The microarray is powerful enough to screen thousands of chromosomal defects in a single experiment. It relies on the principle of hybridization in which millions of chromosome-specific probes are immobilized on a glass side to allow hybridization.
Gene or DNA mutations:
Techniques like karyotyping or FISH are not able to identify gene mutations. Polymerase chain reaction-PCR or DNA sequencing are employed to investigate gene mutations.
PCR can detect known gene defects and can also differentiate homozygous from the heterozygous.
Using the set of primers, the special type of DNA polymerase synthesizes the DNA. Variations in the native PCR like the real-time PCR, nested PCR or ARMS PCR are used to detect different types of gene defects.
Notably, PCR can’t identify polygenic disorders effectively.
The technique is known as DNA sequencing sequence the whole DNA and can investigate unknown mutations as well.
DNA sequencing and microarrays are topmost techniques to study and diagnose genetic disorders.
Related articles:
Other birth defects:
Several biochemical testing and ultrasound methods are employed in the detection of other congenital disorders.
Developmental problems as well as some heart defects can be encountered during the early stage of pregnancy by sonography. However, biochemical tests can’t be performed during pregnancy.
Furthermore, several other birth defects can be detected using the physical examination after birth.
Note that genetic testing like the PCR, DNA sequencing, microarray or karyotyping are the only techniques that can identify congenital defects during the prenatal stage.
Treatment and management:
Birth defects or congenital malformations are more genetic therefore in most cases are not curable. However, through proper mediations, surgeries and some basic care and therapies, babies can live longer, comfortably.
Though those conditions are fewer. For example, down syndrome and cerebral Palsy baby can be taught by speech and cognitive therapies but can’t be treated fully. They have to suffer from mental retardation throughout their life.
In the case of development and reproductive problems, impaired tissues sometimes can be removed by surgeries but there are always risks associated with the surgeries on heart defects.
Here one thing should be taken into account that parenting plays an important role in congenital malformation. Home care and parenting techniques help babies to cope up with various problems faster.
Prevention of congenital conditions:
Conditions such as Down syndrome and other inherited genetic problems occur due to unknown causes there are no such reasons for that (just some assumptions!).
Notwithstanding, some routine medical practice and by avoiding several habits can prevent birth defects.
- Avoid drinking alcohol
- Avoid smoking or drugs
- Avoid tobacco consumption
- Stay relax
- Take some routine medication suggested by a doctor like folic acid supplements and vitamin supplements.
- Follow pregnancy vaccinations without fail.
- Take rest and follow your doctor’s instructions.
Genetic counseling and prenatal genetic testing:
Prenatal genetic testing and Genetic counseling become more important in the case of congenital defects. As we said, genetic techniques are the only detection methods that can detect congenital problems during pregnancy.
Although, the amniocentesis technique is not so safe to perform because of having the chance of miscarriage.
Therefore the prenatal genetic testing is not applicable for all. Then how to know that the baby in the womb is suffering from some birth problems or not.
Here the Genetic counselor in coordination with your gynecologist makes it happen, they decide whether to go for amniocentesis or not.
Genetic counseling is a verbal communication process using which crucial information related to genetic conditions can be gathered.
A genetic counselor investigates your genetic history, asks you several questions to know if some genetic defect is running in your family or not!
Based on the genetic counselor’s decision, your doctor will decide to investigate further. Also, the sonography data is taken into consideration. If the doctor thinks that there is something not right! He or she advises you for genetic testing.
Usually, to known the status of congenital disorders, genetic testing is advised in these cases,
Material age above 35, family history of a genetic or chromosomal defect, previous child with birth defects, familial cancer or stillbirth.
Conclusion:
Conclusively we can congenital defects are majorly originated either due to gene mutations or chromosomal imbalance most. However, recently it is studied that change in gene expression also causes several other types of congenital problems as well.
In addition to this, an inborn error of metabolism is also commonly observed by birth.
FAQs:
What is congenital abnormality?
The congenital abnormalities or anomalies are also known as the birth defect occurs by birth and in most cases are genetic. Congenital problems are associated with developmental, mental, reproductive and cognitive problems in babies.
What causes the congenital disorder? Or what are the reasons for congenital disorders?
In major cases, congenital disorders are genetic in nature. Gene, DNA or chromosomal mutations are common reasons for that. Note that environmental factors, bad habits like drinking, drug or smoking may cause this type of condition.
What are the common congenital problems or conditions?
Though as we said, developmental, mental, cognitive and reproductive problems are most common in birth defects, heart abnormalities, cleft palates, Down syndrome and other mental problems are commonly observed.
What is the most common congenital disorder?
It is not clear which one is most common in the world but the trio we had explained above are the three most appearing birth defects, viz the heart defects, mental retardation and cleft palate.
What are the risk factors for birth defects or congenital defects?
Maternal age above 32, improper parenting, consumption of a drug or unrelated medications, smoking, family history of genetic disorders, previous child with congenital malformations or several pre-existing conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure are some of the risk factors for birth defects.
How are congenital malformations diagnosed? Or what are the techniques to encounter birth defects?
In case of genetic conditions, to encounter chromosome or gene mutations, karyotyping, polymerase chain reaction, RT-PCR, DNA sequencing, DNA microarray of FISH-fluorescence in situ hybridization like techniques are used.
In addition to this, physical examinations and ultrasound techniques are also employed.
How are congenital problems or defects treated?
There are no such common treatments or medication for a group of birth defects. Nonetheless, by medications, surgeries, therapies, counseling or parenting congenital problems can be treated to some extent.
How can birth defects be prevented?
There is no clear guideline for preventing such types of conditions though by avoiding bad habits, smoking, drinking and following some proper guidelines it can be prevented.