“Template DNA in PCR is a single-stranded DNA that provides a starting point for amplification. Explore the role, properties and concentration of template DNA and learn how to optimize it.”
A typical Polymerase Chain Reaction consists of dNTPs, Taq DNA polymerase, PCR buffer, Primers, nuclease-free water and template DNA. All ingredients are equally crucial for PCR, however, without a template DNA, everything is useless.
So template DNA is an essential ingredient in any PCR reaction. In addition, the quality, quantity and concentration of template DNA also play an essential role in a PCR reaction.
I’m a trained geneticist and years of experience in DNA extraction, PCR and related techniques. So I’m the best person to explain this. In this article, I will explain to you the template DNA, its role, and its properties in this article.
Let’s start with the introduction.
Key Topics:
What is template DNA in PCR?
Template DNA or template strand, in molecular biology, is a single-stranded DNA molecule generated by helicase activity and used for replication. Using a complementary RNA primer, DNA polymerase synthesizes a new DNA strand using the template.
In PCR, the template DNA is a single-stranded sequence that provides a primer binding site and starting point for PCR. The amplification is achieved by thermostable Taq DNA polymerase enzyme. Genomic DNA, plasmid DNA, cDNA or purified PCR products can be used as template DNA in PCR.
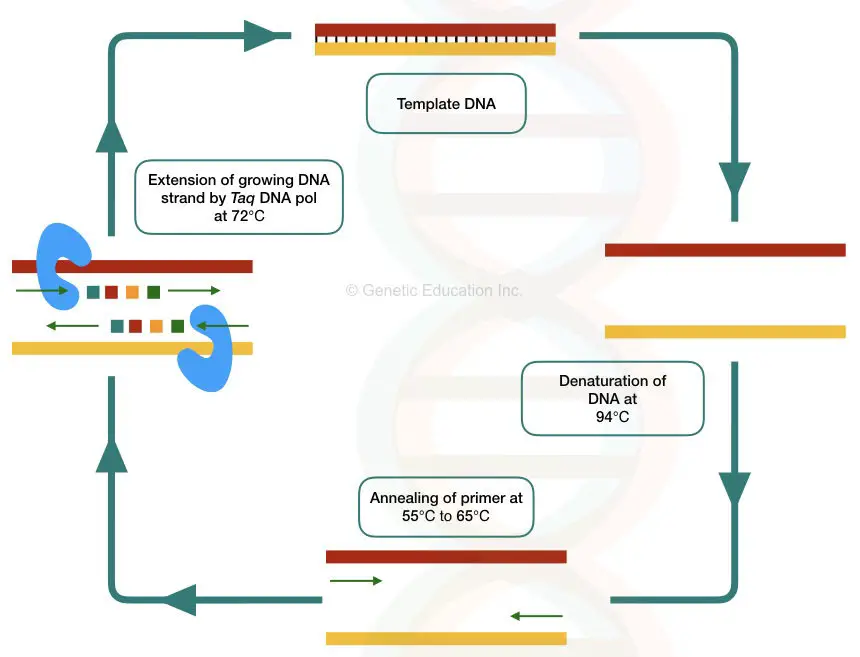
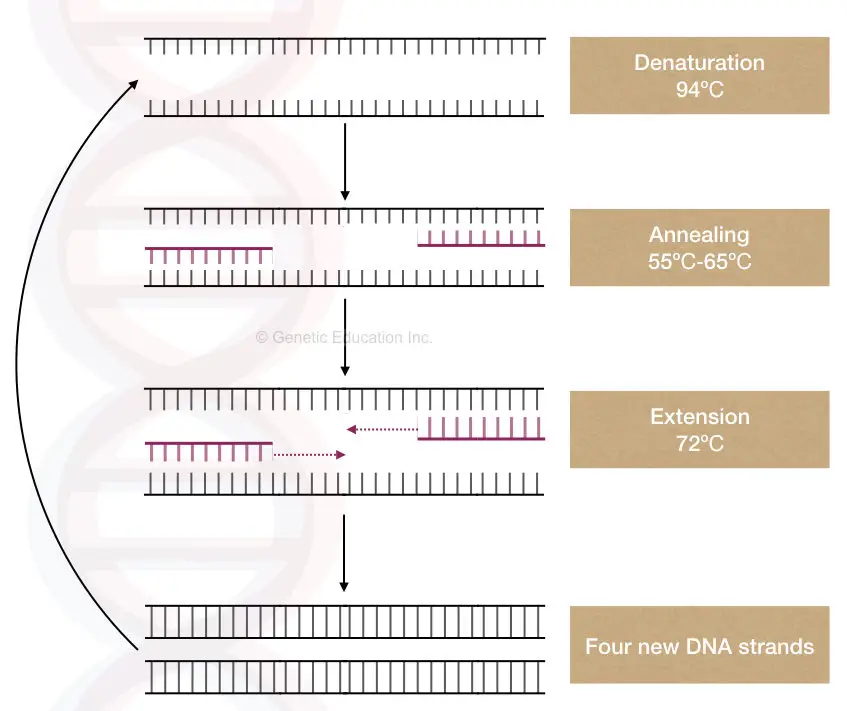
PCR is a temperature-dependent DNA amplification technique. The template DNA here is first, denatured into two single-stranded molecules, anneal with the complementary primers and amplified by Taq DNA polymerase in a cyclic reaction.
To know more about PCR, you can read our previous article. The link is given in the introduction.
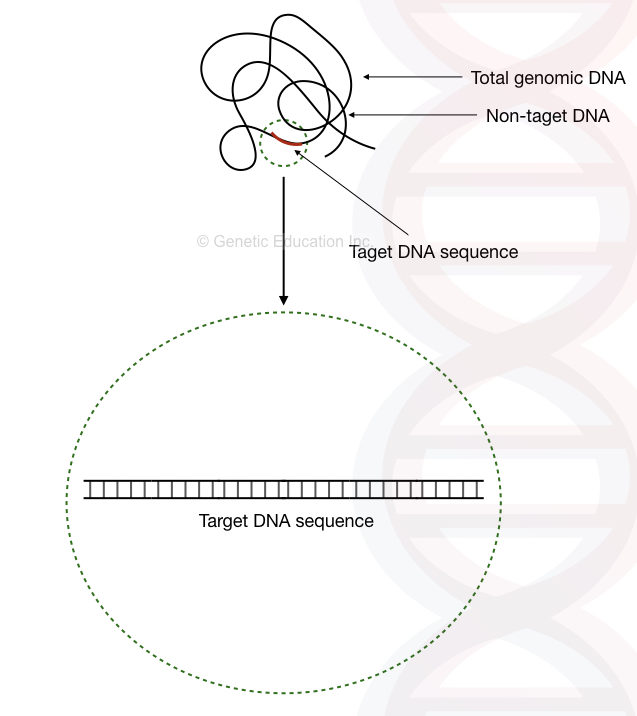
It is important to understand that the template provides a target region for amplification and thus, not the whole template DNA is used as a target. The region which is utilized for amplification is referred to as target DNA while the rest of the sequences is referred to as non-target DNA.
In PCR, the length of the target DNA sequence is usually between 100bp to 5,000bp. However, up to 15,000bp region can be amplified using a specialized long-Range PCR protocol. So, only a tiny portion of the template DNA is utilized for PCR amplification.
The rest of the template DNA, impurities, contamination and chemical traces can impact the PCR reaction, negatively. And should be removed during consecutive amplification cycles.
What is the role of template DNA in PCR?
Template DNA provides a single-stranded complementary sequence for a primer to anneal and a substrate for a Taq DNA polymerase to synthesize the DNA.
At the target location, the template denatures by breaking the hydrogen bonds between two strands. In the next step, the complementary primer binds to the target location which is used by the thermostable Taq DNA polymerase during the extension step.
The Taq Pol uses the template-primer junction as a substrate, uses the 3’-OH end of the primer and initiates new strand synthesis.
What are the properties of PCR template DNA?
Purity:
The template DNA must be highly pure. It should not contain impurities, contamination and traces of chemicals. Other DNA fragments and chemicals used during the DNA isolation process, and reagent impurities can contaminate the template DNA.
Contaminated or impure template DNA leads to reaction failure and false-positive or false-negative results. However, the common impact of contamination is reaction failure.
To get purified DNA, Isolate good-quality DNA. Use DNA with purity ~1.80 at 260/280 nm. Give proper wash to the DNA.
Specificity:
Keep in mind that the template DNA must contain your target DNA sequence or gene and thus it should remain intact.
Integrity:
The template should be free from any degradation. Pure and intact DNA gives excellent PCR amplification. Any degradation leads to abnormal, unwanted or no results in PCR.
Use good quality DNA protocol. Remove the nuclease effectively during the DNA isolation process to obtain intact DNA.
GC content:
The target region from our template should have <45% GC content in order to achieve good amplification. GC content plays a crucial role during PCR, read this article to learn more about the importance of GC content.
Concentration of PCR template DNA:
The concentration of template DNA plays a crucial role in achieving excellent PCR amplification, however, it varies depending upon the requirement and specificity required. The ideal concentration of template DNA is between 10 to 100 ng. per reaction.
I use a 30 to 50 ng template for a 25µL reaction. So for a 50µL, it should be between 80 to 100 ng. Interestingly, recent research reported adequate amplification using only a 10 pg template concentration.
Note that to get desired or adequate results template concentration optimization is required. Optimize your own concentration depending on the results you get with the ideal range.
It is also crucial to keep in note that too high and too low template DNA concentration affect the reaction efficiency and specificity. For example, at higher concentration, the chances of non-specific amplification increases while at lower concentration the chances of reaction failure increase.
| Type of template DNA | Ideal concentration range |
| Genomic DNA | 10 to 100 ng |
| Plasmid DNA | 0.1 to 1 ng |
| cDNA | 100 pg to 10ng |
PCR template DNA Optimization:
So in this last section, I will give you some of the technically proven and important tips that will help you in your PCR experiment.
- Use only high-quality template DNA (Good purity and quantity).
- To maintain the DNA in good shape (integrity) use only TE buffer dissolved DNA. The pH of the TE buffer should be 7.8 to 8.0.
- Add a template in the last to disallow early primer binding and polymerase reaction.
- Dilute the template DNA as per the required concentration. Don’t use it directly in the reaction (with the rough calculation).
- To reproduce good-quality results, carefully observe your results and accordingly adjust your PCR template concentration in the next reaction.
- After reading this entire article, if you still have a question in your mind, how much template DNA do I need to add in PCR, start with 30ng for a 25µL reaction. You will get good results.
Read more: 10 Strategies to Achieve Excellent PCR Amplification.
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, template DNA in PCR provides an initiation point in the reaction. Though the concentration of the template does have a significant impact on the reaction, the concentration of primers, efficiency of PCR buffer and concentration dNPTs play equal roles in the successful PCR.
I hope you like this content. Please share it with your friends and if you have any questions regarding DNA extraction, PCR or electrophoresis, feel free to ask me.

