“A complete haploid set of the DNA present in an organism is a genome, contrary, a gene is a smaller functional part of the whole genome that encode proteins.”
The comparison of Genome Vs Gene is practically non-significant, de facto. However, To understand both the terms very well, we are doing this comparison.
The present topic will help newbies to perceive fundamentals.
Comparing Genome Vs Gene is like comparing the ant and the elephant, indeed.
Let’s understand it by taking the example of cook-book,
“A genome is like a whole cookbook contains information of all the recipes, ingredients, and how to cook it.
Whereas the gene is a specific recipe by reading the information of it we can cook a specific dish (thus protein).”
Read more on DNA: DNA story: The structure and function of DNA
Key Topics:
Genome Vs Gene, an unusual comparison:
A genome contains millions to billions of base pairs. Some organism carries only a few thousand base pairs while some have billions of base pairs.
Whereas,
A gene is a functional sequence of DNA ranging from a few hundred base pairs to several thousand base pairs. For example,
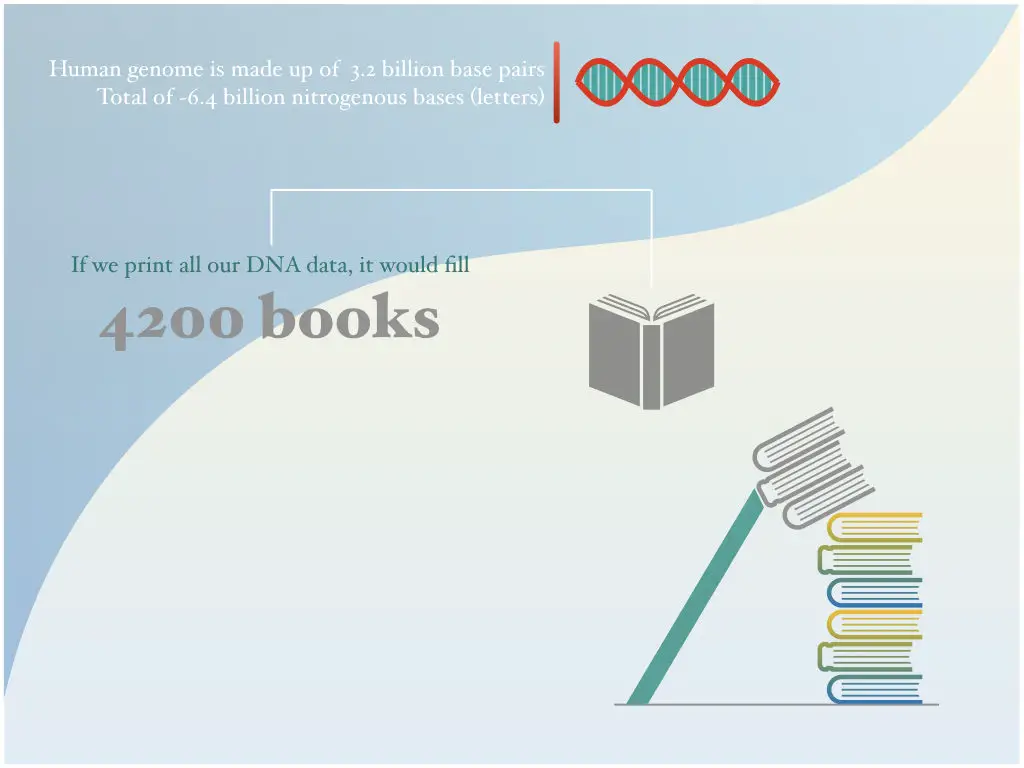
Size of human genomes is 2.9 to 3.2 bbp (billion base pairs), on the other hand, the size of the SRY gene is 800bp (0.8kb), the smallest gene in the human genome
Note: the human DMD gene is the largest gene that exists, having 2.3mbps (megabase-pairs).
Interestingly,
The genome of the Carsonella ruddii, a sap-feeding insect has the smallest genome with only 159662 base pairs and 182 genes.
The Paris japonica sports, a rare Japanese flower has the largest genome size on earth. The genome of it has 130 billion base pairs which are 50 times larger than the human genome.
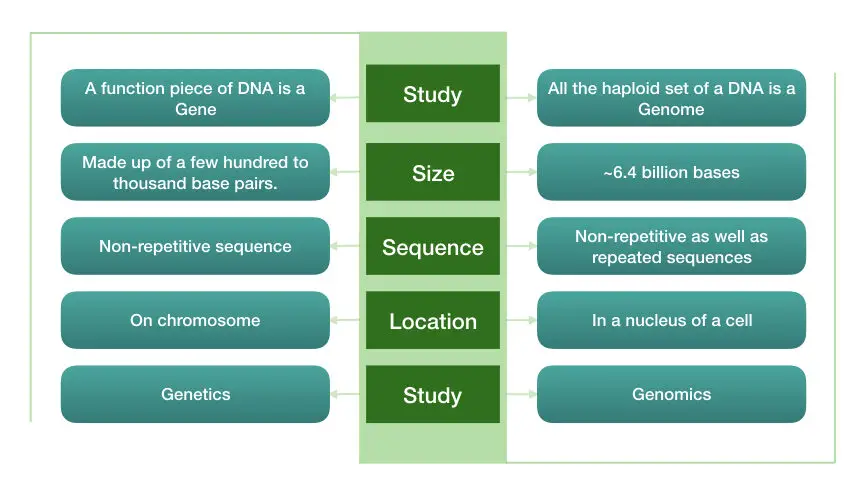
A genome includes functional as well as non-function DNA.
Whereas,
A gene is a dedicated functional piece of DNA.
The exon present is a gene code for a particular protein, on the other side, the genome comprises coding as well as noncoding introns, intervening sequences, pseudogenes, jumping genes, conserved sequences, and other DNAs.
Functionally, a genome encodes proteins as well as maintains gene expression.
Whereas,
Functionally, a gene encodes either structural or functional proteins.
The major portion of a genome is made up of repetitive DNA sequences.
Whereas,
A gene doesn’t have repetitive DNA sequences.
[epcl_box type=”information”]10% of the human genome consists of highly repetitive DNA sequences. [/epcl_box]
Important information:
The repetitive DNA sequences are used as DNA testing tools. STR and VNTR like markers are practiced regularly for criminal verification, parental verification, checking maternal cell contamination, and identification of individuals.
Read more on STR: Short Tandem Repeats (STRs): A Secret of Every DNA Test
Only a single genome is present in an organism.
Whereas,
Several hundred to thousand genes are present in an organism’s genome.
A genome is located in the nucleus of a cell.
whereas,
Genes are located on the chromosome and a single set (23 chromosomes) of chromosomes is called a genome.
Note: several DNA sequences are also present independently from the genomic DNA, present in the mitochondria and chloroplast. Read more on cytoplasmic DNA: Organelle DNA
A major portion of the genome, approximately 97%, is made up of the non-coding DNA.
Whereas,
A gene carries several hundred intervening non-coding DNA sequences called introns and is removed before the final transcript is formed.
Note:
The non-coding introns are not involved in the process of protein formation. It is removed by the process called splicing.
A branch of science includes the study of genome structure, function and regulation is referred to as genomics.
Whereas,
A branch of science deals with the study of gene structure, function, and inheritance is known as genetics.
Comparatively,
A genome is an entire DNA present in the nucleus of a cell.
A gene is a short stretch of DNA.
Some of the genes are not present in the nucleus (mt DNA or cpDNA) called cytoplasmic DNA or non-nuclear DNA.
Note: it is yet not clear that the mitochondrial DNA and chloroplast DNA can be included in a genome or not.
The summary of the article:
Now lets quickly go through the gene and genome.
What is a Genome?
A genome is a complete haploid set of DNA of an organism consisting of all genes. Each genome contains all the information regarding the building and maintaining an organism’s metabolism and development.
Normally, a genome is used to define the haploid set of chromosomes in the nuclei of multicellular organisms. That is why it is often referred to as human genome, mouse genome or fly genome. With time, the definition of the genome has changed.
Now it is also used to define the chromosomes in cytoplasmic organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplasts and the chromosomes of prokaryotes and viruses. Thus it is also referred to as mitochondrial genome, yeast genome and SV40 genome.
The size of genomes varies greatly by DNA content. In other words, a correlation can be taken into consideration between the size of DNA and developmental complexity.
The SV40 and E.coli genome are made up of approximately 5000 bp, 4.6 million bp while a multicellular worm C. elegans and the human genome is made up of 100 million bp 3.2 billion bp, respectively.
Size of several genomes are enlisted below,
- Dog: 2.4bbp
- Mouse: 2.5bbp
- Yeast: 12mbp
- Fruit fly (Drosophila): 170mbp
- Rice: 4.7 mbp
The genome is formed of coding genes as well as non-coding junk DNA. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in the human genome in which 22 homologous pairs are autosomes and 1 pair is a sex chromosome.
Multiple copies of the genome may occur in some organisms. An organism with a single set of each chromosome is called haploid organisms, for example, male ants and some algae carry a single set of chromosomes.
Humans and most of the eukaryotes are diploid organisms.
The sexually reproducing organism has half of the chromosome number in gametes compared to their somatic cells.
The human genome project was conducted in the ’90s for decoding the entire genome of us. Scientists had identified various genes and other DNA sequences of our genome and their functions.
What is a Gene?
Chromosomes are made up of bundles of looping coils, a complex network of DNA and proteins.
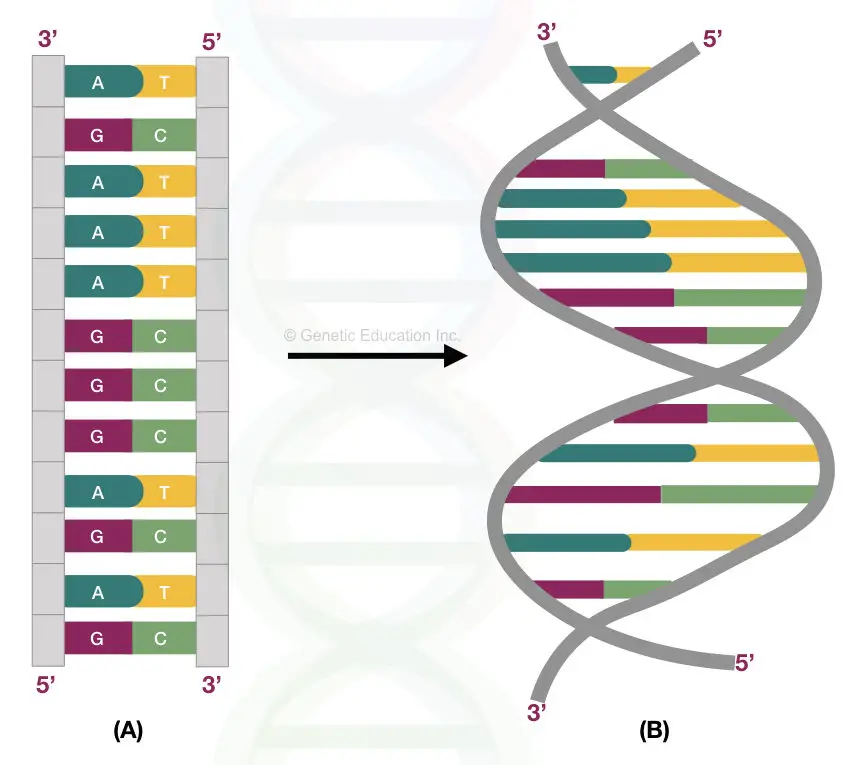
If it is untangled, a six-foot-long double strand of deoxyribonucleic acid – DNA is formed. A polynucleotide chain of DNA is arranged like a ladder made up of nucleotides. There are four types of bases – adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T) are present in DNA.
As we know, rung of DNA ladder is joined by covalent bonds between A-T and C-G. So, there is a pair of nucleotides on each rung of a ladder.
See the ladder-like DNA structure:
There is around three billion pair of nucleotides in each cell. 23,000 various genes are to date identified. A gene is a locus or a sequence stretch on the DNA polynucleotide strand and a unit of heredity.
Genes are mostly known as the blueprint for life. A gene makes either a functional or a structural protein, “it is a recipe for making a protein.”
Genes in a cell don’t synthesize protein directly. Instead, transcription of DNA occurs to do so.
The segment of the DNA to be transcribed is cut by an enzyme and used as a template to form a single-stranded molecule of RNA. The RNA is also a nucleic acid which is made up of the ribose sugar.
Read more on RNA: RNA: Structure and Function
This transcribed RNA is called messenger RNA or mRNA as it carries the message to the cytoplasm of a cell. RNA is then translated into respective proteins with the help of ribosomes.
Each protein helps in determining various traits. This is the central dogma of molecular biology.
The concept of the gene as a mechanism of inheritance was first viewed by Gregor Mendel in 1860. It was an essential conceptual change from, the established concept of Darwin and Hippocrates.
Read more on genetics: Introduction To Genetics: Definition, History, Applications And Branches
[epcl_box type=”notice”]The study of heredity and inheritance of traits is known as genetics.[/epcl_box]
Conclusion:
Though the genome of prokaryotes and eukaryotes are made up of DNA, DNA is not only the genetic material. Some viruses called RNA viruses/ retroviruses have RNA as their genetic material and thus their genome is made up of RNA not DNA.
Recently evolved stain of the COVID-19 coronavirus is also a type of single-stranded RNA virus. Read more on its genome structure and various genes: Novel Coronavirus (COVID-19)- Structure, Genome, and Testing.


