TE (Tris-EDTA) buffer system consists of Tris and EDTA and has a significant role in DNA extraction to dissolve the DNA precipitate.
Biological buffer is an organic substance mix, maintains the constant pH of the reaction and thus protects the biomolecule.
DNA is one such type of biomolecule made up of sugar, phosphate and nitrogenous bases. Commonly known as nucleic acid, other nucleic acids other than DNA is RNA, which isn’t abundantly present in nature.
Read more: DNA: Definition, Structure, Function, Evidence and Types.
To investigate either DNA or RNA, we need to isolate it. During the isolation, a proper buffer system is required to maintain the pH of the reaction and to protect our nucleic acid.
TE buffer system is a type of biological buffer system abundantly applied in DNA extraction and various other DNA-related studies.
Here in the present article, I will explain to you the function, recipe and applications of TE buffer during the DNA extraction.
Quick recap:
| Type | Biological Buffer |
| TE buffer | Tris-EDTA buffer |
| Major components | Tris and EDTA |
| pH | 7.8 to 8.0 |
| Major application | Elute/ dissolve DNA |
Key Topics:
What is TE buffer:
DNA extraction needs a specialized buffer system to protect the DNA from harmful chemical degradation. One such buffer is the TE (Tris- EDTA) buffer system.
Usual DNA extraction protocols give output as precipitate which is impure and in solid form and therefore can’t be used for downstream applications. We need a pure DNA solution to use further.
Separately, Tris and EDTA are used throughout the DNA extraction protocol as components of lysis buffer, elution buffer and washing buffer and helps to achieve our final goal that is to get the pure DNA.
Tris
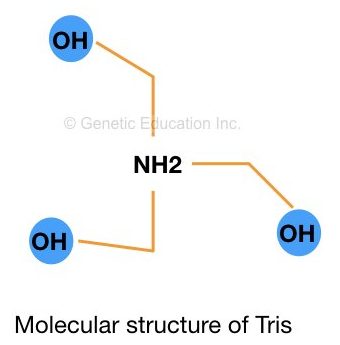
Tris is a (hydroxymethyl)aminomethane having a molecular formula (HOCH2)3CNH2. The major role of the Tris in any biological practice is to maintain the pH of the solution and increase the permeability of the cell wall.
Tris is used in biochemistry, molecular biology and chemistry. The pKa value of Tris is 8.07 (at 25°C). Tris is available in powder form and dissolved between pH 7.0 and 9.0. The structure of Tris is shown in the figure below,
EDTA
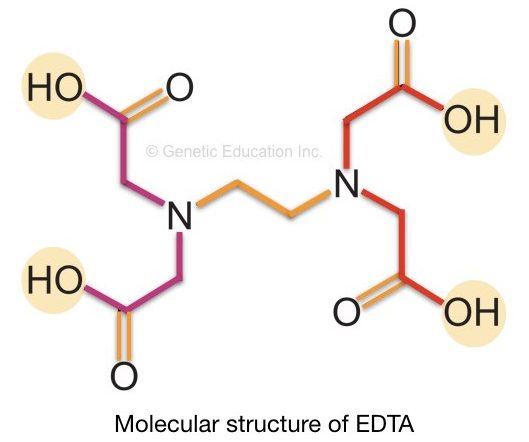
EDTA- Ethylenediamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) has a wide range of applications in medicines, industries, laboratories and cosmetics.
It is a colorless (white as in powder form), water-soluble and organic molecule. However, it can be dissolved in water at high pH (pH nearby 8.0).
The chemical formula of EDTA is C10H16N2O8. The structure of EDTA is shown in the figure below. The EDTA works as a chelating agent in DNA extraction.
It chelates the metal ions present in the enzymes, metal ions work as a cofactor to increase the catalytic activities of an enzyme.
In DNA or RNA extraction, the use of EDTA readily deactivates DNase or RNase enzymes which digest DNA or RNA, respectively. Henceforth, chelation reduces the activities of DNase and RNase.
How to prepare TE buffer:
Recipe for 10X TE buffer
Recipe for the preparation of 10X TE buffer 100ml stock solution.
- 100mM Tris HCl: 1.57gm
- 10mM EDTA: 0.292 gm
- Weigh 1.57 gm of Tris powder and 0.3722 gm of EDTA into the flask.
- Add 98.1 ml of D/W
- Adjust the pH using the HCl and so add only the half amount of the D/W and adjust the pH of the solution with HCl until the pH reaches nearby 8.0.
- Make the final volume of the buffer 100 ml using the D/W.
- In the preparation of TE buffer, pH plays a crucial role in performing a proper function.
Recipe for 1X TE buffer
- Our stock solution is 10X which means the total concentration of the stock solution is 10 times more than the working solution.
- Hence for the preparation of 1X TE buffer, we have to take 1 ml of stock buffer and add 9ml of D/W.
- This will make a 1X working solution from a 10X stock solution.
Or
- 10mM Tris HCl and 1mM EDTA will make directly the 1X of the working solution.
- In order to achieve a good quality of results please autoclave the TE buffer solution before use.
Likewise, you can prepare a 2X or 0.5X TE buffer as per the requirement of the assay.
Importance of Tris EDTA (TE) buffer
As we said earlier, the TE buffer has a significant role in eluting, washing and isolating DNA.
It dissolves DNA or RNA and protects the nucleic acid from degradation.
It is a major constituent of DNA extraction buffer which helps in the lysis of the cell wall and nuclear membrane.
It protects our DNA or RNA from the catalytic-nucleophilic effect of DNase or RNase.
Tris and EDTA are important ingredients of the gel electrophoresis buffer and are used in the preparation of TBE and TAE buffer. Again, during the electrophoresis, the gel running buffer maintains the pH of the environment.
Read more on gel electrophoresis buffer: TAE and TBE buffer.
Further, the TE buffer is used in reviving DNA primers.
TE buffer is a DNA preservative that stores DNA in intact form for a longer period of time, without degrading it.
As the TE buffer prevents DNA degradation, it also can be used as a DNA preservative that has the potential to store DNA for a longer period of time.
Do you Know?
Water is another ingredient that can dissolve the DNA effectively, however, water promotes acid hydrolysis (water is slightly acidic) and therefore can’t be used for long-term DNA storage.
Low TE or TE low EDTA:
The Low TE buffer which is also known as TE low EDTA buffer has significantly important value in forensic analysis and STR mapping. You man wonder what is low TE?
A specialized version, high-quality TE buffer with low EDTA concentration is used for critical downstream processing like forensic DNA analysis. Tris readily maintains the pH while the EDTA chelates ions.
Under higher EDTA concentration the Taq DNA polymerase can’t work efficiently as it requires the Mg2+ ions as a cofactor. Because the EDTA chelates Mg2+ and decreases the efficiency of the Taq DNA polymerase.
The Taq DNA polymerase is an enzyme that governs DNA synthesis artificially and is thus important for PCR analysis. To overcome this problem, we have to use the TE with low EDTA concentration which is known as the Low TE or TE low EDTA buffer.
Generally for the low TE, a two times lower volume of EDTA is used to prepare the buffer. Here is the comparison between normal and low TE buffer
| Tris | EDTA | |
| Te buffer | 10 mM | 1 mM |
| Low TE buffer | 10 mM | 0.1mM |
Preparation of low TE buffer:
10 mM Tris and 0.1 mM EDTA dissolved in the D/W until the pH reaches up to 8.0.
Note that do not change the concentration of the Tris- HCl as it is important to regulate the pH of the reaction environment and to protect the DNA.
Conclusion
Tris and EDTA are two important chemicals used in DNA extraction as a constituent of extraction buffer, elution buffer and as a storage buffer. I have personally used TE as an extraction buffer and believe me, Tris- EDTA buffer worked excellently with the proteinase K DNA extraction method.
Water is the alternative option for dissolving DNA. However, it can not be used for storing DNA for long-term use. Still, if you want to dissolve DNA into water use Milli Q water or DD/W. Remember, do not use tap water.
Tips: For a short-term or single-use, dissolve DNA in water, because of the slight acidity of water the DNA dissolves fast and easily.
FAQs:


Tris buffers should not be autoclaved since pH may change
Might possible, but we do.
Amazing… thank you so much for your efforts…❤️
Thank you Priyanka for your appreciation.
Thank you for your useful information
Good information..
Information on other chemicals and its role in extraction of DNA will be helpful
Thank you, Manoj. I hope this article will help you