“Purine and pyrimidines are aromatic molecules involved in manufacturing the nucleic acid via hydrogen bonding.”
Both purines and pyrimidines are similar to the organic structure pyridine, however, the purines contain one hexose and one pentose ring while the pyrimidine contains a single hexo-cyclic ring.
Purines and pyrimidines both are made up of the aromatic ring having carbon and nitrogen in it.
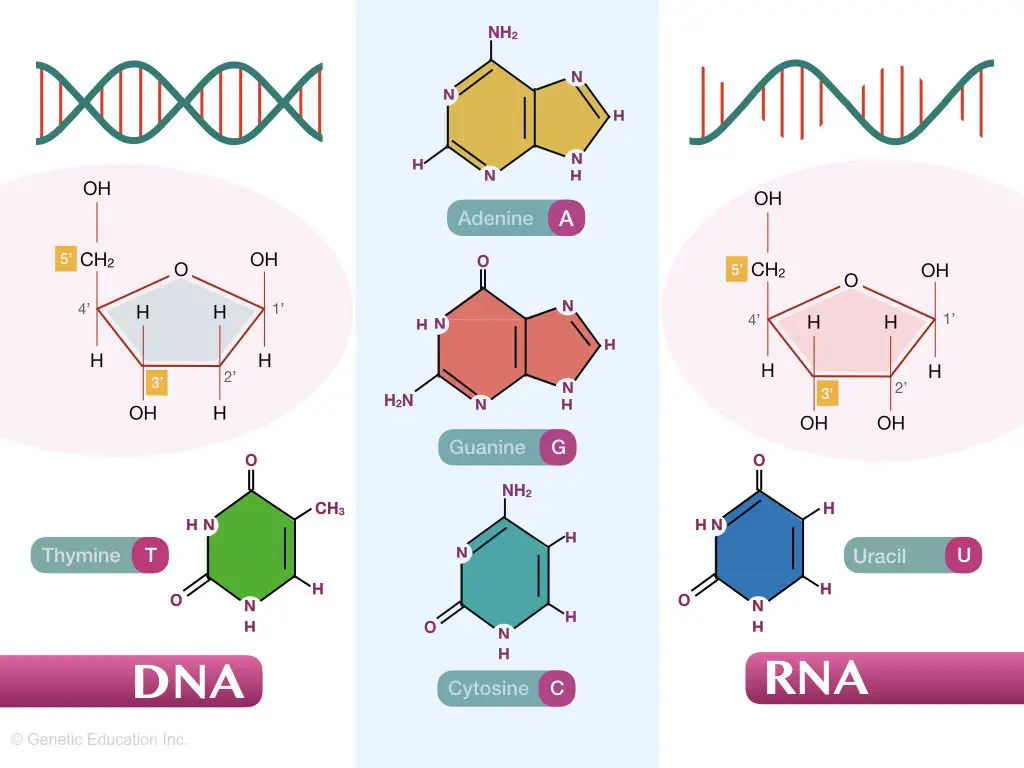
Purines-adenine and guanine and pyrimidine-thymine, cytosine and uracil are involved in making nucleic acids- DNA and RNA.
Purines and pyrimidines are important ingredients of the DNA along with phosphate and pentose sugar.
Interestingly, purines and pyrimidines construct nucleotides as well as nucleosides. The polynucleotide chain is known as DNA.
By forming hydrogen bonds between opposite bases and phosphodiester bonds with the adjacent bases it creates the double-stranded structure of DNA.
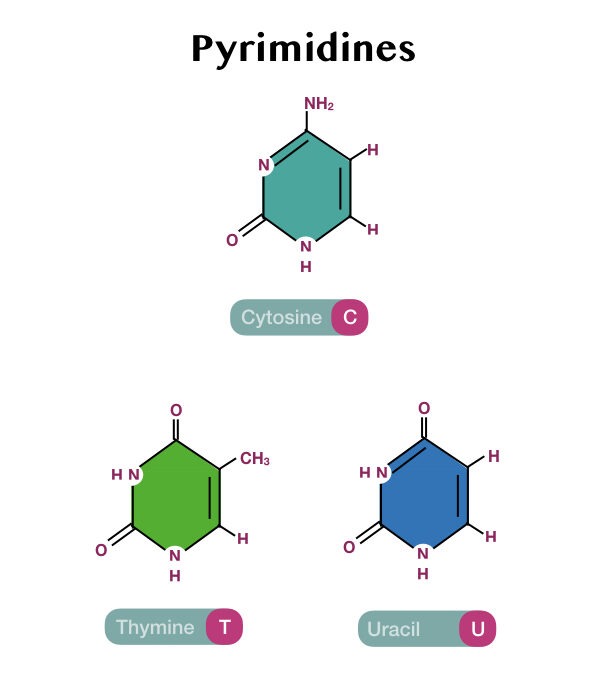
Differences between purines and pyrimidines:
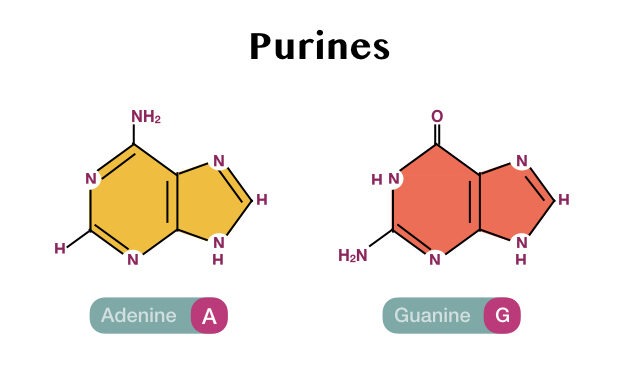
Structurally, the purines are made up of two aromatic rings while the pyrimidines are made up of a single aromatic ring.
In addition to this, the purines contain four different nitrogen atoms while the pyrimidines contain two nitrogen molecules in the ring.
Due to these structural variations, the purines are bigger in size and shape as compared with the pyrimidines.
The overall chemical formula of the purine is C5H4N4 while the chemical formula of the pyrimidine is C4H4N2.
The chemical formula of individual purines and pyrimidines are given in the table below,
| Nitrogenous base | Chemical formula |
| Purine: | |
| Adenine | C5H5N5 |
| Guanine | C5H5N5O |
| Pyrimidine: | |
| Cytosine | C4H5N3O |
| Thymine | C5H6N2O2 |
| Uracil | C4H4N2O2 |
One of the important properties of purine is its solubility in water. Purine is water-soluble while the pyrimidines are miscible (insoluble) in water.
The biosynthesis of purine occurs in the liver, on the otherside, the biosynthesis of pyrimidine occurs in various tissues.
The catabolic product of the purine is uric acid while the catabolic end product of the pyrimidine is ammonia, beta-amino acids and carbon dioxide.
Due to the structural complexity of the purine, the melting point of the purine is higher.
“Note: the melting point is the temperature at which the molecule melts or dissolves.”
The melting temperature of purine is 214°C (417°F) while the melting temperature of pyrimidine is 22°C (72°F).
The molecular mass of the purine is 120.115 g/mol while the molecular mass of the pyrimidine is 80.08 g/mol.
The purines are an important biomolecule of vitamin biosynthesis.
While both purines and pyrimidines are used in DNA and RNA synthesis, energy storage, protein and starch synthesis, cell signaling and enzyme regulation.
Read more:
DNA vs RNA: Differences And Similarities.
Summary of the article:
| Characteristic | Purine | Pyrimidine |
| Bases | Adenine, Guanine | Cytosine, thymine and uracil |
| Structure | Two rings (one is a pyrimidine) | Single ring |
| Formula | C5H4N4 | C4H4N2 |
| Nucleic acid | DNA and RNA both | Thymine and cytosine in DNA while uracil and cytosine in RNA. |
| Biosynthesis | Liver | Various tissues |
| End product | Uric acid | Beta-amino acid, carbon dioxide and ammonia. |
| Function | Vitamine, drug, nucleic acid, cell signaling, enzyme regulation. | The drug, nucleic acid, cell signaling, enzyme regulation. |
Related reads: