“Sanger and Maxam-Gilbert sequencing are foundational methods in DNA sequencing. This article compares these two techniques, exploring the technical reasons why Sanger sequencing became the preferred choice.”
DNA sequencing is a genetic technique that allows us to read a DNA sequence. Henceforth, sequence-level variations can be investigated, which wasn’t possible with previous-generation techniques like PCR, FISH, or karyotyping.
Now what does that mean?
Scientists can examine a gene or DNA sequence associated with a trait or disease. Further, they can identify and discover alterations– like SNPs, insertions or deletions.
Although, now! We have the most powerful sequencing techniques, but the story began around the 1970s or 80s when two different DNA sequencing techniques were developed by different groups of scientists.
In this article, we will deep dive into the technical differences between Sanger and Maxam Gilbert Sequencing and conclude why Sanger sequencing won the race against the competitor and became the gold-standard method.
Key Topics:
What is Maxam- Maxam-Gilbert sequencing
The present DNA sequencing method was developed between the years 1976- 1977. It was considered a pioneer and one of the earliest methods in the sequencing industry. Allan Maxam & Walter Gilbert collectively proposed the chemical degradation method of DNA sequencing.
In the present method, single-stranded DNA is degraded using a set of chemicals, run on the PAGE gel and analyzed using autoradiography. For pyrimidine nucleotides- hydrazine (T + C) and hydrazine NaCl (C), and for purine– dimethyl sulfate (A + G) and piperidine (G) are used to selectively degrade the DNA sequence.
Due to the extensive use of chemicals, the present method is also known as the chemical degradation method. The technical workflow is as follows- DNA extraction, DNA denaturation, DNA labeling, chemical degradation, gel electrophoresis and autoradiography.
On the positive side, the present method doesn’t require any synthesis process and thus doesn’t need polymerase. However, the use of hazardous chemicals, radiolabeling, and limited read length made it difficult to use and automate.
What is Sanger sequencing?
Sanger sequencing is another DNA sequencing technique developed after Maxam-Gilbert sequencing but in the same year in 1977. The technique was developed by Sanger and coworkers and became popular and gold-standard within a few years.
Sanger sequencing principle also relies on chain termination. Instead of chemicals, specialized ddNTPs are used here. The 3’ OH lacked ddNTP when incorporated, it terminates the synthesis and generates varied-size fragments.
Fragments are run on the PAGE gel and analyzed using autoradiography. Nowadays, PAGE and autoradiography are both not required due to extensive automation in the technique.
The automated version doesn’t rely on hazardous chemicals, radiolabeling and autoradiography and thus it is extensively used in genetic research and diagnostics. The workflow is as follows: DNA extraction, chain termination, capillary electrophoresis and analysis.
Read more: Sanger Sequencing vs PCR: Common and Technical Differences.
Sanger vs Maxam Gilbert Sequencing
Now here comes an interesting part of this article.
In this section, we will understand the differences between the old-age techniques and will draw a conclusion as to why one of them will be discontinued.
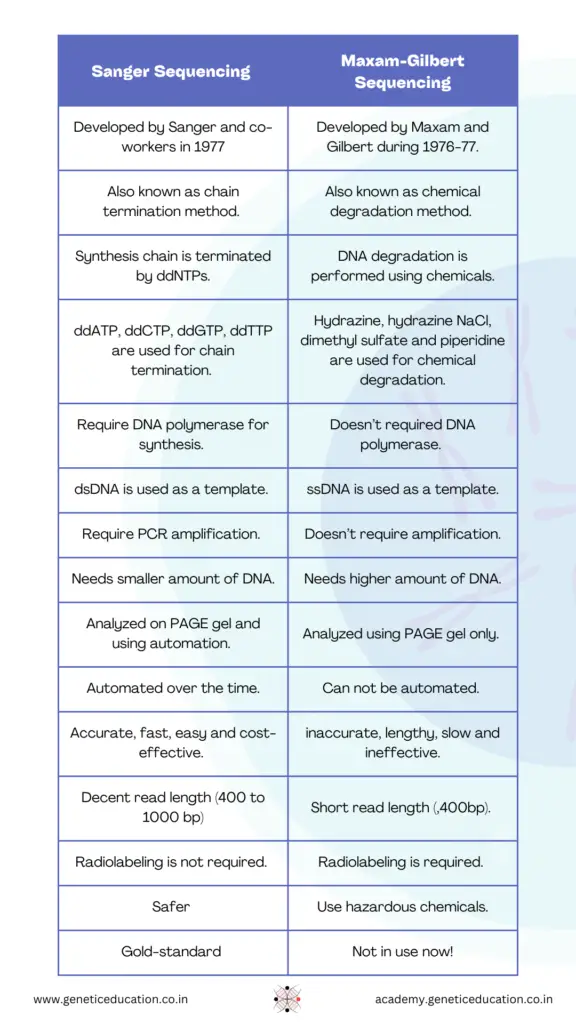
Friedrick Sanger developed the Sanger sequencing technique in 1977, while Allan Maxam and Walter Gilbert developed the Maxam Gilbert sequencing.
The Sanger sequencing works on the principle of chain termination while the Maxam-Gilbert sequencing works on the principle of chemical degradation.
In the chain termination, specialized ddNTPs (dideoxynucleotide triphosphate) are used to selectively terminate the synthesis process at each nucleotide while in the chemical degradation method, chemicals are used to selectively degrade the single-stranded DNA.
Thus, in the Sanger sequencing ddNTPs while in Maxam Gilbert sequencing four different chemicals are used to prepare DNA fragments.
Technically four different ddNTPs- ddATP, ddGPT, ddCTP and ddCTP are used to terminate the synthesis chain. On the contrary, in the Maxam Gilbert, chemicals like hydrazine, hydrazine NaCl, dimethyl sulfate and piperidine are used for T + C, C, A + G and G, respectively.
Sanger sequencing uses synthesis chemistry while Maxam Gilbert sequencing doesn’t use synthesis chemistry.
Hence, Sanger required DNA polymerase whereas Maxam Gilbert doesn’t require any polymerase in the reaction.
In addition, Sanger sequencing needs a dedicated reaction preparation like the PCR, it needs dNTPs, DNA polymerase, buffer, template DNA, primers and ddNTPs while Maxam Gilbert only needs four different chemicals.
On the technical side, Sanger sequencing also needs PCR amplification as a mediation step, while Maxam Gilbert sequencing doesn’t rely on PCR amplification.
Following the amplification point, before Sanger sequencing, a purification step is needed to remove impurities that interfere with the sequencing results. No such purification step is needed in the Maxam Gilbert Sequencing.
Due to the requirement of amplification, Sanger sequencing gives amazing resolution in comparison with the Maxam Gilbert sequencing.
Talking about templates,
Sanger sequencing uses double-stranded DNA while Maxam-Gilbert sequencing uses single-stranded DNA from sequencing.
As amplification is mandatory in the Sanger sequencing, it requires a very small amount of DNA, contrary, Maxam Gilbert sequencing requires a comparatively higher amount of DNA.
The steps in Sanger sequencing are DNA extraction, PCR amplification, cycle sequencing, and gel electrophoresis analysis while the steps in Maxam Gilbert sequencing are DNA extraction, ssDNA preparation, chemical degradation, gel electrophoresis and analysis.
Sanger sequencing can effectively sequence 500 to 1000 nucleotides while Maxam Gilbert has an even shorter read length of up to 400 bp only.
Both techniques initially used radiolabeling for detection, however, Sanger sequencing, over time replaced radiolabeling with fluorescent labeling. Nowadays four different fluorescent colors are used for four different ddNTPs.
The automated Sanger sequencing, which we now have, is safer, faster and more accurate while the Maxam Gilbert sequencing uses hazardous chemicals, slower and inaccurate.
Sanger sequencing uses automated capillary electrophoresis having the power to distinguish a single base change while Maxam Gilbert sequencing fragments can be run only on PAGE gel.
So the automated Sanger sequencing is fast, accurate, easy and safe while Maxam Gilbert sequencing is slower, more error-prone, difficult, labor intensive and unsafe.
Read more:
- A Beginner’s Guide to Sanger Sequencing Results [Before Electropherogram Analysis]
- 4Peaks Review: Easiest Sequence Analysis Software
- Advantages and Limitations of Sanger Sequencing
- Detailed History of DNA Sequencing
- Why Should Life Science Students Learn Sanger Sequencing? – Top 6 Reasons
Wrapping up:
Sanger sequencing is by far the most suitable sequencing method for small-scale projects particularly for gene sequencing. It has become the gold-standard method for research and diagnosis in recent years.
On the other hand, Maxam Gilbert sequencing is mostly obsolete due to safety and technical challenges. However, we should be thankful to both the scientists for their initial contribution to the sequencing industry.
It was their effort that inspired scientists to be continuously involved in sequencing research.
Resources:
Eren K, Taktakoğlu N, Pirim I. DNA Sequencing Methods: From Past to Present. Eurasian J Med. 2022 Dec;54(Suppl1):47-56. doi: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.22280. PMID: 36655445; PMCID: PMC11163357.
Crossley BM, Bai J, Glaser A, Maes R, Porter E, Killian ML, Clement T, Toohey-Kurth K. Guidelines for Sanger sequencing and molecular assay monitoring. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2020 Nov;32(6):767-775. doi: 10.1177/1040638720905833. Epub 2020 Feb 18. PMID: 32070230; PMCID: PMC7649556.
Its like you read my mind You appear to know so much about this like you wrote the book in it or something I think that you can do with a few pics to drive the message home a little bit but other than that this is fantastic blog A great read Ill certainly be back
Oh my goodness! Impressive article dude! Thanks, However I am
experiencing difficulties with your RSS. I don’t know why I am unable to join it.
Is there anybody getting the same RSS issues?
Anyone that knows the answer can you kindly respond? Thanx!!
Hello to every one, it’s truly a pleasant for me to go to see this site, it contains important Information.
Wow, superb blog structure! How lengthy have you been blogging for?
you make blogging glance easy. The full look of your website is magnificent, as well as the
content!
Very good post! We are linking to this great post on our website.
Keep up the great writing.
Hi! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a group of volunteers and starting a new initiative
in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us useful information to work
on. You have done a wonderful job!
Hey There. I found your weblog the usage of msn. That is a very well written article.
I’ll make sure to bookmark it and return to learn more of your useful information.
Thank you for the post. I will certainly return.
It’s really a cool and useful piece of information. I am happy that
you simply shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this.
Thanks for sharing.
Great info. Lucky me I recently found your blog by accident
(stumbleupon). I have saved it for later!
Normally I do not read post on blogs, but I would like to say that
this write-up very compelled me to try and do it! Your writing taste has
been amazed me. Thanks, quite nice article.