“Learn about the differences between two crucial non-coding RNA molecules, siRNA vs miRNA and their role in gene silencing and regulation of gene expression. Explore their definition, length, recognition site, function and importance.”
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) is an important nucleic acid that synthesizes proteins and regulates gene expression. Where the mRNA translates into a functional protein, pseudogene-transcribed smaller non-coding RNAs regulate gene expression using different mechanisms.
These molecules are involved in gene silencing through the process known as RNA interference or RNAi. A few similarities between both are listed here.
- Both follow similar mechanisms to govern genes’ activity.
- Both are processed by the enzyme Dicer in the cytoplasm.
- Both are loaded in the RISC ((RNA-induced silencing complex).
- Both bind to mRNA, and terminate gene expression.
Despite these similarities, they have differences in structure and mechanism of working. In this article, I will explain to you some of the major, important and crucial differences between siRNA vs miRNA.
Stay tuned.

Key Topics:
Difference between siRNA vs miRNA:
1. The full name of siRNA is small interfering or short interfering RNA while the full name of miRNA is microRNA.
2. The siRNA is not conserved between the species while miRNA is highly conserved in the related organisms of species.
3. Structurally, the siRNA is a 21-23 nucleotide long RNA duplex having a dinucleotide 3’ overhang. Whereas the miRNA is made up of 19-25 nucleotide RNA hairpins which form duplex by binding with each other.
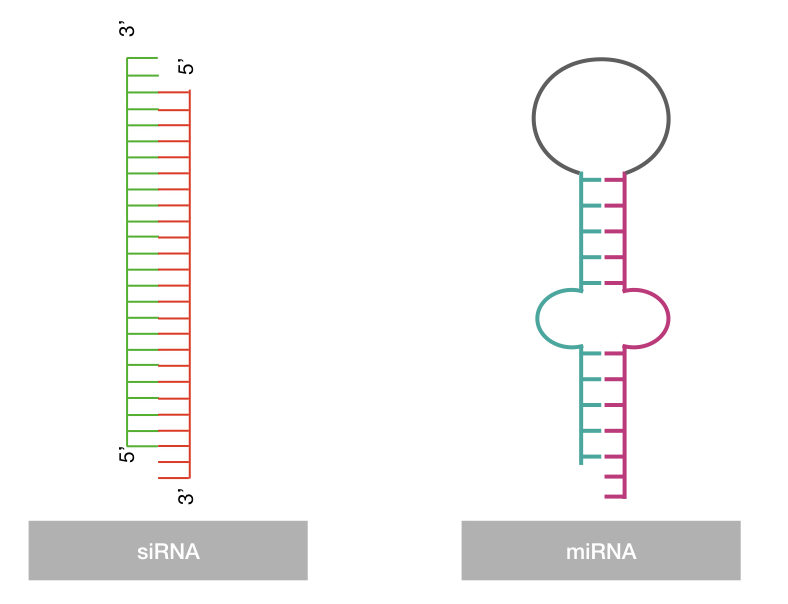
4. siRNA works agains the exogenous RNA while the miRNA works agains the endogenous RNA. The miRNA forms a duplex by forming the hairpin structure (see the image above).
Note that both are non-coding RNAs.
5. The siRNA is manufactured from the heterochromatin or transposons while the miRNA is manufactured from specific genes. Some genes actually transcribe miRNA which can’t be translated into protein.
6. As we talked about, the RISC complex processes both siRNA and miRNA with a different mechanism.
The siRNA only terminates gene expression if it finds the exact complementary sequence on mRNA. On the other side, the miRNA binds imperfectly or at the 3’ untranslated region of the mRNA and aborts the translation process.
Related article: What Is shRNA (Short-hairpin RNA)?
7. For gene silencing, the siRNA required the Ago 2 protein- argonaute protein 2 whereas the miRNA required the Ago protein only but not necessarily the Ago2. Any argonaute family protein can do miRNA-mediated gene silencing.
8. Generally, in addition to ago2, several other proteins such as ago1, ago4, ago7 and ago6 are involved in the siRNA-mediated gene silencing in different organisms. Contrary, only ago1 and ago10 are majorly linked in miRNA-mediated gene regulation.
“Some siRNA binds on the exact complementary mRNA and induce gene silencing by behaving like a miRNA while some miRNA binds to some non-complementary sequences and behave like siRNA.”
9. Interestingly, previous studies reported significant structural differences between siRNA and miRNA. The siRNA is a single duplex while the miRNA is a heteroduplex RNA in structure.
10. In addition to structural differences, the regulatory targets are different for both too. For instance, the siRNA regulates the expression of different genes while the miRNA regulates the expression of similar types of genes or genes having the same origin. Keep in mind that the duo has a direct role in the process of RNA interference but has different effects, targets and the mode of action.
11. siRNA-mediated gene silencing degrades the target mRNA while the miRNA-mediated gene silencing represses translation.
12. Studies also suggest that the siRNA has involvement not only in gene regulation but also in other epigenetic alterations like histone modification and DNA methylation too. On the other hand, the miRNA is solely involved in gene regulation only.
13. So conclusively, the siRNA provides protection against foreign pathogens and genome stability while the miRNA works as an endogenous gene expression regulator.
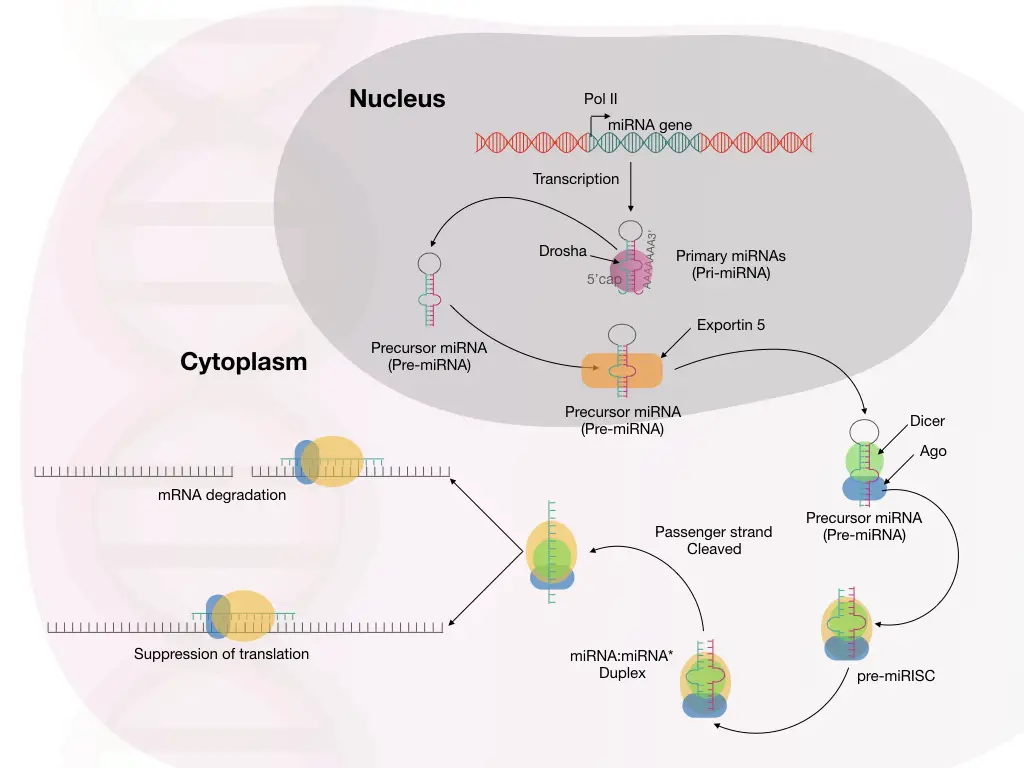
Besides, all these structural and functional differences, the siRNA and miRNA are present in different organisms too.
In addition to these structural and functional differences, siRNA and miRNA vary among organisms too.
14. The siRNA is not found in all mammals but in lower animals and in plants whereas the miRNA is present in all animals and plants including higher mammals.
siRNA and miRNA like smaller RNAs have great values in gene therapy. In the process, an artificial vector transfers the smaller non-coding RNAs into the target genome for target-specific gene silencing.
15. The siRNA is used in gene therapy and as a therapeutic agent while the miRNA is used as a therapeutic agent, biomarker, drug target and diagnostic tool.
16. The main function of the siRNA is to maintain genome integrity against foreign RNA molecules while the miRNA works as a regulator of endogenous genes.
17. A single siRNA binds to single mRNA while the miRNA has multiple action sites for the same as well as different mRNA. More than 100 different target sites are present for a single miRNA molecule.
Summary:
| siRNA | miRNA | |
| Full name | Small interfering RNA | microRNA |
| Site of action | Exogenous mRNA | Endogenous mRNA |
| Length | 21-23nt | 19-25nt |
| ds/ss | dsRNA | ssRNA |
| Duplex structure | Single duplex | heteroduplex |
| Dinucleotide overhang | Present on the 3’ end | Absent |
| Hairpin structure | Absent | Present |
| Manufactured by | Heterochromatin and transposons | Active genes |
| Requirement | Exact complementary sequence on the mRNA | 3’ untranslated region. |
| Binding | Perfect | Imperfect |
| Required protein | Ago2 | Any Ago protein |
| Mode of action | Gene silencing by destroying the mRNA | Gene silencing by translation repression. |
| Involvement | DNA methylation, histone modification and gene regulation | Only gene regulation. |
| Function | Projects agains foreign pathogens and provide genome stability | Endogenous gene expression regulator. |
| Presence | Lower animals and plants | Higher animals, other mammals and plant |
| Applications | Gene therapy and therapeutic agent | Therapeutic agent, biomarker, drug target and diagnostic tool |
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, siRNA and miRNA both have significant importance for a cell to regulate gene expression. Both almost works for gene silencing using a different pathway and mechanisms. mRNA processing (endo and exogenous origin) is the key function of such smaller non-coding RNAs.
Pseudogenes transcribe such smaller non-coding RNA which can’t be translated into a protein. Scientists are now using artificial siRNA which behaves like the endogenous miRNA for silencing some cancer-causing genes although the success rate is too low. It has potential applications in the treatment of disorders like cancer and infections.
If you like this article please share it and bookmark the page.
Sources:
Carthew RW, Sontheimer EJ. Origins and Mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 2009;136(4):642-655. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.035.


