“COMET assay is a single-cell electrophoresis technique which is used to study single and double-strand DNA damage. Learn the concept of COMET assay in this article.”
DNA should remain intact in order to store, transport and express genetic information precisely. However, it’s prone to damage. DNA can be damaged by intrinsic and extrinsic factors, for example— autoimmune anomalies and UV or X-rays, respectively.
Our own replication system, most of the time, repairs our damaged DNA. Despite of that, unrepaired DNA can cause serious health-related issues, for instance— cancer or infertility.
Techniques like single-cell gel electrophoresis– COMET assay help understand and study single and double-strand DNA breaks thereby associated health problems. In the present article, I will explain to you the concept of the COMET test, how it is done, and its applications, advantages, and limitations.
Stay tuned.
Disclaimer: Information provided here is collected from peer-reviewed resources and re-presented in an understandable language. All the sources are enlisted at the end of the article.
Key Topics:
What is a COMET assay?
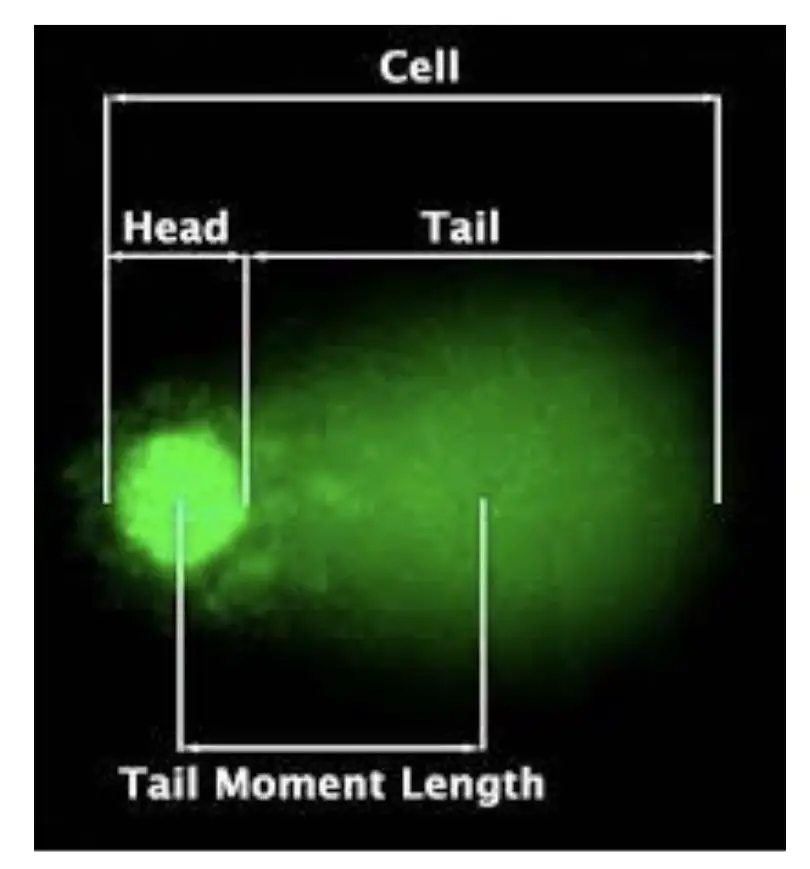
When a single cell is run on gel electrophoresis, the results look like a ‘COMET’ with a definite head and a tail, if DNA damage occurred. Hence, the name “COMET assay” has been given.
In 1984, Ostling and Johnsson (Swedish scientists) had originally developed the technique of comet assay, however, major modifications were done by Singh et al, in 1988 by using alkaline treatment in the main protocol.
It’s indeed a simpler assay than other genetic assays having a combination of native gel electrophoresis and fluorescent microscopy. Here, when a cell is run in a gel, DNA fragments will migrate toward the positive side, smaller fragments run faster and create a shearing/tail-like structure, if DNA is damaged.
At a molecular level, damaged DNA relaxes DNA supercoiling and can run faster in the gel while the undamaged DNA having a higher level of supercoiling will remain intact and can’t run as fast as the relaxed DNA fragments.
The results can be analyzed under a fluorescent microscope. Information provided by a COMET assay includes tail length & size, tail DNA percentage, tail intensity, head size and overall COMET score.
Note that the amount of DNA damaged is directly proportional to the length of the tail.
Despite having a well-established alkaline COMET procedure, the recently developed two-tailed COMET assay is capable enough to study single and double-strand DNA breaks in a single assay. Thus, used in sperm DNA fragmentation studies, particularly.
Principle:
The comet assay relies on the principle of electrophoresis and fluorescence analysis in which charged particles (DNA fragments) migrate under the influence of current and can be tracked using fluorescence analysis.
During the gel run, the fragments run faster than the intact and supercoiled DNA and create a tail-like structure. The use of fluorescent dye (EtBr or any other) helps investigate the results. As the cell migrates under the influence of current in a gel, a comet-like structure is formed with intact DNA in a head and a tail of damaged DNA which looks like an actual comet.
It is crucial to note that the intact head DNA will remain close to the cell nucleus while the fragmented-tailed DNA extends away from the cell nucleus and migrates in the gel.
Process of the COMET assay:
Initially, the COMET assay was developed to study the DNA damage that occurs in eukaryotic cells, however, nowadays it is also used to study the DNA damage that occurs in prokaryotic cells as well.
The steps in the COMET assay procedure are gel preparation, cell embedding, cell lysis, gel electrophoresis, results and analysis
Gel preparation:
Normal-melting-point gel and low-melting-point gel are prepared separately. The gel preparation process would remain the same for both gels. A given concentration of the agarose powder is dissolved in the buffer, heated, cooled and spread on the microscopic slide.
Here, we would study results using a fluorescent microscope, thus the gel is prepared on a microscopic slide. A fluorescent dye (EtBr- Ethidium Bromide) has been added during the gel preparation. Or a gel can be stained separately afterward.
Now the normal gel is prepared and first poured on the slide and allowed to solidify. The low-melting-gel prepared after that.
Cell embedding:
A cell suspension of human, bacterial or any other cells is added to the low-melting gel spread on a microscopic slide. And covered with a cover slip. The gel is cooled followed by the removal of the coverslip.
Cell lysis:
Now we have to lyse cells to release DNA. To do so, a microenvironment is prepared using detergents or high salt concentration which eventually break the cell membrane or wall, and nuclear envelope, and release the DNA.
After cell lysis, DNA fragments can migrate effectively in the gel. So in the next step, we run the electrophoresis.
Electrophoresis:
Electrophoresis is performed using a standard agarose gel electrophoresis setup. An electrophoresis buffer is poured into the tank, the slide is submerged in the buffer and allowed to run for 1 to 1.5 hours depending on the protocol or requirements.
Results and analysis:
As aforesaid, the results can be studied using a standard gel analysis setup or using a fluorescent microscope. The DNA-binding fluorescent dye releases fluorescence upon binding with the DNA and is visualized using a UV source.
Put simply, the concept is almost similar to the native gel electrophoresis. You can read this article to learn more: Agarose gel electrophoresis– Principle, Process, Protocol and Applications.
Protocol:
- Collect 1 to 2 ml blood, sperm sample or any cultured cells under aseptic conditions and transfer it to the falcon tube. 2 to 3 ml of lymphocyte separation media is added to the sample and centrifuged at 1500rpm for 20 to 30 minutes.
- The buffy coat of the mononuclear cells is separated and transferred to another tube.
- The sample is first encapsulated in a low-melting-point gel at 37°C. To do so, 0.5% LMPA and 0.75% NMPA are prepared in PBS and heated in the microwave to melt. (both gels are separately melted and added on a slide one after another).
Note: care must be taken while pouring a gel to avoid bubble formation.
- 200μl melted gel is aspired, poured on a microscopic slide and covered with a coverslip.
- Soon after, the gel is allowed to cool at a 4°C temperature. The coverslip is immediately removed.
- After the slide preparation, it is treated with the lysis solution. The lysis solution would lyse the cell wall proteins. However, the supercoiled DNA will remain linked with the nuclear matrix.
- Detergents like Triton X 100 or high salt and pH solution are used as a lysis buffer. Read more: Lysis Buffer for DNA Extraction– Importance, Recipe and Preparation. Detergent can digest the RNA as well.
- Lysis is performed at 4°C for at least 2 hours.
- Chemical traces and contaminants are removed by washing the slide with distilled water.
- The slide is rested in the electrophoresis buffer for 5 minutes. Note that the buffer should have a high pH for effective denaturation.
- Afterward, the slide is placed in the electrophoresis tank pre-filled with the buffer. Electrophoresis buffer preparation and condition are explained in this article: Agarose Gel Electrophoresis Buffer.
- Run electrophoresis for 20 minutes followed by neutralizing in pH 7.0 solution.
- In the last step, stain the slide with fluorescence dye and observe under a microscope.
COMET Results and Analysis:
So far, we discussed the whole technique with EtBr, however, other DNA-binding dyes like– DAPI (4,6- diamidino-2-phenylindole) and AO (Acridine Orange) are also used. All three dyes have different binding chemistry and hence used for different purposes.
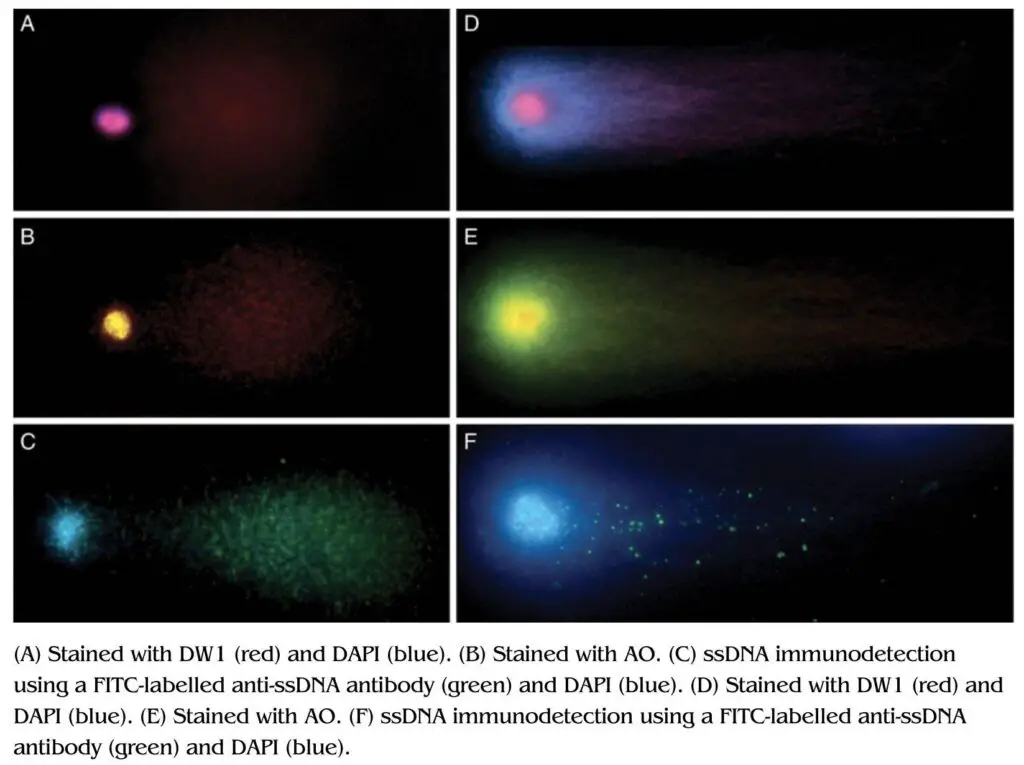
For example, EtBr can effectively intercalate with the dsDNA fragment so employed for the detection of dsDNA breaks and not ssDNA breaks. Contrary, DAPI binds to the DNA major groove and not the ds or ssDNA. Both EtBr and DAPI are widely used for the detection of dsDNA breaks.
Acridine orange can intercalate with dsDNA and ssDNA, and give us different fluorescence signals. The fluorescence signal would be yellowish-green if it is dsDNA whereas the fluorescence signal would be red if it is dsDNA.
Thus, cells treated with the AO can produce an intensive red-head and yellow-green tail fluorescence.
| COMET dye | Application |
| EtBr | Intercalate with the dsDNA and detects dsDNA breaks. |
| DAPI | Intercalate with the DNA major groove and detects dsDNA breaks. |
| AO | Detects dsDNA and ssDNA breaks by producing two different fluorescence signals. |
| SYBR green | Detects dsDNA, less toxic and option for EtBr. |
| Propidium Iodide | Used to stain eukaryotic cells. |
The COMET can be analyzed using computational software with a program for fluorescence analysis. Here, approximately 50 COMETs per slide are analyzed to determine any concrete results.
Now, what you will first observe is the fluorescence image of a cell. If damage is present, you will observe a tail. If not, a circular cell without a tail.

The parameters taken into consideration for results analysis are listed and explained here.
Tail length: Tail length is predominant, most important and commonly assessed to study COMET assay. As aforesaid, the tail represents the amount of DNA damage. The longer the tail the more the fragmented DNA and vice versa.
Tail intensity: The amount of fluorescence emitted by the tail is also taken into consideration for results analysis. However, only the software can do analysis on this basis. Much like other fluorescence assays, background signals can also negatively impact the results here as well.
Head: Head size is also another crucial and visible parameter taken into consideration. The larger the head size, the more intact the DNA is and vice versa. In addition, as the size of the head increases, the tail size and intensity decrease.
Tail moments: This one is the least significant parameter but gives us information regarding the heterogeneity of damaged DNA within the cells.
COMET score: The computational program gives an overall score through the assessment of all these factors in terms of COMET score.
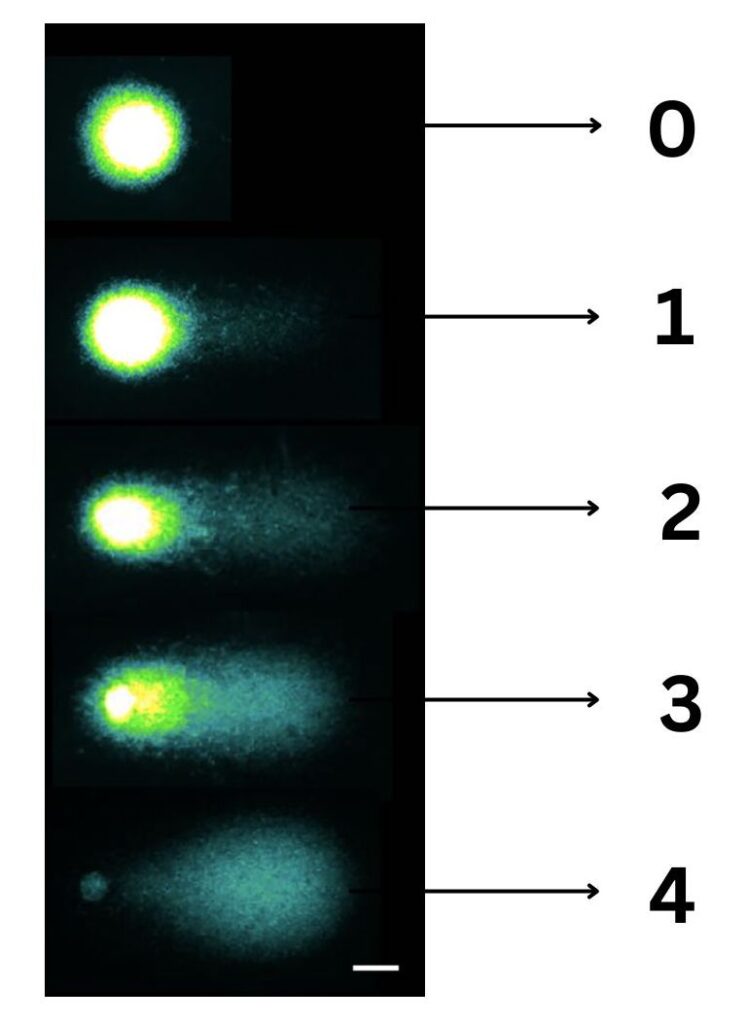
The visual scoring method is also adopted for COMET assessment which is a pretty decent technique. Here, all 100 COMETs being assessed are graded from 0 to 4. 0 with no tail and with almost intact DNA and 4 with whole tail without any intact DNA.
Thus, the total score of the sample being evaluated for all 100 COMETs is between 0 to 400. However, visual scoring certainly is not accurate and crucial for the assessment.
We can observe many COMETs in a single slide and if the slide is not prepared well, we can observe overlapped COMETs, and partial and coupled COMETs, these make overall assessment difficult.
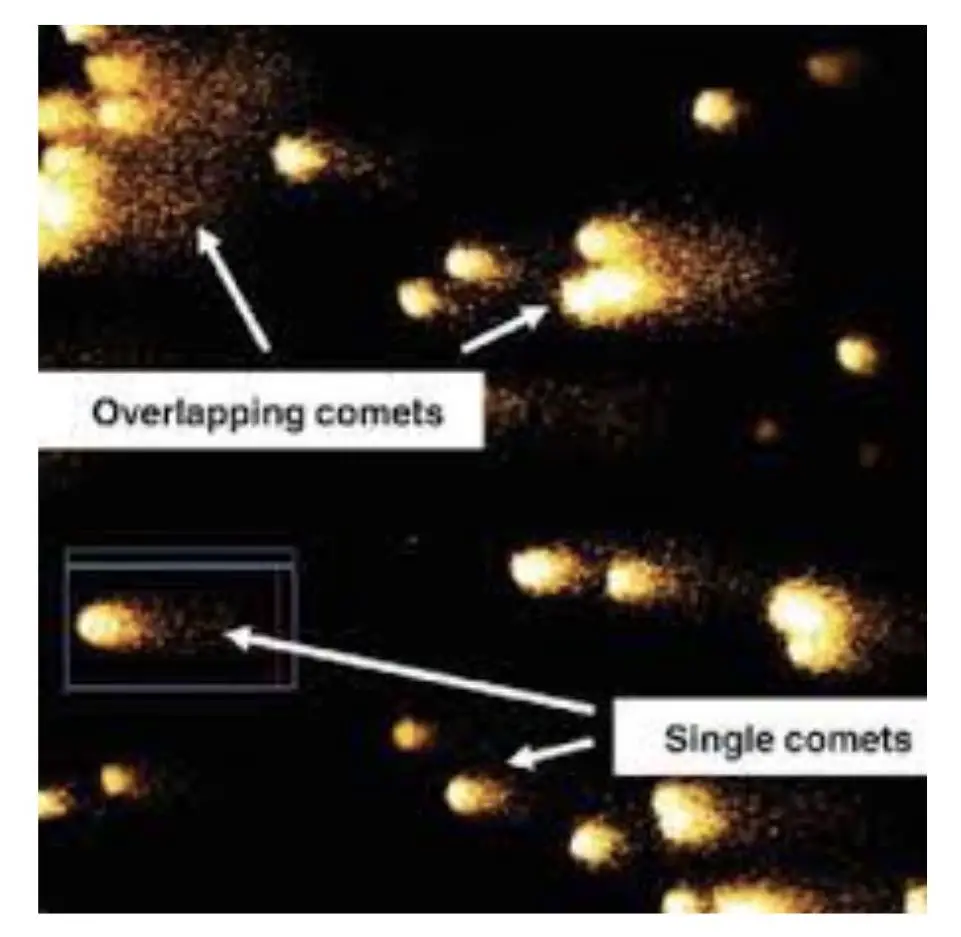
It’s advisable to select a well-distinguished, clearly visible and darkly stained cell for COMET assessment.
Advantages:
The present technique is sensitive, high throughput, cost-effective, easy to perform and simple technique. It also allows researchers to study individual cells, perform comparative studies and real-time monitoring of DNA damage and repair.
Disadvantages:
Despite of its widespread use in the diagnosis, it has several major limitations. It’s a time-consuming and tedious process. It requires manual assessment and lacks standardization. In addition, heterogeneity in damaged DNA also affects the assay negatively.
Wrapping up:
COMET assay is widely used in cancer genetic research and sperm DNA fragmentation studies. Thus, it is crucially important in the field of in vitro fertilization, infertility assessment and other related studies.
We will cover these things in our upcoming topic. We will explain everything about the sperm DNA fragmentation in detail there. I hope this article will surely help you to understand the COMET assay. You can surely use this knowledge for your research and clinical testing.
Sources:
Olive, P., Banáth, J. The comet assay: a method to measure DNA damage in individual cells. Nat Protoc 1, 23–29 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.5.Lu Y, Liu Y, Yang C. Evaluating In Vitro DNA Damage Using Comet Assay. J Vis Exp. 2017 Oct 11;(128):56450. doi: 10.3791/56450.

