“DNA and RNA polymerase synthesize DNA and RNA, respectively. Explore some of the common and uncommon differences between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase in this article.”
Every science student knows about DNA and RNA but do you know who synthesizes them? DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are two important enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of nucleic acid.
Enzymes are the class of proteins that helps in catalyzing various biological reactions. Both DNA and RNA polymerases are a class of polymerase enzymes that governs the underlying mechanism of constructing nucleic acid.
While both have a similar function, each one has a unique characteristic that makes them unique. In addition, DNA and RNA polymerases are crucial players in the central dogma process, they govern different reactions for different purposes. And thus, are so crucial.
In this article, I will explain how and why DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase are different. I will also list and explain several crucial differences in this scheme. This article will help you to understand the central dogma process more precisely.
Read more: What is DNA replication?
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
Differences Between DNA polymerase vs RNA polymerase:
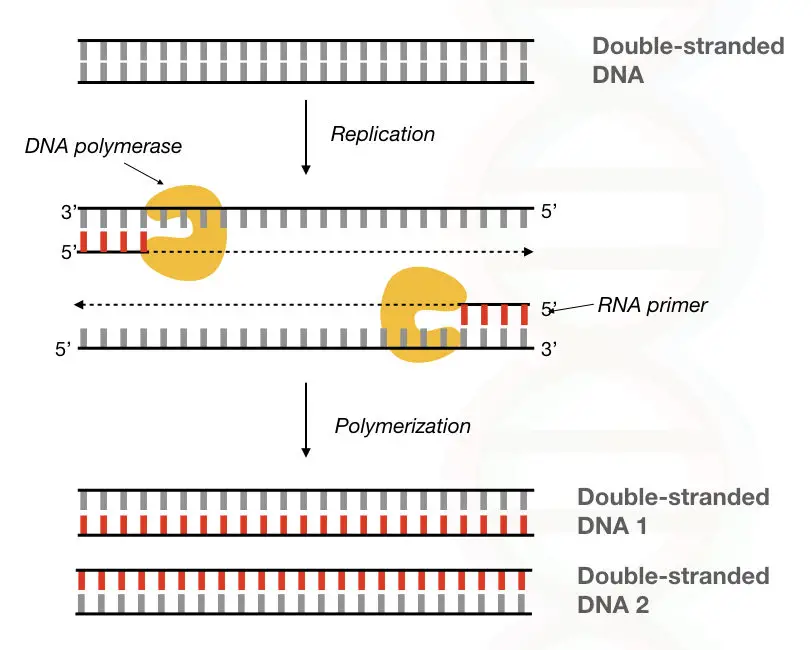
The very first difference, as aforesaid, is that DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA while RNA polymerase can synthesize RNA.
During the DNA replication or repair process, DNA polymerase catalyzes the nucleotide addition process on the growing DNA strand. While RNA polymerase catalyzes the ribonucleotide addition process during the transcription of DNA into RNA.
Thus, DNA polymerase works during replication and DNA repair while RNA polymerase works during transcription.
The end product of DNA polymerization is double-stranded DNA while the end product of RNA polymerization is a single-stranded RNA.
The reason behind that is, in replication a single-stranded DNA synthesizes another single-stranded DNA using DNA polymerase. While in transcription, a single-stranded DNA synthesizes single-stranded RNA using RNA polymerase.
Importantly, DNA polymerase always required a primer to initiate DNA replication. Primers are short and single-stranded DNA/RNA molecules. Contrary, RNA polymerase does not require primers to initiate RNA synthesis.
The reason behind that is, DNA polymerase requires a free 3’ OH end for replication initiation. Note that enzyme primase provides a short primer to the template strand. However, RNA polymerase can add nucleotides directly without the need for a free 3’ OH end.
Therefore, the synthesis process catalyzed by the DNA polymerase is not de novo while the synthesis process catalyzed by RNA polymerase is de novo.
It is important to note that DNA polymerase requires additional enzymatic help by topoisomerase and helicase for unwinding and releasing DNA tension during replication. Whereas RNA polymerase does not require such enzymatic help. However, a holoenzyme is needed for the activation of RNA polymerase.
The DNA polymerase adds deoxyribonucleotide to the growing DNA strand while the RNA polymerase adds ribonucleotide to the growing RNA strand. (instead of thymine, the RNA contains uracil).
Although both polymerases belong to the same family, DNA polymerase is a multifunction and multi-lobed structure while RNA polymerase is uni-functional and single-lobed.
DNA polymerase consists of two different lobes for polymerization and proofreading activities. While RNA polymerase only consists of a single lobe for only polymerization activity.
The proofreading domain or lobe governs the proofreading activity, also known as exonuclease activity. During the process, DNA polymerase moves back to the growing DNA strand, the exonuclease domain removes the mismatch and creates a gap. The polymerase domain repairs this gap through its polymerization action.
Contrary, RNA polymerase lacks the exonuclease domain and exonuclease activity, and can only perform polymerization.
Due to this reason, DNA polymerase has a lower error rate while RNA polymerase has a much higher error rate.
Fascinatingly, research suggests that the polymerization rate of DNA polymerase is approximately 1000 nucleotides per second (prokaryote) while the polymerization rate of RNA polymerase is 40 to 80 ribonucleotides per second only.
In addition, DNA polymerase has high processivity. It can remain attached to the template DNA for a longer period of time while RNA polymerase has lower processivity power as it can only synthesizes short RNA fragments.
Therefore, DNA polymerase is faster, more accurate and more efficient while RNA polymerase is slower and least accurate.
At the end of DNA synthesis, two DNA duplexes (4 separate single-stranded DNA) are manufactured. While during RNA synthesis only two different single-stranded RNAs are formed from the DNA.
DNA polymerase has three different subtypes while RNA polymerase has five different subtypes (eukaryotes).
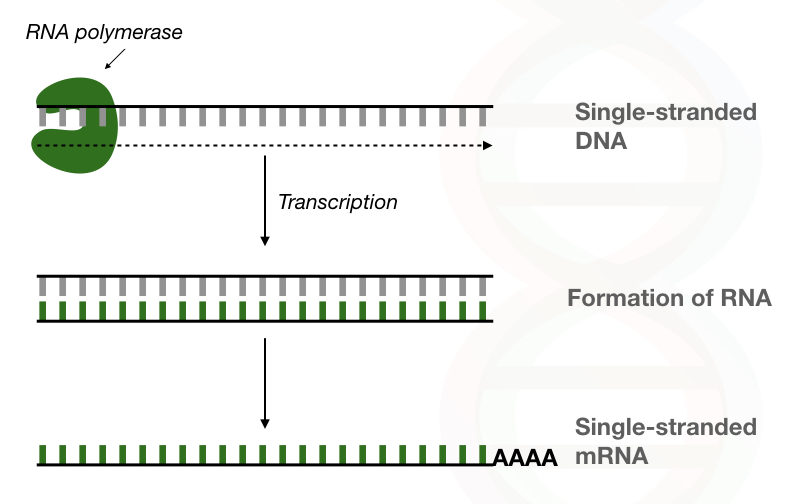
It is interesting to note that DNA polymerase-governed DNA synthesis is continued till the very end, thus, synthesizing entire chromosomal DNA. But the RNA polymerase-governed RNA synthesis terminates when it finds the stop or termination codon.
Both govern the catalytic reaction in different stages of the cell cycle. DNA polymerase functions during the S1 phase of a cell cycle while RNA polymerase functions during the G1 and G2 phases of a cell cycle.
One important difference that must be discussed here is the requirement of additional elements for synthesis. DNA polymerase does not require any additional elements like promoters to initiate replication. It occurs from start to end and covers the entire genomic DNA.
Conversely, RNA polymerase requires a promoter as a recognition sequence, near the site of action to start synthesis. Promoters are specialized, non-coding DNA sequences located near the transcription start site. One such sequence in eukaryotic promoters is the TATA box.
The summary of the differences between DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase is shown in the table below,
| Difference | DNA polymerase | RNA polymerase |
| Synthesize | DNA | RNA |
| Activity | Polymerization and proofreading | Only polymerization |
| Process | Involved in replication | Involved in transcription |
| Nucleotides | A, T, G and C | A, U, G and C |
| Cell division | During S1 phase | During G1 and G2 phase |
| Additional enzyme | Helicase and topoisomerase | Holoenzyme |
| Error rate | Very low (due to proof-reading activity) | Very high |
| Speed of polymerization | High | Low |
| Efficiency | High | Low |
| Process | Not de novo | De novo |
| Primer | Required | Not required |
DNA polymerase in a nutshell:
DNA polymerase is an enzyme that synthesizes DNA in all living organisms and is thus present in almost all organisms on Earth. It helps in replication to copy DNA using the single-stranded primer- either DNA or RNA.
DNA polymerase lacks de novo synthesis activity and requires a free 3’ OH group for conducting the synthesis. It has polymerization and exonuclease domains, and due to that can perform both functions.
It has 5’ to 3’ polymerization activity and 3’ to 5’ and 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity. Prokaryotes and eukaryotes contain 5 and 4 different polymerase families, respectively.
It takes the help of DNA helicase and topoisomerase during the catalytic activity for DNA unwinding. It has higher accuracy, speed, precision and polymerization rate.
Some other functions of DNA polymerase are V(D)J segment recombination, gap filling, antigen diversity, maintaining the length of telomere, DNA repair and somatic hypermutation.
If you want to learn more about the different types of DNA polymerase, its function, mechanism of action and other related information, read our article: Multifunctional DNA polymerase.
RNA polymerase in a nutshell:
Like DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase is also abundant in all living organisms with the function of synthesizing RNA. It synthesizes single-stranded RNA during the transcription process.
It does not need topoisomerase or helicase but does require a holoenzyme for proper catalytic action. It lacks proofreading activity. Therefore, it shows a high error rate during the RNA synthesis.
The RNA polymerase is slow, and inefficient, adds nucleotides 40 to 50 per second and synthesizes only short RNA segments.
Conclusion:
In 1956, Arther Kornberg made a significant discovery by identifying the first DNA polymerase. This breakthrough finding revolutionized our understanding of genetic processes. Both DNA polymerase and RNA polymerase play vital roles within a cell.
Errors in the function of these polymerases, whether it’s DNA polymerase or RNA polymerase, can lead to abnormalities with serious genetic consequences. Incorrect addition of nucleotides during replication or transcription can result in the synthesis of abnormal polypeptide chains. This, in turn, leads to the production of abnormal or non-functional proteins.
The accurate and precise activity of polymerases is crucial for maintaining the integrity of genetic information. Understanding the impact of polymerase errors emphasizes the importance of these enzymes in preventing genetic problems and ensuring the proper functioning of cells.
I hope you understand the importance of both types of polymerase. Do let me know in the comment and share this article.



excellent! thank you very much! shared it with my friends desperately in need of explanation!
Thanks Max
Thanks for your infomation, easy to read easy to understand. Cheer up ^^
Thank you Toeii B