“A chromosome is the most condensed form that appears during the metaphase while the chromatid is less condensed than chromosomes and appears once during the interphase.”
A complex and coiled network of DNA and proteins is known as chromosomes. It carries all the genetic material of a cell and transmits it to other cells and so to generations.
Every organism has different numbers of chromosomes on which all DNA is located which makes a genome of an organism. The function of chromosomes is to make DNA fit in a cell. If you want to learn more about chromosomes, their structure, function, and other information, please read our previous article: What is chromosomes?
In the present article, our major focus will not be on what a chromosome is but here we are discussing some of the differences between chromosome and chromatid. Also, the objective of writing this article is to make you understand both terms.
Related article: Inside Chromatin: Definition, Structure, and Function.
Key Topics:
Chromosome vs chromatid:
At the final stage of DNA packaging, the most condensed form of DNA forms a chromosome. Thus DNA on chromosomes is tightly packed.
On the other side, the chromatid is less condensed than the chromosomes. The DNA in it is loosely packed in comparison with the chromosomes. If we compare the packaging capacity of both, the chromatid is 50 times less condensed than the chromosomes.
The most prominent shapes of chromosomes appear during the metaphase of the cell cycle. Although the chromosomes appear throughout the cell’s life, the chromatid structure only appears during interphase.
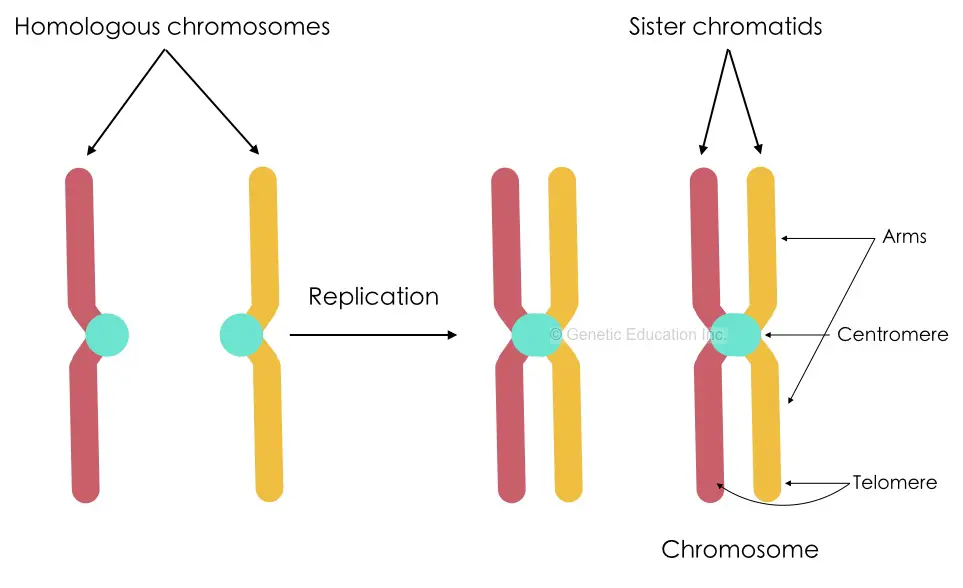
Two sister chromatids attach with a centromere and form a chromosome while a network of chromatins forms different chromatids.
The chromatin is a bead-on-string-like structure made up of nucleosomes which makes chromatids in the final stage of condensation.
In a pair each chromosome comes from two different parents thus even though chromosomes are homologous it might have different copies of genes for different traits. Contrary, each sister chromatids are exactly the same or we can say identical.
The basic unit of both is DNA! But the chromosomes are involved in the inheritance of genetic information and transfer it from one cell to another and one generation to another while the chromatids function for various DNA metabolic pathways, DNA modeling and remodeling.
Two sister chromatids join together and form a chromatid and two chromatids finally make a chromosome. On the other side, a chromosome is a single heredity unit inherited from each parent.
The structure chromosome appears with the centromere while the chromatid is a single entity that forms the chromosome.
The chromatids appear during the cell division viz during mitosis and meiosis while the chromosomes appear throughout life. The chromatids are involved in DNA duplication.
Using a cytogenetic technique known as karyotyping or a karyotype test chromosomes are studied. The technique is conventional and culture-based. Cells are cultured and harvested. Using the banding technique such as GTG, Q-banding or NOR- banding various chromosomal abnormalities are detected.
On the other side, the same technique is used for the detection and study of chromatids but with a few modifications.
In the conventional karyotyping method, for the detection of chromosomes, metaphase chromosomes are developed and cultured while in the sister chromatid exchange, interphase chromatids are studied. Recombination and exchange of genetic material between chromatids are studied by sister chromatid exchange assays.
Chromosome in a nutshell:
The chromosome is an X-shaped structure having all the information or genetic information of a cell. Structurally a chromosome is made up of two arms that are p and q arms, telomere and centromere.
The telomere located on the edge of a chromosome protects genes while the centromere helps to hold two chromatids. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans.
Chromatid in a nutshell:
The chromatid appears during interphase, is attached to the centromere and makes a chromosome. It is made up of a network of chromatins. A cytological assay known as a sister chromatid exchange study helps to find out alterations and translocations between two chromatids.
The basic unit of a chromatid, the chromatin is made up of the nucleosome assembly. The nucleosome is a complex network of histone protein and DNA.
Conclusion:
Chromosomes are an important unit of life on which DNA is located. It is made up of chromatids which is a network of bead-on-string structures. DNA packaging plays an important role in fitting DNA in a cell by different levels of an organization. If you want to learn more about a present topic please read this article: DNA packaging in eukaryotes.
Sources:
Cooper GM. The Cell: A Molecular Approach. 2nd edition. Sunderland (MA): Sinauer Associates; 2000. Chromosomes and Chromatin.