“Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR gene, inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern.”
When two the mutated allele inherited together results in homozygous recessive disease conditions.
The Cystic fibrosis is a genetic condition mostly affects the lung, pancreas and kidney. Because of the mutation in a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, a faulty protein is produced which affects the mucus-producing glands and tissues.
The CFTR gene is located on chromosome 7 at 7q31.2 which encodes a mucus-producing protein. The gene is first identified by Lap-Chee Tsui in 1989.
The CFTR protein is made up of the 1,480 amino acid. Though 1,200 mutations are discovered in a CFTR gene which causes the cystic fibrosis, the most common mutation of CF is deletion, located at amino acid 508 and thus it is called delta F509 or ΔF508.
In the present article, we will answer one of the most common questions, “how is cystic fibrosis inherited.” but before that let me brief you what the cystic fibrosis is.
The CFTR protein is located in every epithelial cell of our body which produces the mucus.
The mutant CFTR gene produces an abnormal protein product results in thick and sticky mucus which causes blockage in lungs, digestive system and kidney.
The CFTR protein is present in the cells of lung, liver, pancreas, heart, immune system, intestine and sweat glands.
In addition to this, the mutation also causes electrolyte and water imbalance in a cell, therefore, higher sweat chloride level is observed in CF patient.
The common symptoms of cystic fibrosis are:
- Thick and sticky mucus
- Lung infections
- Allergic to common pollutants
- Cancer of digestive tract
- Diabetes
- Infertility
- Kidney dysfunction
- Malnutrition
- Gastrointestinal complications
- Heart failure
- Liver dysfunction
- Muscle and bone complication
- Problem in breathing
- Frequent salt loss
- Urinary infections and incontinence
As the severity of the disease increases the complications are also increases.
How is cystic fibrosis inherited?
The cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder in which two mutant alleles causes the disease.
In the autosomal recessive condition, the chance of the inheritance of the disease is 25% while in the autosomal dominant inheritance the chance of the disease is 75%.
The person remains normal in the carrier condition, in which one mutant and one normal allele are present.
Suppose if both the parents are carriers of the disease, then the chance of the inheritance of cystic fibrosis mutation is shown into the figure below,
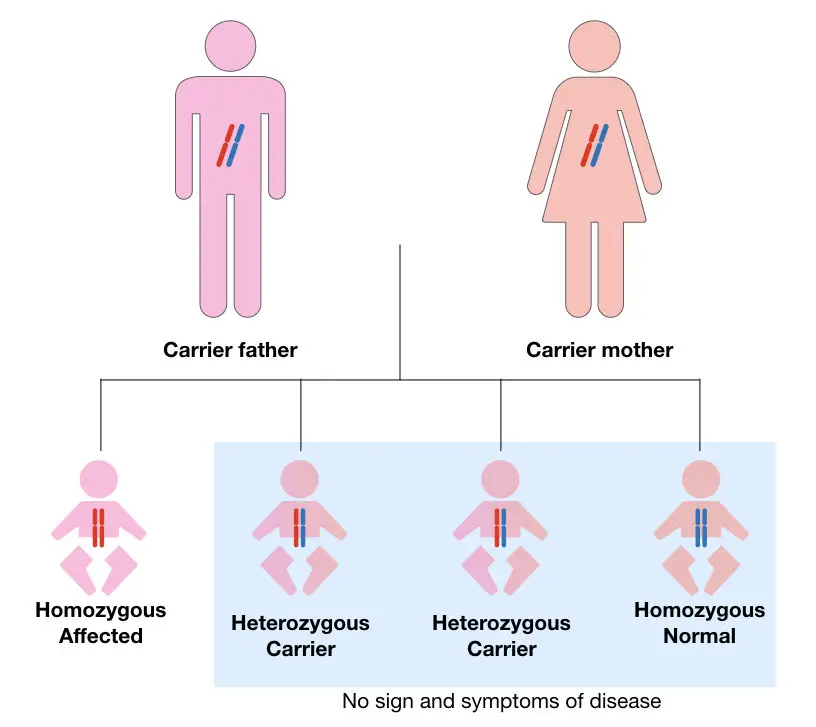
As you can see the figure, if both the parents are heterozygous, which means they do not have any signs of cystic fibrosis but they carry one mutant allele for it.
25% of the offspring becomes affected with the disease which means one out of every four children may be affected with the disease because of the presence of the both mutant CFTR gene alleles.
These type of inheritance is called an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
However, 75% of the progeny remains normal, still, 50% become a carrier for the disease.
Now see, the next image shown below,
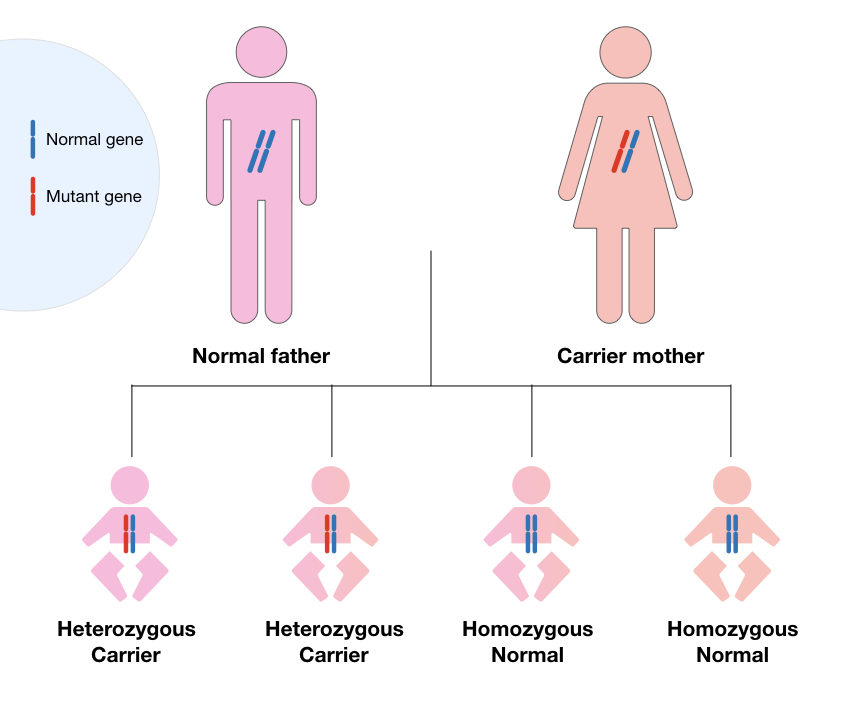
If one of the parents is a carrier for the disease, All the individuals from the offspring remain normal in which 50% are carriers and 50% normal.
Similarly, if one of the parents are affected, all the progenies become a carrier (heterozygous), however, the chance of this type of condition is very rare because infertility is one of the major problem associated with the cystic fibrosis.
The cystic fibrosis is commonly present in northern Europeans, 1 in the 20 people are a carrier for the cystic fibrosis worldwide.
One of the most common and inexpensive tests for detecting the CF is sweat test, which measures the amount of the chloride in sweat, nonetheless, the carrier can not be screened using the sweat test.
Using the molecular genetic testings such as polymerase chain reaction or DNA sequencing carrier as well as the mutant for the CF can be detected.
The most common mutation in the cystic fibrosis is deletion- ΔF508, using the sequence-specific primers in PCR, the disease can be screened.
Although the severity of the disease is depended on the amount of the mutated protein, Real-time PCR analysis must require for quantification of the mutant gene.
Autosomal recessive vs autosomal dominant:
In the autosomal recessive condition, the presence of two alleles cause the disease, thus the chance of occurrence of the disease it only 25%.
In the autosomal dominant condition, only single mutant allele causes the disease, thus homozygous dominant as well as all the heterozygous are affected with the disease. The chance of the occurrence of a disease is 75%.
Related article: Genetics Basics: A Beginners Guide To Learn Genetics.
Conclusion:
An autosomal recessive inheritance pattern of the cystic fibrosis occurs due to the presence of two mutant alleles.
As the signs and symptoms are not observed in the normal condition, prenatal genetic testing helps parents to take a decision for their upcoming child.
If any of the individuals of your family is suffering from cystic fibrosis, please contact the genetic counsellor. He will advise you what to do next.
Sources:
- Winikates, Kristina, “Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Gene”. Embryo Project Encyclopedia (2012-01-01). ISSN: 1940-5030. http://embryo.asu.edu/handle/10776/2323.
- Cystic fibrosis foundation.