“DNA primase is a type of RNA polymerase which synthesizes smaller RNA primers complementary to the ssDNA for starting the DNA replication.”
Not only RNA but in some organisms, it also synthesizes the DNA too for the beginning of replication.
Furthermore, it also synthesizes RNA primers for the lagging strand Okazaki fragments.
Replication is a process that globally happens in all organisms on earth. It replicates DNA.
It is a process in which under the control of the enzymatic catalytic reactions, new DNA strands are synthesized from the parental strands.
The process of replication is a necessary process required for all, it copies the DNA, inherit it to the daughter cell during the cell division,
And hence inherited DNA from parents to their offspring.
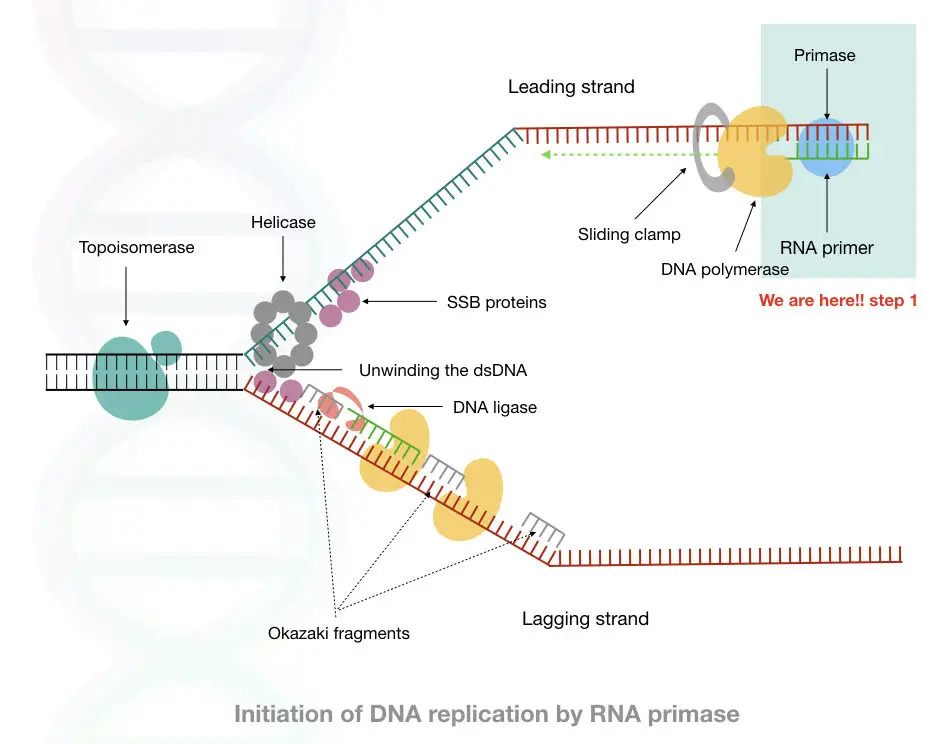
Different enzymes catalyze different steps such as unwinding the DNA, providing the primers, binding to a single strand, unstraining the DNA and synthesizing the DNA.
Furthermore, in the final step DNA ligase fills all the gaps by creating phosphodiester bonds.
In the present series of articles, we will discuss each and every enzyme and protein involved in the replication.
We are here now,
Read our article on DNA: DNA story: The structure and function of DNA
The very first enzyme for starting our replication is the DNA primase. The content of the article is:
- What is DNA primase?
- Structure of DNA primase
- Types of DNA primase
- What is the function of DNA primase?
- Conclusion
Key Topics:
What is DNA primase?
Although DNA replication starts with double-stranded DNA unwinding, before that the DNA primase synthesizes the primer for starting the Replication.
Read more on replication: General process of DNA replication.
The DNA primase is the enzyme that synthesizes a short, single-stranded, DNA or RNA oligo chain necessarily required for starting the replication.
The primer is a short single strand of RNA (in the case of eukaryotes), ranging from 8 to 12 nucleotides, complementary to the starting bases of the leading strand of DNA.
See the image below,
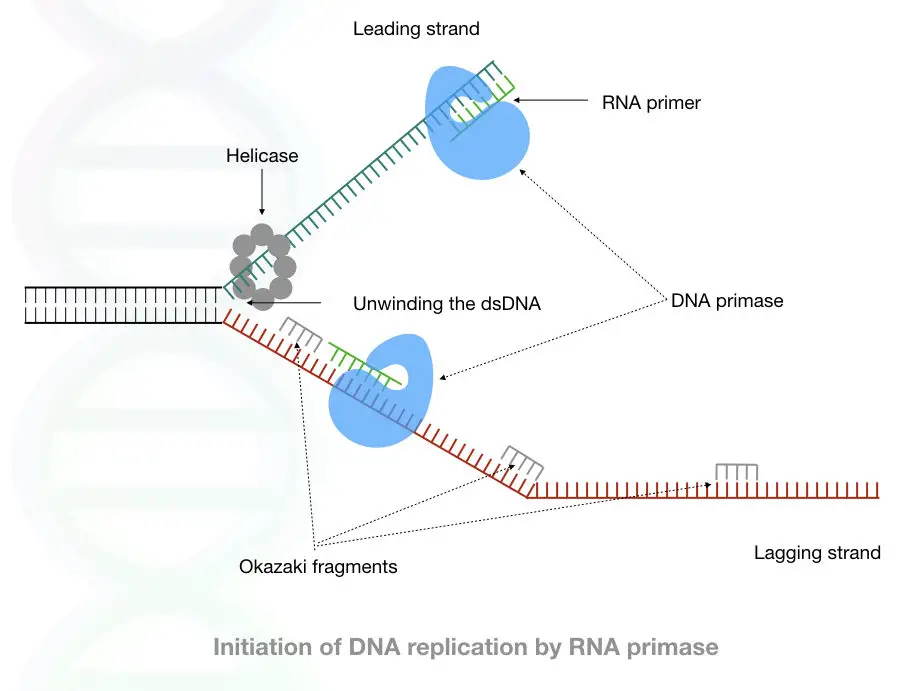
Now as we all know that the DNA polymerase can synthesize the DNA by adding the nucleotides then why DNA primase is needed in DNA replication?
The DNA polymerase can not able to add nucleotides until and unless two of the major event occur.
The first, unwinding of DNA.
The DNA polymerase can only work on the ssDNA and use it as a substrate, it required a single-stranded DNA at where the subunit of DNA polymerase settled and recognized the nucleotides on the strand.
Second is the 3’ end,
Until and unless the DNA polymerase can not find the 3’-OH group, it can not add nucleotides.
Thus here, the RNA primer provides a free 3’-OH group as well as the substrate to bind with the DNA.
Once the polymerase binds on the DNA-RNA hybrid, it immediately starts the addition of nucleotides. See the image below,
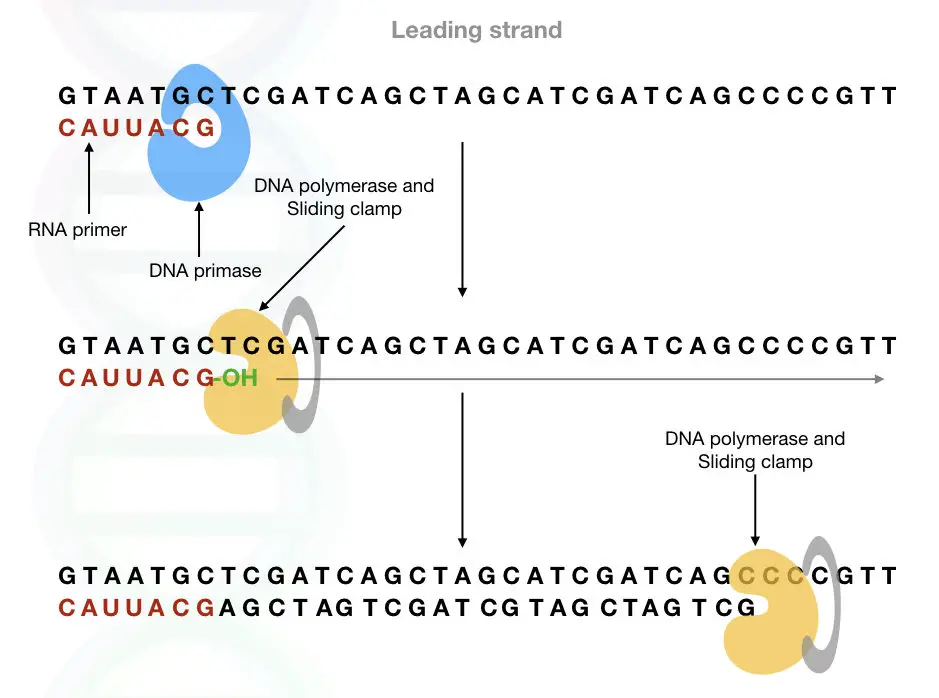
Therefore, DNA primase must be needed at the beginning of DNA replication.
Note: At the end of the replication, as the RNA can not be a part of DNA, the short RNA primer is removed from the newly synthesized DNA strand by DNA polymerases’ 5’ to 3’ exonuclease activity.
The polymerase once again inserts nucleotide in place of the RNA primer and finally, the gap between them is filled by the phosphodiester bonds formed by the universal sealer DNA ligase.
Structure of DNA primase:
Two different types of DNA primase are naturally present in eukaryotes as well as in prokaryotes.
Read more on prokaryotic DNA replication: Prokaryotic DNA replication.
In all eukaryotes (also, in archaean) the DNA primase is made up of one large and one small subunit.
It is a type of heterodimeric protein.
The smaller catalytic subunit is called PriS or Pri1 while the larger subunit is called PriL or Pri2.
The PriS is the catalytic subunit having an ATP binding site involved in the RNA synthesis.
Nonetheless, PriL also has some important functions to do.
The larger subunit of the enzyme determines the single-stranded RNA product size as well as stabilizes the smaller (PriS) subunit.
Studies on model organisms suggest that the absence of the PriL leads to the inactivation of the entire DNA primase.
Thus, it is believed that it might involve in the activation of the small subunit.
Types of DNA primase:
AEP primase:
Archaeo-Eukaryote Primerases, AEP DNA primase found in the eukaryotes and Archaean.
It is a heterodimer made up of two subunits.
It can synthesize DNA as well as RNA primers.
We already discussed the structure of the eukaryotic primase.
DnaG:
The DnaG is a monomeric single protein that only synthesizes the DNA primer.
A cashew shaped DnaG is made up of the three subunits:
- A central subunit made up of the six alpha-helix and five beta-sheets.
- The phosphotransfer domain for transferring of metal ions.
- The side subunit made up of some alpha helix and beta subunits having NH2 and COOH terminal groups on both the ends.
De novo synthesis of DNA can not be possible by DNA polymerase, the RNA polymerase named DNA primase synthesizes the DNA or RNA de novo for the starting of replication.
The gene PRIM1, primase subunit 1 encodes human DNA primase. It encodes for the primase involved in the synthesis of RNA for Okazaki fragments. The molecular weight of the protein is 49KDa.
The gene is often called p49.
Another gene involved in the synthesis of DNA primase is PRIM2 or p58.
This gene encodes a larger subunit of the primase of 58KDa.
Function of DNA primase:
The main function of DNA primase is to synthesize RNA/ DNA molecules during replication.
However, the primase performed its function by forming two different complexes at two different places.
First, it forms the “heterotetrameric complex” with the DNA polymerase alpha subunit and B subunit (both the subunits of primase binds to two subunits of polymerase hence called the tetrameric complex).
This complex governed the primase activity at the leading strand by adding a single RNA primer.
Another complex is called primosome is formed by DNA helicase and primase complex. Primosome mainly works at the lagging DNA strand by adding multiple Short RNA primers (6 to 8 oligos) between the Okazaki fragments.
The primase-helicase, primosome complex also functions in prokaryotes in which it unwinds the dsDNA as well as incorporates primes at the lagging strand.
Although, the primer synthesized in the prokaryotes is only two to three nucleotides long.
Besides its major role in primer synthesizes, the DNA primase is also involved in the non-homologous end-joining, terminal end transfer, polymerization and DNA repair mechanism.
Interestingly,
Though it is an RNA polymerase sometimes it incorporates deoxyribonucleotides to the 3’ end of the DNA, independently from the template.
However, the rate of dNTPs addition is limited and slow.
Interesting information:
The DNA primase is an RNA polymerase that synthesizes the RNA, although as like the other polymerases if it required a 3’ OH group or not, is not cleared.
Apart from its role in RNA synthesis, the DNA primase also helps in ending the DNA replication and stopping the progression of leading strand synthesis by halting the replication fork.
Unknown fact:
Due to some extra-subdomain fusion in the DNA helicase, some helicase also possesses primase-like activity.
One of the important points we must have to discuss here,
The DNA primase is an RNA polymerase.
The RNA polymerase is also required in the synthesis of different RNA molecules like mRNA, tRNA and rRNA.
Is both RNA primers are the same or different?
The RNA polymerase involved in the synthesis of different RNA molecules required fully extended and replicated DNA molecules while the RNA polymerase (the DNA primase involved in the replication) only required a single-stranded DNA as a template for short RNA synthesis.
Research on E.coli suggests that the DNA primase synthesizes RNA from the single-stranded DNA starting with the GTA.
Furthermore, The RNA polymerase involved in the synthesis of different RNAs work independently while,
The RNA polymerase, the primase works complexing with other enzymes like helicase or DNA polymerase.
Its affinity to bind with the helicase and requirement of ssDNA as a template makes the DNA primase works dedicatedly in DNA replication only.
Furthermore, it also works in DNA repair, maintenance of telomere and chromosomal stability.
Conclusion:
DNA primase is an initiator of DNA replication and must require to start replication. However, for in vitro replication or PCR, DNA primer is used instead of RNA primer because the Taq DNA polymerase used in PCR can not have exonuclease activity.