“A type of lab test used to find out any changes in a DNA sequence, gene, or chromosome which causes genetic abnormality is known as a genetic test.”
DNA is a building block of every organism on earth. It is an inheritance unit, pass on genotypes to subsequent generations. A functional stretch of DNA called a ‘gene’, consist of only 3% of our genome, rest is non-function junk DNA.
The genes are located on chromosomes, 23 pairs of chromosomes are present in a typical somatic cell. Overall, all the DNA of us regulates our life and are located on chromosomes.
Any change in a DNA sequence (called a mutation), causes abnormal genotype and consequently results in abnormal phenotype. A genetic test is used to detect mutations that occur in genes. If you want to learn more on difference between genotype and phenotype read this article:
DNA tests and chromosome tests are two common types of genetic tests used not only for the diagnosis of disease but also for other various purposes. For example, a DNA test is employed for DNA fingerprinting as well as HLA typing too.
Besides, the genetic test is used in other fields also. In the present article, we will try to understand what a genetic test is and how it is done. Also, we will discuss various types of DNA testing methods and their applications. The major focus area of the article is:
- What is genetic testing?
- How is genetic testing done?
- Type of genetic testing
- Pros and cons of genetic testing
- Cost of genetic testing
- Conclusion
Read our article on DNA: DNA story: The structure and function of DNA.
Key Topics:
What is genetic testing?
A genetic test is used to study the DNA, gene or chromosomes.
“Detecting mutations in either DNA or chromosome associated with a genetic disorder using a genetic technique is referred to as genetic testing.”
Genetic testing is also known as genome testing majorly used for diagnosis of inherited genetic disease, rare genetic conditions, chromosomal anomalies, and cancer.
Definition:
“A laboratory genetic testing method employed in order to detect genetic differences or genetic disorders of an organism is defined as genetic testing.”
The genetic test is used to;
- determine the reason for the occurrence of the genetic disease.
- identify mutations or changes associated with the genetic disease.
- Genetic status of an individual (whether he or she is normal, affected or carrier for particular disease).
- For identification of a gene associated with the disease.
- To determine the severity of the disease using gene expression assays.
Although many genetic conditions are now characterized, some are still unknown to us. For example, we know that one extra chromosome (chromosome 21) is responsible for down syndrome, A point mutation is HBB gene causes sickle cell anemia. But the exact reason for the occurrence of cancer is still unknown to us.
Fascinatingly, in recent days, genetic testing is practiced in predicting genetic conditions. Also, scientists can determine the chance of occurrence of genetic disease in upcoming generations correctly. We can’t identify all genetic disorders using the present technique, nonetheless. So we can say it isn’t a fully functional medical test.
More than 2000 genetic tests are now available for diagnosis of different genetic conditions. We can say it is a part of genetic counseling where a genetic expert advice someone to go for a genetic test.
Moreover, genetic testing is a complex process, even a medical professional can not interpret results without taking the help of a genetics expert. Emotional, social, and ethical issues are associated with genetic testing thus one must need a concern before doing a genetic test.
How is genetic testing done?
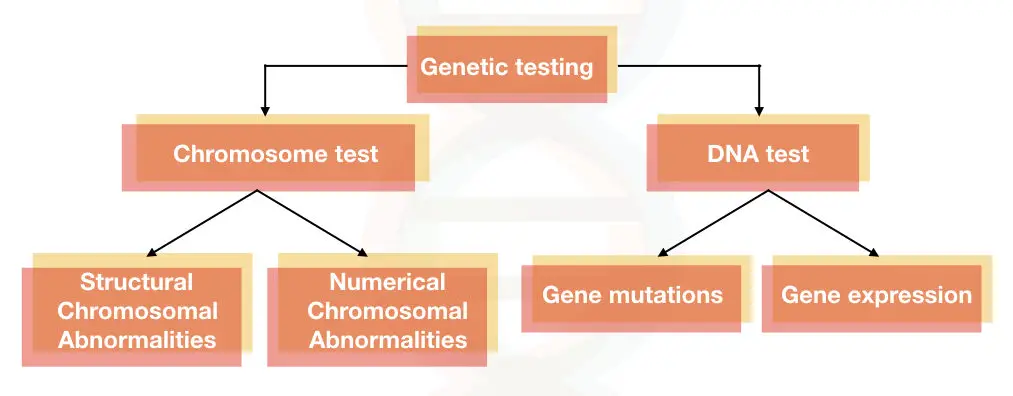
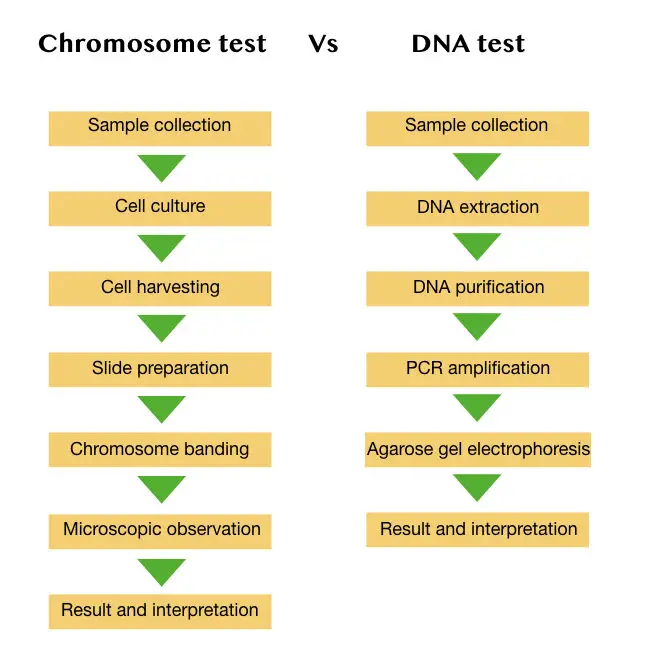
Depending upon what we want to study, two major types of genetic tests are employed; DNA test and chromosome test. Both the test are different and are used for different purposes.
People consider the DNA test as only genetic testing but the chromosome test is also one of the types of genetic tests available. Now let’s understand how both the test works.
DNA test:
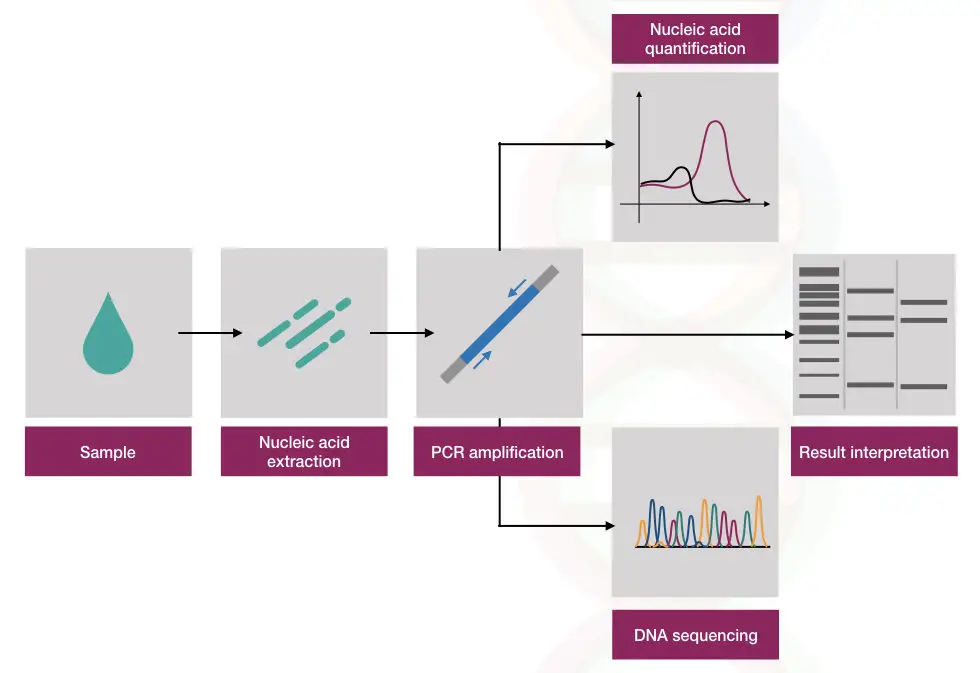
A DNA test is often known as a molecular test or gene test used prominently for the diagnosis of single-gene disorders. Also, using a DNA test one can predict the genetic status of a patient whether he or she is a carrier for the disease or suffering from it or not. Majorities of DNA testing is based on the polymerase chain reaction.
The very first step in DNA testing is DNA extraction.
Any of the bodily fluid of cells type are used for DNA testing. Blood, buccal swab, saliva, cell suspension, hair, amniotic fluid, chorionic villi, solid tissues or any other type of body tissue are used for DNA extraction.
Depending upon the type of cell, the methods for DNA extraction varies. Some of the common types of DNA extraction methods are enlisted in the article given below,
However, the main goal of DNA extraction is to provide high-quality DNA to perform a genetic test. The extracted DNA must have purity nearby ~1.80 and a quantity of more than 100ng. Interestingly, It has one additional benefit over the chromosome test. DNA can be stored for a longer time.
If you want to learn more about DNA extraction, go and check out this article first: 10 Secret Tips for DNA Extraction to Get Good Results.
Now, we have DNA, we can repeat the DNA test for a patient many times that can not possible in the chromosome test. Once the DNA is extracted, it is sent for the PCR amplification.
In a simple language, we can say that the polymerase chain reaction is a heart for molecular genetic testing. In almost, all molecular genetic techniques it is required. Single gene disorders like thalassemia, sickle cell anemia, and cystic fibrosis are now diagnosed only using the conventional gradient PCR.
The amplified DNA sample is now sent for DNA sequencing where the sequence of DNA is determined. DNA sequencing has a power o determine known as well as unknown mutations associated with disease or gene.
In addition to this, gene expression can determine using real-time PCR as well.
Gene expression: The amount of a gene in a particular cell or tissue can be determined by gene expression studies. The severity of the disease can be measured, consequently.
Chromosome test:
A chromosome test is used for the detection or identification of numerical or structural abnormalities associated with chromosomes. We have already discussed the chromosome test in our previous article. Please read it here: Chromosome test.
Here I am only giving the outline of it,
In order to get a good amount of metaphase cells, the sample is first cultured. Once the cells are grown, banding is performed to study chromosomes or related disorders.
An expert then arranges the chromosomes according to their numbers and trying to identify any changes in it. The bunch of several genes deleted or inserted on a particular chromosome can be distinguished by chromosome banding. Furthermore, numerical changes can also be encountered.
Notably, a lot of experience and expertise required to interpret the results of the chromosome test.
If you are really interested to learn more about chromosome test, karyotyping and how to prepare a karyotype to go and check out this website on it: www.karyotypinghub.com
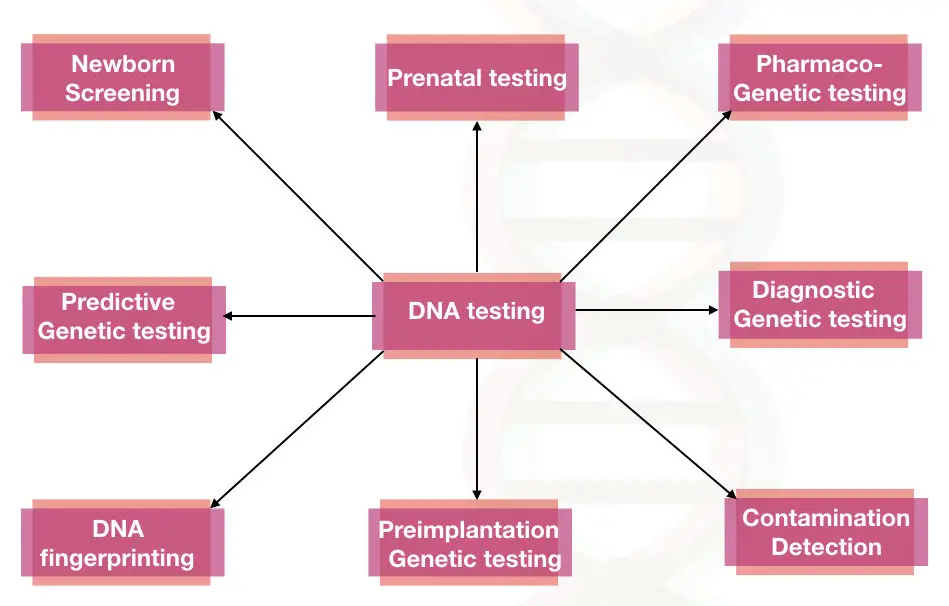
Type of genetic tests:
Disease diagnosis testing:
Both, the DNA and chromosome test is used for diagnosis of genetic disorders. Inherited, non-inherited, and rare genetic disorders are identified. New mutations or changes related to the disease can also be identified.
Based on the phenotypic symptoms a particular test recommended by the geneticist. Diseases like sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, Huntington’s disease, cystic fibrosis, cry-du-chat syndrome, down syndrome, Patau syndrome, Edward syndrome, etc are now being treated using the genetic testing based diagnosis.
[DNA test: sickle cell anemia, thalassemia, Huntington’s disease, and cystic fibrosis.
Chromosome test: cry-du-chat syndrome, down syndrome, Patau syndrome, and Edward syndrome.]
Even several types of cancer are now diagnosed using the genetic testing method. For example, chronic myeloid leukemia is now diagnosed using the chromosome test while breast cancer or cervical cancer are now diagnosed using molecular genetic methods.
Related article: Philadelphia Chromosome, BCR-ABL1 Gene Fusion And Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.
Carrier testing:
A carrier is a genetic condition in which a person carries one copy of a mutant gene but remains normal. Signs and symptoms of the disease are not observed in a carrier, nonetheless, it can pass a disease gene to the next generations.
If the father and mother both are a carrier for one particular disease, there is a possibility that the fetus may carry the disease. Genetic testing helps in the identification of carriers and disease conditions too.
Prenatal testing:
Prenatal genetic testing gives the power to us for deciding the fate of the fetus. Before birth, using genetic testing, normal, disease or carrier status of the fetus can be determined.
The prenatal genetic testing is prescribed more for high-risk pregnancies and couples having a history of genetic disorders. Various structural or numerical chromosomal problems, DNA and gene mutations are screened using the present method.
For prenatal diagnosis, the amniotic fluid or chorionic villi sample is collected, which proceeds either for cell culture, DNA extraction or both. Nowadays a new age genetic testing method is evolved known as cell-free fetal DNA which is non-invasive, safer and faster.
Related article: Cell-Free DNA Test- What is it and How to do it?
Newborn screening:
A drop of blood collected on the paper from the newly born baby and send for DNA testing. The DNA is extracted from the sample and different genetic tests are being performed on it. In addition to this, several biochemical tests are also performed.
It is required in case of the genetic disease treated during the prenatal stage of the pregnancy. Newborn screening for phenylketonuria, sickle cell anemia, congenital hyperthyroidism are nowadays compulsorily done in almost every country.
If any genetic abnormality occurs treatment for that started earlier.
Predictive genetic testing:
The predictive genetic testing is performed to predict the genetic condition of a person or fetus. It tells us the chances of suffering from a genetic disease. Pedigree analysis of family and genetic testing both one at once to conclude or predict the condition.
This type of genetic testing is also known as presymptomatic or predictive genetic testing.
By identifying a particular mutation associated with the disease, one can actually predict the chance of occurrence of disease. It is often used in the prediction of cancer.
Preimplantation genetic testing:
The preimplantation genetic testing is practiced during the in vitro fertilization. A few cells are taken from the growing embryo and a DNA test is performed to detect genetic abnormalities if any. The present type of genetic testing method is highly sensitive in comparison with other methods because we have to perform the entire test from a few cells.
Thus, instead of wasting it on different PCR-based diagnosis methods, the DNA sample is directly sent for DNA sequencing or DNA microarray analysis.
Both techniques have the power to screen thousands of mutations in a single run. Notably, preimplantation genetic testing is one of the most growing fields of genetics.
Pharmacogenetic testing:
Pharmacogenetics is also a trending application of DNA testing in which a DNA test helps in determining which medicine and how much dose is effective for some disease. Besides these, a DNA test is also used for several non-diagnostic applications as well.
Some of them are enlisted here:
DNA fingerprinting:
A kind of genetic test known as DNA fingerprinting or gene test is routinely practiced in the forensic science to identify criminals and investigate the crime scenes.
DNA is someone’s unique identity, no two people in the world have a similar genetic profile.
A sample is collected from the crime scene (it might be hair, blood or any body fluid) followed as DNA extraction and PCR amplification. The DNA profile of suspects and samples of the crime scenes are matched in order to check the relation or to solve the crime.
Therefore, we can say it is used for the identification of a person, actually and establishing the relationship between two people.
Detection of contamination:
A DNA test has the power to distinguish two different cell populations, if mixed or contaminated. and hence used in the detection of maternal cell contamination.
Genealogical studies:
One of the fascinating applications of DNA tests in recent days is to determine one’s ancestry or ethnicity. There are lots of articles, blogs and videos on this topic, so we are not discussing it in detail here.
Read more: Genetics Basics: A Beginners Guide To Learn Genetics.
Pros and cons of genetic testing:
Genetic testing is one of the best diagnostic methods available now, yet it has several advantages as well as disadvantages. Here in this section, we have enlisted some of the pros and cons of it.
Pros of genetic testing:
The genetic testing method is unmatched, no other diagnostic method is more effective than it.
Inherited as well as rare disorders are identified using the genetic testing method.
The genetic testing method is a more accurate and reliable method.
It is method is rapid, gives results within a day, however, the chromosome test takes 3 to 4 days for giving results.
A physical risk associated with genetic testing is very less.
The test results give a sense of relief for the families having a genetic test and help them to make a decision for their child.
It is also used in preventing genetic disorders too. Parents can make a decision to abort a child or not if has a genetic condition. However, the decision entirely depends on the parent.
A genetic test is a “lifesaver test”, preventive actions can be taken earlier if the results are positive. Nonetheless, the negative results eliminate the need for unnecessary screening tests. Hence saves money.
Using the DNA test one’s ethical background can be established.
In a nutshell, a genetic test makes families happy.
Cons of genetic testing:
The chromosome test is time-consuming and the chance of results failure is also high in it.
The genetic testing is a costly diagnostic method.
Ethical, social, emotional, and financial issues are involved in genetic testing. If someone’s baby is positive for a genetic test, he or she may felt guilty and undergo depression.
The use of an invasive sample collection method makes it restricted to use.
Collecting amniotic fluid or chorionic villi carries a risk of miscarriage.
One of the major limitations of genetic testing is uncertainty.
A positive result does not always mean that the person may suffer by the disease, similarly, a negative result does not mean that the person is safe, or he or she may not suffer by the disease.
Related article: Common FAQs- Chromosome Test.
Cost of genetic testing:
The cost of genetic testing varies from test to test, some tests are too costlier, for example, whole-genome sequencing or whole chromosome microarray while some are cheap.
The test cost for a genetic test is 100$ to 2000$ or more.
On an average, the cost of chromosome test is between 42$ to 50$ (3000 to 5000 INR), while the cost of the DNA test is between 50$ to 500$ (3500 to 35,000 INR).
Conclusion:
I advise all to go for a genetic test once before the marriage, who knows you might be a carrier for some genetic disease. Respect the decision of your genetic counselor, in case of positive results, take action with discretion. Also, avoid blaming each other.


Comments are closed.