“The larger deletion on chromosomes that can be detected by the karyotyping technique is known as the deletion syndrome or chromosomal deletion syndrome.”
We know chromosomes, right! We have articles on it, you can read it here if you don’t know! : What is a chromosome?
It s X shaped structure on which DNA is located and present in a cell nucleus. The chromosomes are present in a pair in somatic cells, for example, 23 pairs in the human.
One set from father and another from mother inherited into progenies and likewise, genes and DNA inherited into the next generation.
But nothing is as simple as we are discussing. Some intrinsic and extrinsic factors may hinder this process.
We know it as a mutation. At DNA or gene-level it is referred to as gene mutation while at chromosome level it is referred to as chromosome mutation.
When some portion of chromosome (carrying some genes) may be inserted, inverted, translocated or deletion, it can cause serious health problems.
Such problems are majorly associated with the mental, developmental, reproductive and cognitive factors of a person.
Thus it is crucial to study chromosomal alterations. Chromosome deletion is one of them. Here in the present article, we are going to discuss on chromosome syndrome and some common examples of it. We will give you a list of various deletions on different chromosomes.
Let us start the article,
Key Topics:
What is a deletion syndrome?
When a deletion on the chromosome is harmful to the person or creates a health-related problem, the type of chromosomal deletion is known as deletion syndrome.
Note that when we are talking about the deletion syndrome we will not consider minor or a few base deletion in it. We can say, it the deletion is detectable using conventional karyotyping, then it is known as deletion syndrome.
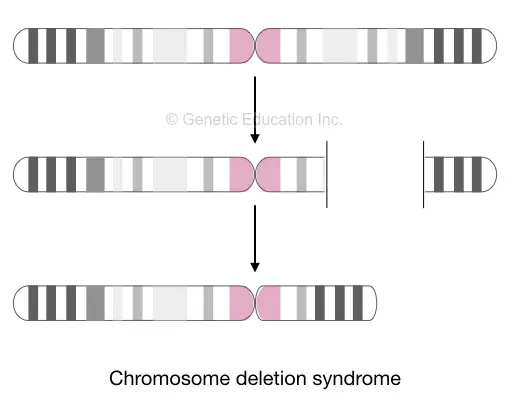
Chromosome deletion:
Larger deletions, terminal deletion, microdeletions and interstitial deletions are common types of chromosomal deletions.
Larger deletions: often known as chromosome syndrome in which a major portion of the p or q arm of the chromosome deletion. This deletion causes very serious health problems.
Terminal deletions: When a portion of a chromosome deletion from the terminal part or telomeric part of the chromosome. Usually, the telomeric region is less gene-rich or gene absent regions.
Still, it is associated with abnormalities.
Microdeletion: Such type of chromosomal deletions are so tiny that can’t be detected using the karyotyping method. It also causes health-related problems.
Microdeletions are detected using FISH-fluorescent in situ hybridization and chromosomal microarrays.
Interstitial deletion: The middle portion of chromosomal arms deletion. This deletion type is more severe as the arms are the gene-rich regions. Many genes may deletion in interstitial deletion.
Related article: Chromosome 6p Deletion- A reason for no hunger, no pain and no sleep.
Cause:
Besides some of the extrinsic factors, the event of chromosomal deletion occurs randomly, during the cell division and recombination.
The inheritance pattern of deletion syndrome is unknown as it is a random process. Note that most of the deletions are non-inherited congenital conditions.
If parents don’t have any deletions their child may have! The chances and reasons for that are unclear and unknown.
In addition to this, none of the extrinsic factors are yet proven to be involved in chromosomal deletions.
Top 6 deletion syndrome:
Now let us check out some of the common chromosomal syndromes.
- 22q11.2 deletion syndrome
- 22q deletion syndrome
- 5p deletion syndrome
- 3p deletion syndrome
- 1p36 deletion syndrome
- 4p deletion syndrome
22q11.2 deletion syndrome:
The 22q11.2 deletion occurs due to the removal or deletion of the middle portion of the chromosome 22 at the q arm. It is also known as conotruncal anomaly face syndrome. It is known as DiGeorge syndrome too.
The present chromosomal anomaly is non-inherited and occurs randomly during the cell division in the fetus therefore it’s congenital. However, it is considered as autosomal dominant in some cases.
One of the chromosomes from the pair of 22 got the deletion randomly and cause several problems in the fetus.
Notably, in comparison with other deletion syndromes, the 22q11.2 deletion is huge in which around 30 to 40 different genes got deletion from the chromosome. Based on the amount of deletion the number of genes got deleted may vary. It occurs 1in 4,000 newborns worldwide.
The sign and symptoms of the condition are associated with the heart and immune system, broadly.
In the case of the family history of 22q11.2 deletion or any chromosomal deletion, the doctor suggests prenatal genetic testing for the analysis of chromosomes. Prenatal karyotyping is advisable in these cases.
5p deletion syndrome:
The 5p deletion is known as the Cir-du-chat syndrome and denoted as -5p, cytologically. In the present condition, some portion from one of the chromosome 5 on the p arm got deleted.
Loss of multiple genes associated with intellectual disability and mental development results in severe abnormalities associated with intellectuality.
Much like the other deletion syndrome, the 5p del is also a type of non-inherited condition, occurs randomly.
1 in 20,000 to 50,000 newborns suffer from the cri-du chat have intellectual disabilities and microcephaly in common. The cry of the baby sounds like a cat hence the name is given.
Notably facial and other developmental disabilities are also seen.
4p deletion syndrome:
The 4p deletion syndrome is also referred to as Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome. Hirschhorn and Wolf describe the condition of 4p deletion in 1961 and 1965, respectively.
The present deletion syndrome is very rare and occurs in 1 in 50,000 newborns worldwide. Again much like the other condition, the 4p del is further a non-inherited condition.
However, the families having history deletion syndrome may have a chance for 4p deletion.
The present condition affects different bodily systems and responsible for abnormal facial features, delayed growth, intellectual and mental problems and many others. Note that the severity of the abnormalities is proportional to how to portion of chromosome 4 is deleted.
3p deletion syndrome:
The 3p deletion syndrome is the rarest among the rare chromosomal anomalies. Only a few cases worldwide reported. In the present condition, some portion of the p arm of one of the chromosome number 3 got deleted.
The event occurs randomly like the other ones and the severity of the condition depends on the amount of deletion on p arm. Approximately 5 to 70 genes may be deleted in different cases which comprise around 150kb portion.
Abnormal motor skills, delayed development and intellectual disabilities are commonly observed in patients. Other abnormalities may appear subtle.
1p36 deletion syndrome:
1p36 deletion is a non-inherited chromosomal anomaly that occurs by the deletion of the p arm of chromosome 1. Again, the present condition is rare occurs o1in 5,000 to 10,000 newborns randomly.
A patient has heart, kidney, genitalia and gastrointestinal problems. Also, hypotonia and swallowing difficulties are seen.
Some common symptoms: deep-set eye, midface hypoplasia, pointed chin, and dysphagia.
Detection methods of chromosome deletion syndrome:
The deletion syndromes are the larger chunks of chromosome deleted. The chunks are more than 100kb in size. Thus we can’t PCR it!
Using the conventional cytogenetic technique known as karyotyping is enough to detect larger deletions.
For karyotyping usually, Blood, bone marrow, amniotic fluid or chorionic villi sample is taken and cultured to get metaphase.
The metaphase chromosomes are stained and banded using the Giemsa and GTG, respectively. Based on the differential banding pattern on chromosomes a computer software or an expert evaluate the results.
In case, the results sometimes cross verified using the FISH as well. Read this article to learn the technique: What is karyotyping?-definition, process, steps, advantages and disadvantages.
Or
We can visit this site to marker the skills of karyotyping, Giemsa staining, GTG banding and preparing karyotypes. Visit karyotypinghub.com.
Conclusion:
Some deletion syndromes are very common while some are very rare! Most of the deletion syndromes are non-inherited and occur randomly during the cell division.
Although it is congenital and occurs by birth only. Conventional cytogenetic techniques are more than enough to screen the present condition.