“Discover the role of an RNA primer and a DNA primer in two different DNA synthesis processes. Learn about each type of primer including their significance and applications, in this article.”
The terminology ‘Primer’ is well-known among life science and molecular biology students. It holds significant importance in kickstarting the DNA synthesis process not only in a cell but also in a lab.
The two types of primers that we know are RNA primers and DNA primers. Each has its importance, as DNA primers are popularly used in PCR while a cell uses RNA primers for DNA replications.
Interestingly, replication and PCR both processes synthesize DNA. A cell replicates to copy the DNA while PCR amplifies and copies a target DNA. In this article, we will look at the importance of RNA primers and DNA primers preliminarily.
We will also discuss some common differences between RNA and DNA primers.
Related article: What is DNA Replication?- Steps, Enzymes and Process.
Key Topics:
What is an RNA Primer?
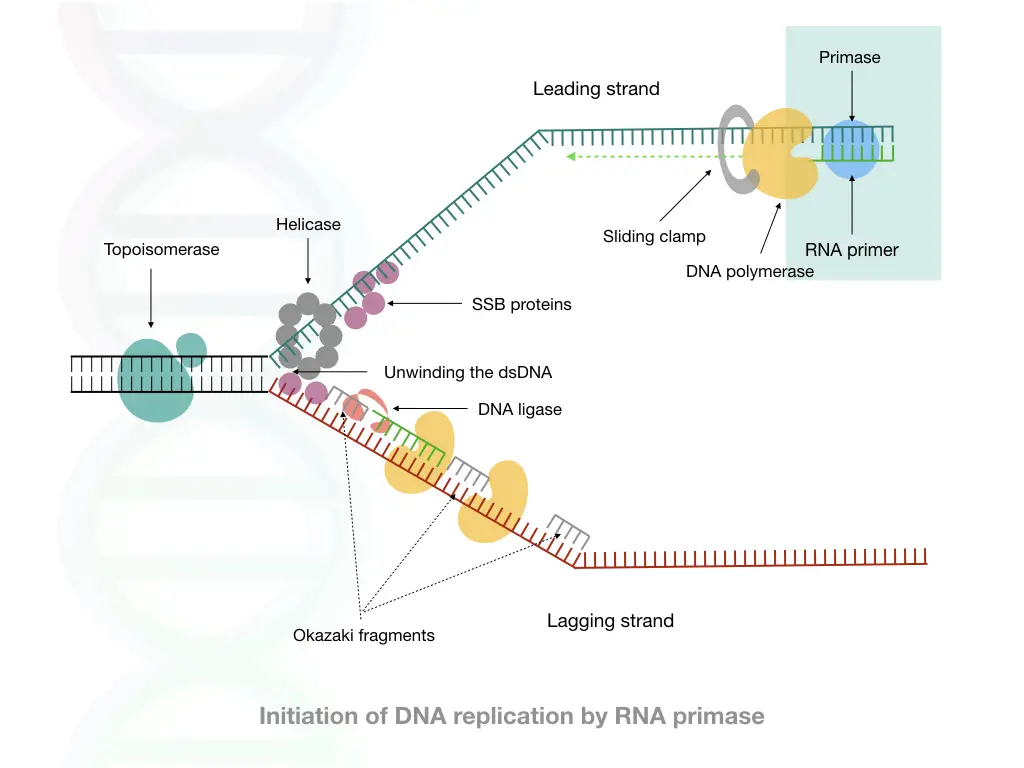
A cell uses an RNA primer to conduct replication. It is a process to synthesize new DNA through enzyme-governed catalytic reactions. RNA primers play a crucial role during the initiation of replication.
An RNA primer is a short and single-stranded RNA sequence. Enzyme Primase synthesizes short stretches of RNA primers for replication. It is a class of enzymes belonging to RNA polymerase enzymes.
Now the question is, why do we need RNA polymerase during replication?
DNA polymerase governs the whole process of DNA synthesis during replication. However, it has one unique limitation. DNA polymerase can not perform de novo synthesis, meaning, it can’t replicate a single-stranded DNA directly unlike RNA polymerase.
It needs a free 3’-OH end to kickstart the process. So the RNA primer provides a single-stranded complementary strand with a free 3’-OH end for DNA polymerase. Once the RNA primer finds the complementary location, DNA polymerase starts strand elongation by adding nucleotides.
After successful completion of replication, another polymerase with an exonuclease activity finds the RNA primer, removes it and fills the gap with complementary nucleotides. Detailed replication investigation suggests that two types of RNA primers have been used.
A 10 to 18 nucleotides long primer for the leading strand synthesis and an 8 to 10 nucleotide-long RNA primer for the synthesis of Okazaki fragments at the lagging strand. Note that both primers are synthesized by the same polymerase enzyme.
Another reason is that no DNA polymerase can synthesize DNA primer (as they do not have a free 3’ OH end) and thus only an RNA primer exists for a cell for replication initiation.
Properties of RNA primers:
- Short 8 to 18 nucleotides long.
- Single-stranded.
- Complementary to the replication start site.
- Short lifespan.
- Susceptible to degradation.
Importantly, an RNA primer is highly prone to degradation by nuclease activity and thus has a very short lifespan. It is also very fragile and can be removed or degraded by heat or chemical treatment.
Due to these reasons, and the lack of exonuclease activity of Taq DNA polymerase, PCR needs DNA primers and not RNA primers, though it is also a process of DNA synthesis.
What is a DNA primer?
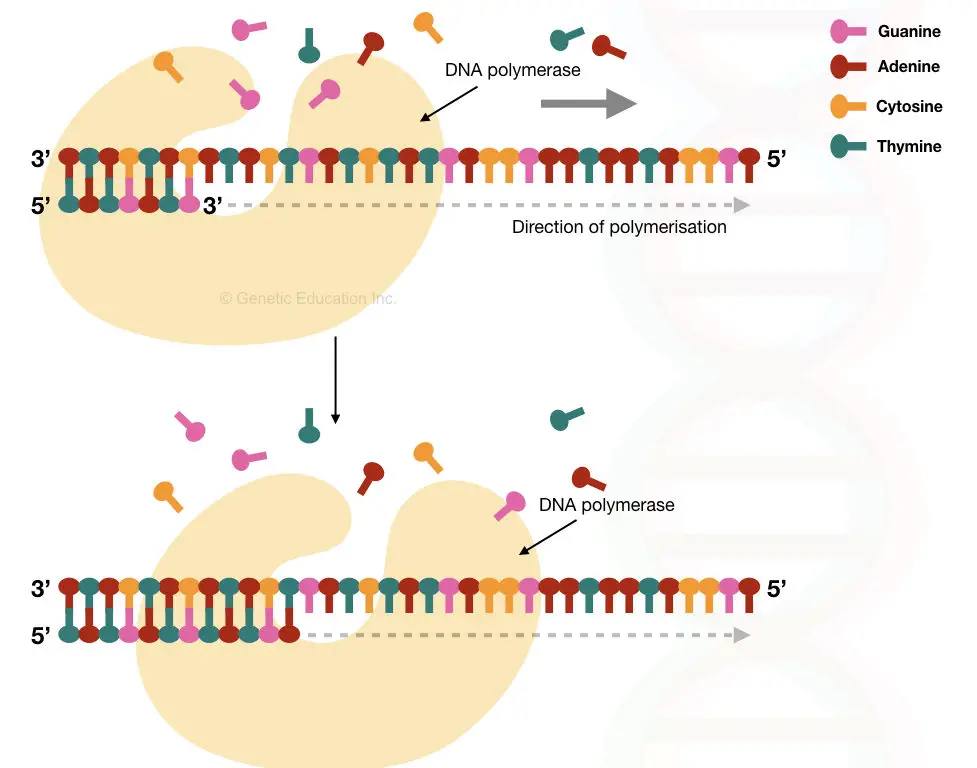
DNA primers are widely used in in vitro applications like– PCR or DNA sequencing. They can be synthesized artificially and have a long shelf life compared to RNA primers.
A set of DNA primers (forward and reverse primers) has been used for the amplification of sense and complementary antisense strands during PCR. Taq DNA polymerase governs the synthesis process as it can efficiently work at a higher temperature.
Taq Pol also needs a free 3’ OH end which is provided by the DNA primers for initiating temperature-dependent DNA amplification. The properties of DNA primers are listed here.
Properties of DNA primers:
- Single-stranded polynucleotide chain.
- Short– 18 to 22 nucleotides long.
- Contain 45% GC content.
- Should have an annealing capacity between temperatures 52 to 66ºC.
- Lack of self-complementation.
We have written an amazing article on this topic. You can read it here: PCR primer design guidelines.
Differences Between RNA Primer vs DNA Primers:
We have prepared an amazing comparative table that shows the differences between RNA primers and DNA primers. Take a look here.
| RNA primers | DNA primers |
| Used during a cell’s DNA replication. | Used during PCR and DNA sequencing. |
| 8 to 18 nucleotides long and single-stranded nucleotide strands. | 18 to 22 nucleotides long and single-stranded nucleotide strand. |
| Unstable at a higher temperature. | Very stable at a higher temperature. |
| Highly prone to degradation by nuclease. | Less prone to degradation by nuclease. |
| Removed from the final strand by exonuclease polymerase activity. | Remains with the newly synthesized strand. |
| Synthesized by primase. | Synthesized artificially. |
| It consists of Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Uracil nucleotides. | It consists of Adenine, Cytosine, Guanine and Thymine nucleotides. |
| It is a ribonucleotide chain. | It is a deoxyribonucleotide chain. |
Similarities between DNA Primers and RNA Primers:
- Both DNA and RNA primers are long polynucleotide chains.
- Both are single-stranded and short sequences complementary to the target location.
- Both are used for the synthesis of DNA or copying DNA.
- Both DNA primers and RNA primers are used as a starting point for DNA synthesis.
- Both provide a free 3’ OH end for DNA polymerase.
- Both also provide a substrate for DNA polymerase enzymes.
Read Further: Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Wrapping up:
This is a short introduction to RNA primers and DNA primers and I hope you like it. This module will truly help in learning the replication process as well as the basics of polymerase chain reaction.
If you would like to learn more about the primer design process, Replication and PCR, the links are given in this article. Read those articles, and share this article in our circle.
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter for the latest blogs, articles and updates, and never miss the latest product or an exclusive offer.



nicely explained, thank you