“The Ct value is a value used to quantify the absolute amount of nucleic acid present in a sample. It is the number of cycles from where fluorescence increases significantly.”
A little bit confusing, right! Don’t worry the present article helps you to understand this sentence thoroughly. But before that, we need to understand some basics about PCR, qPCR, RT-PCR and all those things!
Genetic studies highly rely on two techniques viz PCR and DNA sequencing in which the PCR is more important. Kary Mullis had originally developed the technique Polymerase chain reaction which has the power to amplify a gene.
To conduct a gene study, scientists need a huge amount of template or target DNA or gene, PCR amplification facilitates copies of DNA. Although in modern times, only to amplify a gene isn’t sufficient.
Gene quantification gives researchers an idea regarding how many templates nucleic acid is present in a sample and that is the base to develop a quantitative method or qPCR that measures the template DNA or gene.
Among many variations of conventional PCR, the best modification is qPCR. The entire technique relies on fluorescence chemistry. In addition to this, the RT- PCR or reverse transcriptase PCR even quantifies the mRNA present in a sample, again the chemistry of detection is the same as qPCR with minor modifications.
PCR and associated modified techniques are used in many fields from research to diagnostic and from microbiology to environmental science. The qPCR and RT-PCR collectively used in the quantification of mRNA, gene expression studies, microbial studies, measuring infection and identification of template nucleic acid.
Conventional PCR relies on a simple principle of a temperature gradient or rapid change in temperature to facilitate amplification, the concept of qPCR is however different! If you want to learn more about what are the differences between PCR and qPCR, you can read this article: Differences between PCR vs qPCR.
There are many technical things one needs to understand in order to learn the concept of quantitative PCR or RT- PCR. Here in the present article, I will try to explain to you the concept of qPCR and related terms used in it. I will also concentrate to explain the concept of Ct value, what a Ct value is, its importance and factor that affects it.
Key Topics:
What is a Ct value in qPCR or real-time PCR?
Other names of Ct value are; threshold reaction (Ct), reaction threshold (Ct), Crosspoint (Cp), quantification cycles (Cq), threshold point (Pt) or take-off point (TOP).
Definition:
“The Ct value is often known as the ‘threshold cycle’ or ‘cycle threshold’, is the measurable number of PCR cycles from where the fluorescence signal crosses the base (threshold) line.
Let’s first understand a bit about the fluorescence chemistry of qPCR.
The whole quantification technique depends on the principle of fluorescence emission in which when the template nucleic acid either DNA or RNA amplifies in the reaction it emits the fluorescence, a detector detects it. In the end, the machine collects all the signals and measures all the templates.
This is a brief explanation.
There are two methods for that, Hydrolysis probe-based detection method and the intercalating dye-based method. The dye-based technique isn’t so commonly practiced but used for research purposes. In this method, a dye interacts with the double-stranded DNA when amplification occurs and gives a fluorescence signal.
The hydrolysis probe-based method is one of the most common, trusted and widely used technique in qPCR. Here probes specific to templates, hybridize and give fluorescence signals.
Briefly, in the probe-based technique, probes are designed having a reporter dye and the fluorescence dye. When a set of PCR primers amplifies the template, the probe hydrolyzed, fluorescence dye released and emit fluorescence. As we said, the machine collects signals as a positive amplification of the template.
Although many other things happen in the reaction (that only computer software knows!). Notably, dye on a probe has some fluorescence left, a machine first collects all the signals at the initial stage, measure it and create a baseline.
“Gel eletrphoresis isn’t employed in quntification of nucleic acid and hence can’t be used in qPCR, results of qPCR are obtain as a graph. Each sample creates an unique peak.
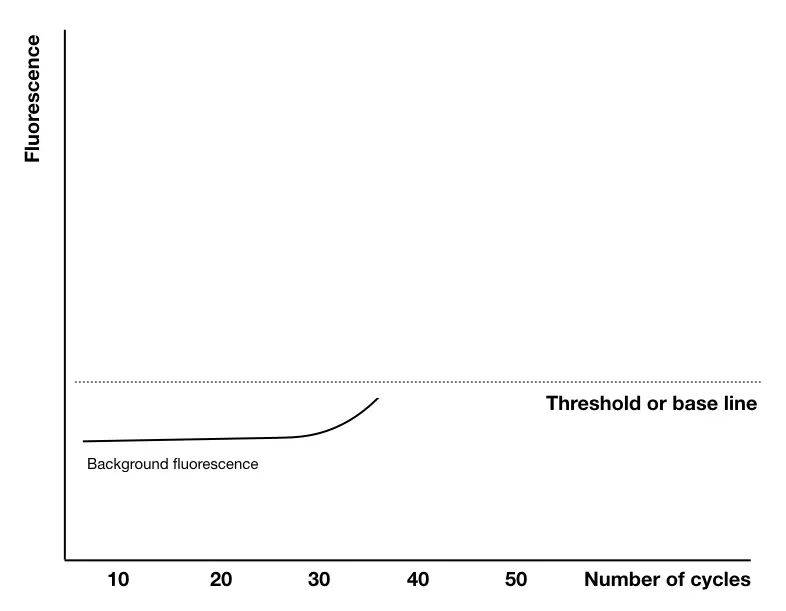
Any signal obtained below this line, the detector detects it as a background noise or background signals- an unamplified one!- keep in mind this point.
Learn more on RT-PCR: Real-time PCR: Principle, Procedure, Advantages, Limitations and Applications.
Now when the reaction starts entering into the exponential phase, templates start amplifying. Reaction utilizes reagents, Taq DNA polymerase starts amplifying the template, probes are hydrolyzed and fluorescence emitted.
From this point, our Ct value came into the picture. The machine starts collecting the data of Ct value means the threshold cycle data.
A base-line is a no template zone, as we said, none templates amplified but as the cycles progress, template amplification initiates. Substantial positive amplification signals are obtained above the threshold line.
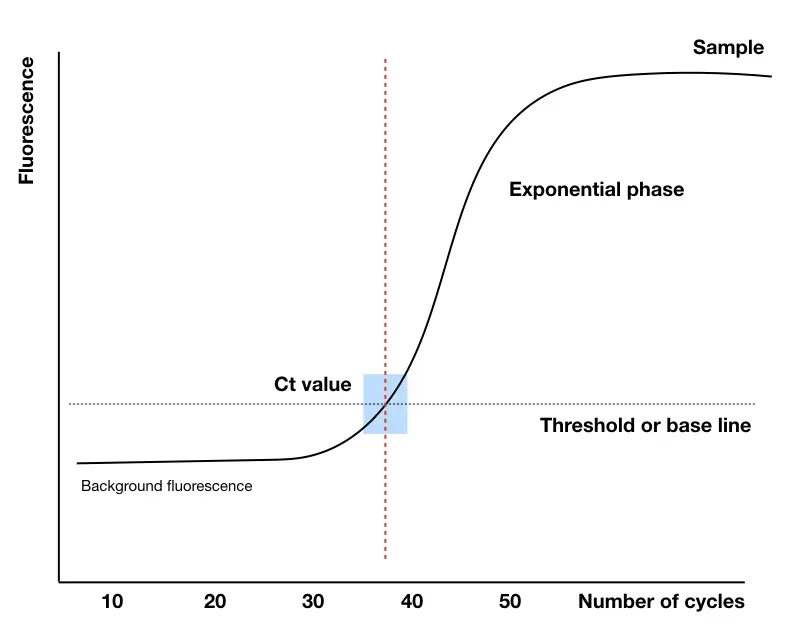
Ct value:
The number of cycles from which the reaction curve raises above the threshold line or intersects with it, is our Ct value. Simply, in a positive reaction amplification, a number of cycles required to cross the threshold line or exceeds the threshold in our Ct value from which machines start quantifying the nucleic acid.
If you are still confused, this sentence will make it more clear,
The Ct value or threshold value is inversely proportional to the amount of nucleic acid present in a sample, which means If there are abundant templates, fewer cycles it takes to amplify and quantify henceforth results in a lower Ct value.
If the sample contains fewer templates, the Ct value goes high at it takes more cycles to progress the reaction. The average Ct value is near or around 29 to 30 cycles indicating a sufficient amount of template nucleic acid present in the sample.
Range of Ct value:
The Ct value varies from sample to sample the amount of nucleic acid present in a sample varies. Although it is categorized broadly into three categories.
- Samples with an abundance of nucleic acids: Ct <29.
- Samples with fewer nucleic acids: Ct >38 or 38 to 40.
- Positive reaction with a moderate level of nucleic acid: Ct between 30 to 37.
Note that when a Ct ranges above 38 or between 38 to 40 or more, it indicates contamination, infection or less nucleic acid present in a sample.
Factors affecting Ct values:
The qPCR technique is a sensitive and sophisticated molecular genetic technique having 80 to 90% accuracy. Nonetheless, a few factors affect the specificity and sensitivity of the reaction. Those are;
Master mixes, the specificity of reagents, Reaction efficiency, Passive reference dye, quality and quantity of template, the activity of Taq or reverse Taq polymerase, sample handling errors and biological events.
Quality and quantity of templates:
When the quality of template nucleic acid isn’t so good or not present in a sufficient amount, the Ct value changes or samples can’t be quantified correctly.
Use an adequate amount of starting sample, as well as pure nucleic acid.
Master mixes:
Master mix is a reaction cocktail to perform the quantitative amplification containing chemicals and reagents needed in the reaction. The pH and salt concentration of the solution of mastermix can influence fluorescence emission and consequently the Ct value. Henceforth should be checked periodically.
When using an in-house (lab-made) master mix, check the pH and salt concentration of the cocktail first before use. Further, check manually for visible sal precipitations.
The activity of Taq and reverse transcriptase:
The important factor in PCR reaction is the polymerase which catalyzes the synthesis of DNA. The activity of Taq or reverse transcriptase may degrade in reaction or over a period of time.
Kindly check the status of polymerase or its activity before use. As templates aren’t amplified correctly it gives a false Ct value.
Sample handing error:
Yet another common error in qPCR is the sample preparation or sample handling error. Those are improper DNA or RNA isolation. RNA is prone to RNase degradation which needs to isolated in strict aseptic conditions. Contaminant during isolation hinders the amplification and quantification during qPCR, alters the Ct value, resultantly.
Passive reference dye:
As we explained above, with the fluorescence dye (FAM) another passive reference dye ROX is also there on probes whose ratio decides the reaction value. When the ROX activity got reduced or present in a lower amount, the reaction values chances, typically increase which alters the Ct value as well.
Reaction efficiency:
Now, this is something very interesting. The reaction efficiency of the qPCR shouldn’t be 100% which indicating the doubling of target nucleic acid. Around 87 to 90% efficiency is achieved by healthy practice.
Quality of master mix, the annealing temperature of primers, activity of polymerase and the quality of templates are some of the factors that decide the reaction efficiency.
Biological events:
When the gene expression changes or goes up/down due to treatment response, drug dose or any other factor, the Ct value changes. To study the gene expression correctly, an extra reference gene or housekeeping genes are amplified along with the sample.
It provides a reference value for normal gene expression.
Ct value and gene expression:
An important use of the qPCR technique is to study gene expression. But as we said, we can’t quantify the amount of mRNA without any reference values because it eventually altering the Ct value and without the reference, we can’t predict how it happened, is it due to technical error (factors mentioned above) or really change in gene expression.
Researchers use a special set of genes as a reference whose gene expression remains normal almost in all cells and tissues, those are “housekeeping genes”.
Housekeeping genes are a basal cell maintenance set of genes that performs normal and common functions for all cells.
Therefore their expression remains constant in all cells, for example, GAPDH, alpha-tubulin, ubiquitin and actin. With a target gene, a set of housekeeping genes are also amplified in the reason.
It gives an idea about the change in the Ct value and gene expression. The method is known as the Livak method or Calling Delta-Delta Cq.
The acceptable range of ct value for qPCR:
The Ct value below 35 or between 27 to 30 or nearly 32 is Ok or acceptable if using the SYBR green method.
Note that the Ct value changes from sample to sample but still it must be lesser than the no template Ct value or lower than the negative control. However, there are many factors that decide the Ct or alter the Ct values of the assay but that should be encountered practically only.
There are many statistical and mathematic equations are involved in the process of calculating the number of templates, the accuracy and other factors that are involved in the qPCR that we can’t do manually.
Conclusion:
Ct value is though not valued more but is an important term for understanding the qPCR. Quantification is only done based on the Ct value, however other factors are crucial as well.
A number of the cycles it takes to start amplification or emit fluorescence- the Ct value is used to measure the level of infection in various biological samples. The quantitative RT-PCR method is used in the coronavirus SARS-COV2 infection measurement which is based on the Ct value as well.
Sources:
What is a Cq value? – Bitesizebio


