“Choosing the right DNA extraction method is crucial for getting higher yields and better purity. This guide offers how you can choose the best DNA extraction method for your experiment and what factors to consider while choosing the one for you.”
Your journey with genetic studies begins with DNA. You first have to face and learn DNA extraction. It’s an empirical scheme needed during any genetic experiment dealing with DNA. Hence, every student should have to learn it, from the very beginning.
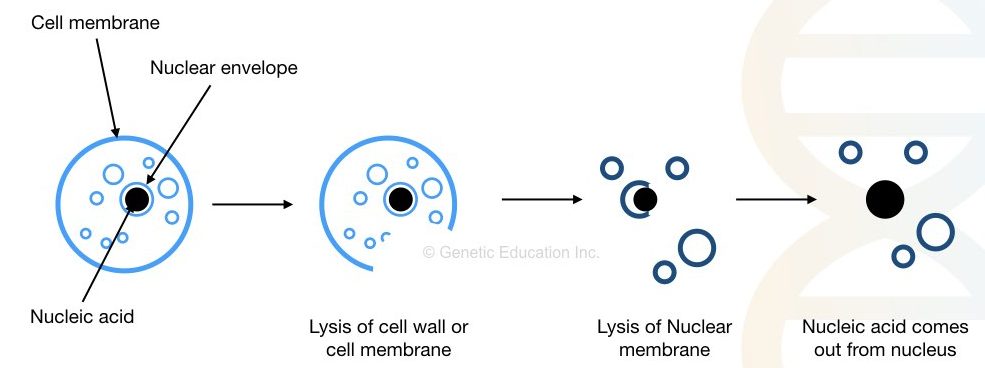
DNA extraction, often known as DNA isolation, is a process to separate or isolate DNA from any biological material. It can be isolated from cells having DNA. Common materials for DNA extraction are body tissue, bacterial culture, plasmid, plant parts, environmental samples or any other samples having biological material.
It’s a sensitive technique that, although, doesn’t need any specialized instrumentation setup but only high-end expertise. Meaning, the quality of DNA you will obtain, highly depends on how you perform it. In addition, it also depends on which protocol or scheme you choose to isolate DNA.
Therefore choosing the right DNA extraction scheme is a critical decision in any genetic experiment. At Genetic Education Inc. we usually re-discover the knowledge, but our immense expertise and years of experience in genetic research can lead us to share technical knowledge with students.
In this article, I will explain a step-by-step process using which you can choose the best DNA extraction protocol for your experiment. I will also enlist and demonstrate factors that affect the selection process. The present module will strengthen your practical skills and help you better choose and perform DNA extraction.
Stay tuned.
Download our ebook: DNA Extraction to PCR.
Key Topics:
Factors affecting the selection of DNA extraction method:
Research question:
The research question is, “what you would do in your research.” According to your research question, design your study and choose the suitable DNA extraction technique. Also, determine the need for your question too.
Depending on the quality and yield required for the experiment, choose the DNA isolation method. For instance- highly pure and high-yield DNA is required for DNA sequencing but not for restriction digestion.
So based on your downstream starting material, you need to choose and list the possible DNA extraction methods that work. However, the very next factor is to consider the sample type.
| No. | Types of the research question |
| 1 | Prevalence of breast cancer in Southeast Asia. |
| 2 | How have antibiotic-resistant influenza strains evolved? |
| 3 | Determination of lead-spot disease-causing fungus in plants |
Sample type:
The success of any genetic experiment highly relies on the DNA extraction scheme chosen based on the sample type. No scheme is universally accepted for all sample types. Common samples for DNA extraction are blood, saliva, body fluid, solid tissue, plant parts, bacterial culture, plasmids, environmental samples, etc.
For instance, Proteinase K-based CTAB DNA extraction method is universally adapted for plant DNA extraction, while the PCI method is widely used to isolate DNA from blood samples. Sample type has a direct impact on the purity and yield obtained.
Why sample types are important because the cellular structure and composition vary among organisms. This factor should also be taken into consideration as well.
| No. | Types of the research question | Sample type |
| 1 | Prevalence of breast cancer in Southeast Asia. | Human blood sample |
| 2 | How have antibiotic-resistant influenza strains evolved? | Nasal swab. |
| 3 | Determination of lead-spot disease-causing fungus in plants | Plant leaves. |
Cell structure and composition:
Choosing only the sample type isn’t sometimes enough to impose any DNA extraction scheme. Which organism you are doing research on and what cellular composition they possess also impact the success rate.
For instance, it’s quite obvious that isolating DNA from organisms having rigid cell walls is difficult compared to organisms having a smooth cell membrane. Thus, additional chemical preparation and physical lysis protocols are required for samples like plant material.
At the same time, no fancy setup or chemical preparation is required for smooth-celled bacteria, however, to avoid bias, plasmid DNA must be removed from bacterial genomic DNA isolation. Learn about the organism and its cellular composition before selecting the DNA extraction method.
| No. | Types of the research question | Sample type | Target organism | Cell structure |
| 1 | Prevalence of breast cancer in Southeast Asia. | Human blood sample | Human | Smooth cell membrane |
| 2 | How have antibiotic-resistant influenza strains evolved? | Nasal swab. | Influenza virus | Smooth cell coating (No cell wall) |
| 3 | Determination of lead-spot disease-causing fungus in plants | Plant leaves. | Fungus | Cell wall (rigid or smooth) |
Compare DNA extraction methods:
A Plethora of research is going on every day. Newer methods and revolutionary processes, kits, and instruments are ruling the market. Thus, it is important to choose an appropriate experimental scheme for DNA extraction.
For any sample type or experiment, you have at least three options now– manual/chemical-based isolation, ready-to-use spin-column kit, magnetic-bead-based isolation, or automated extraction. Compare every DNA extraction method considering the cost, purity, yield, and ease of experiment, and choose the best one.
| DNA extraction method | Type | Purity and yield |
| Phenol: chloroform: isoamyl alcohol. | Chemical- chemical DNA separation. | Moderate. |
| Proteinase K DNA extraction method. | Enzymatic DNA separation. | Good. |
| CTAB- DNA extraction method | Chemical- chemical DNA separation. | Moderate. |
| Spin-column DNA extraction. | Solid phase DNA separation. | Excellent. |
| Magnetic bead-based DNA extraction. | Solid phase DNA separation. | Excellent. |
| Automated DNA extraction. | Solid phase or chemical DNA separation. | Excellent. |
Cost and time:
Is your DNA extraction method costly? Is the process time-consuming? Ask these questions before selection. The scheme you select should be cost-effective, if not, must save time. For instance, a master’s student looks for a cost-effective option while some outbreak infection testing laboratory looks for a time-saving kit.
Usually, manual methods are super cheap but at the same time are time-consuming while ready-to-use kits are super fast but are costly. Nonetheless, kits provide excellent yield and purity for limited sample types.
Quality and quantity required:
Now here is an important question. What yield and purity your experiment seeks? For instance, usually high yield and moderate quality DNA can be sufficient for hybridization and restriction digestion.
But utmost purity and yield are required for experiments like microarray or DNA sequencing. However, keep in mind that your selected method should not compromise the quality of DNA obtained and in addition, it should have scope for optimization as well.
Automation and high throughput:
If you require high-throughput DNA processing, automation must be on your checklist. Automated DNA extraction methods are fast, error and contamination-free, and also give you the flexibility to work on other modules and increase throughput.
Nonetheless, automation is super costly. But it can be the best-suited scheme for processing a large number of samples for high-throughput DNA. If you would like to strengthen your knowledge on this topic. I have written an amazing comparative article on this topic, you can read it here: Manual vs Spin-column vs Automated DNA extraction.
Health hazards and safety:
Safety should be the priority. Evaluate if the method can use any chemicals that can risk your safety. For example, in the PCI method, the use of phenol and chloroform may compromise your safety; processing viral infection samples using manual methods may risk your safety.
Accordingly, choose the DNA extraction method. Use enzymatic isolation for common sample types, kits for some special samples, and automated extraction for infectious samples.
Sensitivity, reliability, and reproducibility:
The chosen method should be sensitive enough for excellent downstream performance, reliable to use, and reproducible in everyday experiments. These three parameters should not be dissolved by any means.
Choose the method which is sensitive enough, reliable, and reproducible.
Labor-extensive:
Manual methods required extensive solution preparations so are laborious. The lab personnel has to do extra pre-preparation before isolation. Keep in note that the selection should also be based on labor extensiveness as well. The method should require minimal pre-preparation and less human effort.
It eventually saves time, and cost and improves efficacy.
A step-by-step guide to choosing the best DNA extraction method:
- Step 1: define your research question and determine what you have to do in your experiment.
- Step 2: Determine what type of sample you are going to process. Accordingly, search for the isolation scheme and select methods.
- Step 3: Determine the organism from which you have to isolate the DNA.
- Step 4: Study the cellular structure and composition of the target organisms.
- Step 5: Review the literature regarding the sample you select and the organism you target for the study.
- Step 6: Do a comparative assessment of available DNA extraction methods based on the quality and quantity, manpower, cost, and automation involved in the experiment.
- Step 7: Check if the method is safe to use or not.
- Step 8: Check required utilities, instruments, and chemicals are present in your lab or not.
- Step 9: Ask the expert.
- Step 10: Check the method and validate it.
Related articles:
- DNA Extraction From Dried Blood Spot Samples: Protocol + Comprehensive Guide.
- Is Manual DNA Extraction Still Relevant in 2023?
- Advantages and Limitations of Spin Column DNA Extraction Technique.
Wrapping up:
In conclusion, choosing the right DNA extraction method is a crucial decision in any genetic experiment. The success of downstream applications, in which a huge amount of investment is involved, depends on the choice. Thus, it’s indeed an important decision.
Any DNA extraction method should be faster, easy to perform, safe, sensitive, reproducible, and reliable, and at the same time should have high purity and yield. Nonetheless, closely examine your experiment before making a decision.
I hope you like this article and this will help you to make the decision. Please subscribe to us and allow notifications.


