“Guanidine thiocyanate is a standard reagent of RNA lysis buffer and is effective against inactivating proteins. It is also available commercially and we can prepare a working solution in our lab.”
RNA extraction is the process of separating RNA (nucleic acid) from a cell. It, however, isn’t as straightforward as the DNA extraction method. A good lysis buffer recipe and additional optimization are two factors to achieve success in this scenario.
The composition of the RNA cell lysis buffer may vary from lab to lab and manufacturer to manufacturer, although the basic foundation will always remain the same. For example, the use of Guanidine thiocyanate, a common RNA extraction ingredient.
People usually fail to achieve quality extract and yield because they don’t know how to use Guanidine thiocyanate in the lysis buffer, in which combination and with which chemicals. They even can’t get the results because they don’t know the basic function of Guanidine thiocyanate.
Our daily readers know that I’m a geneticist and have huge experience in nucleic acid extraction, PCR and other genetic technologies. I tried and tested many combinations of Guanidine thiocyanate, and thus, I can say, I have a decent working hand on RNA extraction.
In this article, I will explain to you the basic function of Guanidine thiocyanate and why it is used in RNA extraction. I will also provide some protocol in which you can use it and a recipe to prepare the solution of Guanidine thiocyanate as well as the lysis buffer recipe too. The present intervention would probably support your RNA extraction endeavor and surely helps to get a good extract.
Stay tuned.
Key Topics:
What is Guanidine thiocyanate?
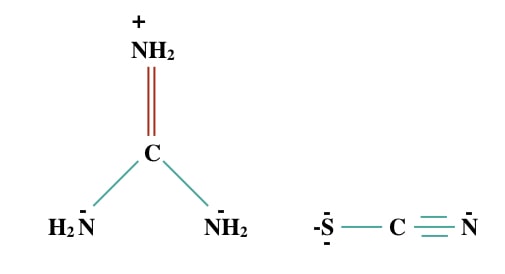
Guanidine thiocyanate is a chaotropic salt often known as guanidine isothiocyanate as well. So first let me clarify that do not confuse your mind, both are synonyms and both are the same. It is abbreviated as GTC or GITS. The chemical formula of GITS is C2H6N4S having a 118.16 g/mol molecular mass.
It is a white powder crystal that is soluble in water at 20°C and becomes colorless. It is also important to know, before using, that Guanidine thiocyanate is a hazardous chemical. It can harm lab personnel upon inhalation or contact with the skin so care must be taken while handling.
General information, properties and other information regarding the GITS are given here.
| Name | Guanidine thiocyanate |
| Synonyms | Guanidine isothiocyanate, Guanidine rhodanide. |
| Chemical formula | C2H6N4S |
| Molar mass | 118.16 g/mol |
| Storage temperature | 20 to 25°C |
| Melting point | 120- 122°C |
| Appearance | While crystal |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Solubility | Water-soluble at 20°C |
| Solution | Colorless |
| pH | 4.8 to 6.0 |
| Sensitivity | Light sensitive |
| Specific gravity | 1.152 |
Structure of Guanidine thiocyanate:
Functions of Guanidine thiocyanate:
The GITC is a chaotropic salt and a strong protein denaturing agent. What it does do is that it degrades hydrogen bonds between water thereby weakening the hydrophobic property and destabilizing protein. Put simply, it digests the protein part.
Some literature also suggests that it can also destabilize the lipid part as we. Henceforth, it is an effective cell lysis agent that has the powerful property to denature cellular protein and cell wall lipids.
This property of GITC, in RNA extraction, also does another favor. Guanidine thiocyanate deactivates the nucleases- DNase and RNase present in the sample. RNase is a prevailing entity and hence fails our RNA extraction intervention. However, DNase is not such a big problem in DNA extraction.
Most often the proteins denatured by Guanidine thiocyanate are those that bind strongly with the nucleic acids but hydrolysis other proteins as well.
So using the GITC in RNA cell lysis buffer effectively inactivates RNase and protects our precious RNA and succeeds our nucleic acid extraction, although the process is pH-dependent.
It is also important to understand that we are using the acid Guanidine thiocyanate which separates RNA from other cell components when used along with the phenol and chloroform. And thus it is a key ingredient of commercially available RNA extraction solutions like Tri-reagent, Trizol, etc.
I have explained the Trizol protocol for RNA extraction, you can read it here: Effectual Trizol protocol for RNA extraction.
It is also used for DNA extraction as well with the same function.
Preparation of Guanidine thiocyanate solution:
- 4M Guanidine thiocyanate
- 25mM sodium acetate
- 1mM EDTA
Dissolve Guanidine thiocyanate at 60 to 65°C, allow to cool and add 25mM sodium acetate and 1mM EDTA at set pH 6.0 to 6.4.
Thermo fisher scientific proposed another recipe to prepare Guanidine thiocyanate for cell lysis which is as stated.
- 4mM Guanidine thiocyanate
- 55mM Tris
- 25mM EDTA
- Triton X100
- Bromophenol blue
Dissolve 472.75gm GITC into 400 ml 0.1M Tris at pH 7.6.
Add 350ml 0.1M Tris to make the final volume 750ml.
Add 0.5M and 50ml EDTA + 30ml Triton X100.
Add DEPC- treated water to make a final volume of 1000ml or
0.05% w/v BPB.
I have written an article on DEPC water, you can read it here: 11 ways to use DEPC-treated water.
Current research:
Chomczynski and Sacchi, 1987 first formulated the use of Guanidine thiocyanate in phenol-chloroform isoamyl alcohol protocol and described the thorough role of Guanidine thiocyanate in RNA extraction.
Scallan et al., 2020, tested the same recipe of Guanidine thiocyanate containing buffer to extract the viral RNA of SARS-CoV 2 and manifested that the 4M GITC is sufficient enough to get a decent amount of viral nucleic acid.
Guanidine thiocyanate can be used in combination with the PCI method of RNA extraction and is an excellent composition for RNA extraction so far. I have described the protocol in the previous article.
The 4M GITC formulation is also used in the silica-based and magnetic-bead-based techniques as a lysis buffer. Automated RNA extraction assembly uses a secrete isolation buffer but certainly contains Guanidine thiocyanate.
RNA Extraction Protocol using Guanidine Thiocyanate
Protocol 1:
The combination of Guanidine thiocyanate with PCI (viz phenol: chloroform and isoamyl alcohol) is unmatched. Thousands of literature online reviewed this protocol with a minor modification.
I have already discussed this protocol in my previous article and the link is given in the above section, somewhere.
- Perform all the pre-preparation, prepare reagents and do all the necessary sterility practices before initiating the experiment.
- Take 50 to 100 mg tissue or cell culture, add 1 ml of guanidine and phenol (commercially available) solution and incubate at room temperature for 5 to 10 minutes.
- Add 0.2ml chloroform and mix vigorously and incubate for 2 at room temperature.
- Centrifuge the sample at 5000 rpm for 15 minutes, collect the supernatant and precipitate using 1 ml isopropanol.
- Wash the sample following the washing procedure and resuspend into the nuclease-free water.
Protocol 2:
SDS-based buffer solutions are used to separate nucleic acid from bacteria and plasmids to improve the yield output. The general overview of the protocol is as follows.
- Prepare tissue lysate. Read this article to learn more: Tissue homogenization techniques.
- Add adequate volute of SDS + guanidine thiocyanate.
- Use proteinase K if required.
- Centrifuge the sample, collect the supernatant and precipitate using salt and isopropanol.
- Resuspend pellets in nuclease-free water.
Protocol 3:
Guanidine thiocyanate can also be used with CTAB for plant RNA extraction. Here is the general overview of the protocol.
- Lyse plant tissue or perform tissue homogenization.
- Use liquid nitrogen to fine-grind the plant tissues.
- Add CTAB solution and proteinase K and guanidine isothiocyanate (I already have explained how to use CTAB and Proteinase K in our previous articles).
- Mix well and centrifuge the sample.
- Collect supernatant and precipitate using sodium salt + isopropanol.
- Resuspend into nuclease-free water.
Optimizations:
Use can use DEPC-treated water to dissolve pellets
If precipitates do not appear, incubate the sample with alcohol overnight at -20°C.
Use DNase to remove DNA contamination.
Follow standard purification processes to purify the RNA, use alcohol purification or collect a specific type of RNA using the electrophoresis technique.
Wrapping up:
Current research and present intervention establish Guanidine thiocyanate as an important ingredient for RNA extraction. However, it is also useful in DNA extraction as well, but less advisable as many standard and useful DNA extraction protocols are available.
It is also important to keep in mind that Guanidine thiocyanate has health hazard properties and thus refers to the common lab safety manual first. Importantly, GITC is light-sensitive so keep it away from light.
At last, follow common RNA extraction precautions to avoid problems; take necessary training before performing the extraction. Broadly the steps are as follows.
Resources:
Scallan, M. F., Dempsey, C., MacSharry, J., O’Callaghan, I., O’Connor, P. M., Horgan, C. P., Durack, E., Cotter, P. D., Hudson, S., Moynihan, H. A., & Lucey, B. (2020, April 13). Validation of a Lysis Buffer Containing 4 M Guanidinium Thiocyanate (GITC)/ Triton X-100 for Extraction of SARS-CoV-2 RNA for COVID-19 Testing: Comparison of Formulated Lysis Buffers Containing 4 to 6 M GITC, Roche External Lysis Buffer and Qiagen RTL Ly… | bioRxiv. bioRxiv; www.biorxiv.org. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.04.05.026435v2.
Chomczynski, P., & Sacchi, N. (1987). Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analytical biochemistry, 162(1), 156–159. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.1987.9999.