“Sequence information of DNA linked with associated proteins like histones can be obtained by performing high throughput DNA sequencing, such technique is known as ChIP-Seq.”
Highlights:
- ChIP-seq was developed by Barski and Johnson in 2007.
- The technique originally studies those chromatins associated with the binding proteins to investigate gene silencing and DNA binding sites.
- Prior sequence information isn’t required as the technique reads DNA precipitated with protein, impartially.
Read more: What is DNA footprinting?- Principle, Steps, Process and Applications.
Now, this article is very in-depth. So to understand the present method you should have some prior basic information on DNA protein interaction, sequencing, immunoprecipitation (in general) and other basic epigenetic things.
I am going directly to explain the method ChIP-seq, hoping that you have basic knowledge of the topic.
The ChIP-Seq is powered by chromatin immunoprecipitation assay and DNA sequencing in order to know which DNA sequences are linked to the protein and are epigenetically silent.
Chromatin is a structure made up of nucleosomes arranged bead-on-string-like. The network of protein H2A, H2B, H3, H4 and H5 links to DNA and forms the nucleosomes.
The nucleosome forms chromatin and chromatids. The sister chromatids are linked to the centromere and form a chromosome. The intention to follow this process is to make DNA fit inside a cell.
Read more: DNA packaging in eukaryotes.
A tightly wrapped chromatin assembly is transcriptionally inactive. The histones interact with DNA and make it transcriptionally inactive or silent, is also known as epigenetically inactive chromatins.
The ChIP method is used to detect how much DNA is linked with the proteins during chromatin formation. And using the ChIP-Seq method that DNA is determined and analyzed.
Let’s start with the introduction and how it works.
Key Topics:
What is ChIP-Seq?
To understand the present type of sequencing method, we should have to first understand how the chromatin immunoprecipitation assay works!
Put simply, it’s a precipitation assay in which the protein associated with the chromatins is precipitated and determined using the antigen-antibody interaction mechanism.
The antigens are localized on chromatin and interact with the antibodies we apply to the assay. Results are analyzed using the qPCR or microarray (ChIP-chip). This is the simple explanation of ChIP.
The precipitated protein DNA complex can be studied by real-time PCR or sequencing. It actually detects the modification of histones associated with the DNA which regulates the transcriptional activities.
By combining the ChIP assay with the high throughput DNA sequencing, we can investigate the DNA associated or linked with the histones. Hence, we can study the total event of transcription and gene regulation.
Note: histone modification is one of the mechanisms involved in epigenetic silencing.
First, before the ChIP-seq technique was developed, another method known as “ChiP-chip” was used to study epigenetic regulation through DNA protein interaction.
The chiP-chip technique is a modification of native microarray, in which the probes complementary to the DNA sequences (involved in the chromatin formation) are immobilized.
Hybridization is performed using the fragmented labeled DNA, simultaneously. The histone DNA complex is precipitated and co-precipitated to obtain DNA for microarray.
The major limitation of the present method is the prior sequence information. We need to have sequence information associated with the chromatin formation in order to design the microarray probes and chip.
Also, the sensitivity of the hybridization is too low. Henceforth, to overcome the present limitation ChiP-seq technique was developed in 2017.
How to perform a ChiP-seq assay?
The ChiP-seq method is DNA sequencing based on a high throughput next-generation sequencing technique, a bit complicated compared to conventional sequencing.
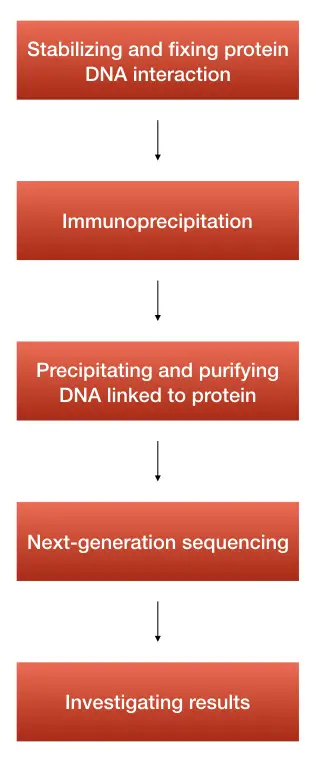
The ChiP-seq assay works on the principle of next-generation sequencing by massively parallel sequencing and counting reads simultaneously. Here million of shorts counting reads are generated and sequenced.
The first step in the ChiP-seq method is to perform chromatin immunoprecipitation, protein-DNA interactions are precipitated. After that, the DNA associated with the histones is co-precipitated and purified using the DNA purification kit.
Soon after, the DNA is trimmed in order to generate sticky ends to bind with adapters. The fragments of DNA should not exceed more than 500bp.
Every single DNA is ligated with adapters to generate DNA libraries.
In the next step, the DNA is allowed for sequencing, every single DNA piece is sequenced in a massively parallel fashion.
Through the bridge amplification method, every DNA sequence is amplified and read.
The machine gathers and stores sequence information which is used to study various genome-wide protein interactions and their role in epigenetic silencing.
Steps:
Stabilizing and fixing the protein DNA interaction using formaldehyde as a crosslinker agent.
After that, the chromatins are fragmented by sonication in fragments of 150 to 500bp. When using the nuclease to do the same, the technique is known as n-ChIP.
In the next step, immunoprecipitation is performed using a specific antibody against a protein to investigate.
DNA is again co-precipitated and purified. Usually, a ready-to-use DNA purification method or spin-column-based DNA purification technique is advisable for ChIP-seq.
Purified fragments are allowed for library preparation in order to sequence them. DNA libraries are made using 10 to 15ng DNA.
DNA amplification is performed, if required and fragments of 200 to 300 bp are allowed to the sequence.
Once the sequence of various fragments is read, using a ‘peak calling, sequences are mapped, aligned and analyzed against the reference genome, computationally.
Here is the list of five common “histone marks” commonly employed in ChIP-seq advised by Roadmap Epigenomics Consortium:
| Histone marks | Full name | Associated with |
| H3K9me3 | H3 lysine 9 trimethylation | Heterochromatin |
| H3K4me1 | H3 lysine 4 monomethylation | Enhancer region |
| Hy lysine 27 acetylation | Enhancer region | |
| H3K36me3 | H3 lysine 36 trimethylation | A transcribed region in gene bodies |
| H3K27me3 | H3 lysine 27 trimethylation | Polycomb repression |
| H3K4me3 | H3 lysine 4 trimethylation | Promoter region |
Peak calling:
One of the important terms commonly used in the ChIP-seq method is the peak calling which maps or identifies significantly enriched loci or regions in the genome.
Why perform ChiP-seq?
Mutations cause genetic abnormalities in a person which are a definite change in the sequence of DNA like deletion, duplication or insertion. But another type of polymorphism known as epigenetic alterations is also caused by severe problems and is largely associated with various types of cancers.
Those epigenetic alterations are a change in the level of gene expression. Histone modifications, chromatin remodeling, methylation and acetylation are several factors that influence the epigenetic profile of a person.
Histones interact with DNA and make nucleosomes which finally form the chromatin. Interaction of histones with DNA makes it transcriptionally inactive or we can say epigenetically silent. Simply put, a protein can’t be transcribed from it.
Therefore a necessary protein can’t be formed, what happens next we know, right!
The assays like ChiP, ChIP-chip and Chip-seq facilitate studies on DNA, and histones interaction occurs in chromatin, consequently, helps in studying the epigenetic profile.
Applications of ChIP-seq:
Here are some of the outstanding applications of the present assay.
- Genome-wide profiling and studying DNA binding proteins
- To locate the protein binding and interaction sites in a genome.
- To identify the transcriptional inactive DNA sequencing and their interaction with histones.
- Identify transcriptional binding sites.
- Study interaction of genes and proteins and their activity can be measured.
- Studying transcriptional activity.
- Studying gene expression of various genes and mapping of it on chromosomes.
Apart from its use in Histone-DNA interactions, it is also used in DNA methylation, nucleosome positioning, chromatin remodeling and other studies too.
Quality control:
Real-time PCR or real-time quantification should be performed prior to sequencing to measure the amount of DNA and its sequence length. Also, the quality and quantity of DNA have to check first.
Various techniques advised by the manufacturer are recommended for quality control.
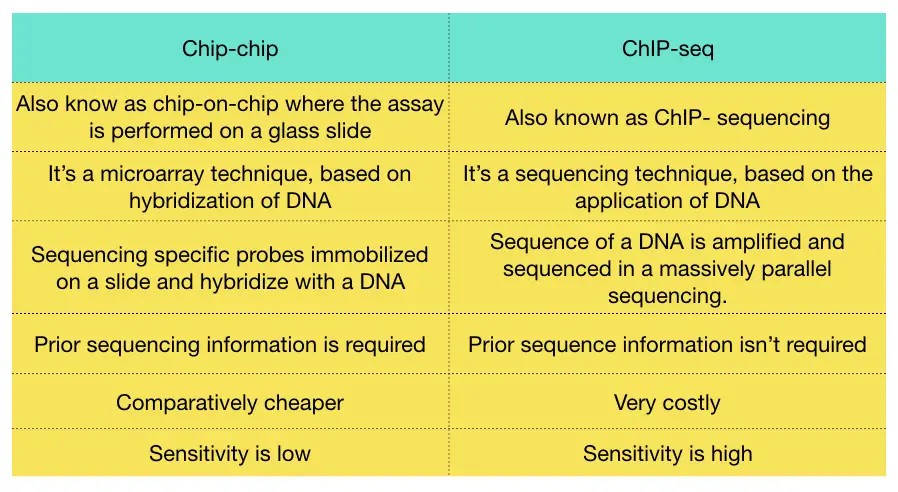
ChIP-chip vs ChIP-seq:
The ChIP-chip technique is based on DNA microarray while the ChIP-seq technique is based on DNA sequencing, the next-generation sequencing method is used to perform the chip-sequencing.
The ChIp-chip technique relies on the principle of DNA hybridization in which the sequence-specific probes are hybridized on a glad slide known as a chip. The DNA protein complex allows hybridization on a chip.
In the chip-seq method, the DNA is sequenced in a massively parallel manner based on the principle of bridge amplification. The DNA sequences are amplified and detected by the machine.
The chip-chip method is cost-effective comparatively while the sequencing-based method is highly costlier. However, the chip-seq method is highly accurate than the conventional microarray-based method.
The sensitivity of the experimental assay of the chip-seq method is very high comparatively.
Limitations of ChIP-seq:
Even though the present technique is powerful and versatile enough to study various DNA binding domains and protein DNA interactions, there are some technical limitations of the present method.
As It includes many manual sample preparation steps chances of contamination are high.
The second most limitation is the selection of antibodies, not all antibodies immunoprecipitate and if can, may not perform well for ChIP seq. Antibody selection has a significant impact on the success of the assay.
The sequencing platform chosen is yet another important factor, limiting the success of the ChIP-seq. NGS- next-generation sequencing relies on massive parallel sequencing, hybridization and amplification therefore chances of false-positive results are higher in it.
Conclusion:
ChiP-seq is nowadays widely used in cancer research and genome-wide association studies. It is more accurate than the conventional microarray-based ChIP-chip method.
Also, various pathways of genes and their regulation and involvement in various diseases can be investigated using the present assay. However, highly powerful next-generation sequencing, powerful computer and computational tools and a team of genomic and bioinformatics experts are needed to set up this type of assays.