“Trisomy 21 also known as the Down syndrome is a type of chromosomal aberration occurs due to the extra copy of chromosome 21 or its part.”
In 1866, John Langdon Down described the clinical features of trisomy 21, and hence from his name, it is known as the down syndrome.
A type of aneuploidy, trisomy 21 is more prevalent than other types of trisomies so far and can be detected using the ultrasound, karyotyping and cell-free DNA testing. However, other marker tests are now available for screening of down syndrome in early pregnancy.
Aneuploidies are common chromosomal abnormalities or more precisely we can say chromosomal aberrations originated due to the numerical or structural chromosomal alterations.
In humans, alterations in the chromosomal number (known as aneuploidy) cause serious health and medical problems.
Many mental and physical abnormalities occur due to the trisomy 21 in which mental and intellectual problems are more commonly observed in the patient. Although, the severity of the disease depends on the type of trisomy.
In the present article, we will discuss one of the most common chromosomal aberrations known as down syndrome, DS, trisomy 21 or DNS.
Content of the article:
Key Topics:
What is trisomy 21?
Due to the imbalance of the chromosomal distribution, the present condition occurs. Mental retardation, gastrointestinal anomalies, neuromuscular weakness and intellectual disabilities are commonly observed in the patient with trisomy 21.
The mortality rate of the patient with trisomy 21 are very less though, sometimes severe developmental and intellectual problems are observed in some patients.
Historically, the representation of the disease was documented in the form of pictures during the 15th or 16th century.
The common type of facial feature of trisomy 21 observed in all patients, they look like the same even, some animals with the down syndrome shows similar facial features. This differential facial feature of down syndrome observed since ~2500 years.
But before John Langdon Down’s observation, Bernal and Briceno identified several sculptures representing the trisomy 21 conditions.
In addition to this and before the findings of John Langdon Down, Esquirol described phenotypic conditions associated with the trisomy 21.
Interestingly, the chromosomal basis of the down syndrome or trisomy 21 was established by Waardenburg and Davenport in 1932.
During 1959, Jacobs form the USA and Lejeune J from France identified the extra copy of chromosome 21 from the patients of trisomy 21. Because of their findings, the Down syndrome was named as trisomy 21.
Information: do you know during the 18th-century trisomy 21 was known as “Mongoloids”, the reason is that the babies with down syndrome look like the Mongolian people.
Cytological indications: 47, XX, +21
Definition:
“Due to the uneven distribution of chromosome 21 during the meiosis, an extra copy of chromosome 21 present with a pair, causes serious developmental and intellectual problems called down syndrome or trisomy 21.”
Causes:
Similar to other types of trisomies, the trisomy 21 also originated due to the random even known as non-disjunction.
During the cell division of germ cells- meiosis, the imbalanced distribution of chromosome 21 causes the DS, an extra copy of chromosome 21 is not the only reason, however.
Translocation is another reason for the down syndrome condition.
When the germ cell with the extra copy of chromosome 21 involved in the fertilization, the DS originated.
Complete trisomy 21:
A copy of the entire chromosome 21 present in a genome, in all cells of the fetus. Approximately 95 to 97% cases of down syndrome are with complete trisomy 21.
Phenotypically the condition is more severe shows a wide range of developmental and intellectual disabilities.
Mosaic trisomy 21:
The third copy of chromosome present in some but not all cells of the body hence in mosaic trisomy condition, the symptoms and sign of the disease depend on which type of cell having the extra chromosome.
Less than 2% of cases with down syndrome are mosaic. The severity of the disease is less in comparison with the complete trisomy.
Translocation trisomy 21:
Likewise the trisomy 13, translocation is another reason causes down syndrome-DS. 3 to 4% of cases with DS are diagnosed with the translocation trisomy.
In this case, some portion of the chromosome 21, translocated to other chromosomes, usually, translocation with 14 and 15 are reported commonly.
Notably, the phenotypic profile of the disease is based on the portion of chromosome 21 translocated.
As per the recent research, from the 200 genes of the chromosome 21, only a few are responsible for phenotypic abnormality in down syndrome and hence if those candidate genes are translocated, it can cause serious health issues.
Unlike the other conditions mentioned above, translocation trisomy can be inherited and because of this reason, it is also known as familial Down syndrome. The risk of occurrence of down syndrome is high with carrier mother than father.
Symptoms of trisomy 21:
Developmental and intellectual disabilities are more commonly observed in all cases of trisomy 21. Some of the common phenotypic abnormalities of down syndrome are given below,
- A typical flattened face or facial features
- Absence of nasal bone
- Slant up and almond-shaped eyes
- Thick and short neck (thickness more than 6mm)
- Small hands, feet and ears
- Palmar crease
- Poor muscle tone
- Average to short hight
- Protruding tongue- a tongue that tends to stick out of the mouth frequently
- Excessive flexibility
- Intellectual disability with lower to mild or moderate IQ level.
- One of the important symptoms of the Down syndrome or trisomy 21 is their “always smiling face, innocence and honesty” (add smiley)”
Pictures of trisomy 21:

Genetics of chromosome 21:
A total number of 46 chromosomes (23 pairs) are present in us on which the entire genetic material of us- the DNA is located and inherited from one generation to other.
Chromosome number 21 is a smaller acrocentric chromosome consist of 1.5% portion of the human genome.
With more than 200 known genes the total size of the chromosome 21 is approximately 49Mb.
Research suggests that an extra copy of some genes are called the gene dosage imbalance is responsible for a different type of phenotype in down syndrome.
Some of the dosage-sensitive genes are:
COL6A1, ETS2, SLC19A1, ITSN1, ERG, SIM2, DSCAM, JAM2, PTTG11P, OLIG1, OLIG2, DYRK1A and APP.
The global prevalence of the trisomy 21 is 1 in 800 to 1600 babies, though it is non-inherited.
Notably, as we said earlier, 2% of translocation trisomy 21 are inherited.
Screening of trisomy 21:
The screening of trisomy 21 is done in a sequential manner starting from some physical examination of a fetus to the advanced biochemical and genetic testing.
Maternal age is on the first indication for the screening of any type of aneuploidy. Mothers above 35 age are more at risk for the down syndrome or trisomy 21.
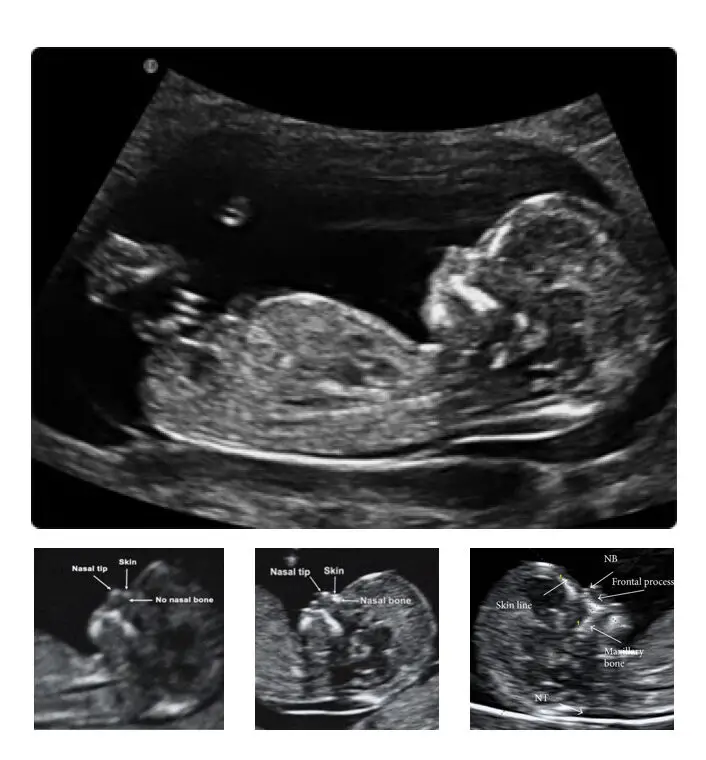
In the next step, during the first trimester, the NT test or NT screening is done. The thickness of the neck area is measured, thickening of nuchal fold greater than or equal 6mm is categorised under DS.
Nuchal translucency is the first marker test used for the screening of trisomy 21.
During the second trimester, PAPP-A, Beta-hCG or AFP or a combination of all three tests is performed, also known as serum marker test.
| Marker | Probability of down syndrome |
| Maternal age | 95% |
| NT (nuchal translucency) Nuchal fold measurement test | 45 to 50% |
| Combination of PAPP-A, beta- hCG, AFP | 94% |
| Absence of nasal bone | 73% |
| Pyelectasis | 25% |
| Combination of All markers | 97% |
The absence or presence of nasal bone and diameter of the renal pelvis are also used as a marker for the screening of the DS.
Besides all these marker tests, in the final stage of the down syndrome screening, cytological analysis practises for validating the results or indications of the above tests.
The presence of the extra copy of chromosome 21 is detected using chromosomal analysis test.
Diagnosis methods:
Ultrasound and chromosomal analysis (karyotyping) are two methods commonly employed for the detection of trisomy 21, likewise the other trisomies.
However, as we said in earlier article cell-free DNA testing- a type of non-invasive prenatal screening practised for screening and diagnosis of trisomy 21.
Ultrasound:
Early physical abnormalities are encountered using the ultrasound, during the first trimester.
The present method is non-invasive and highly accurate.
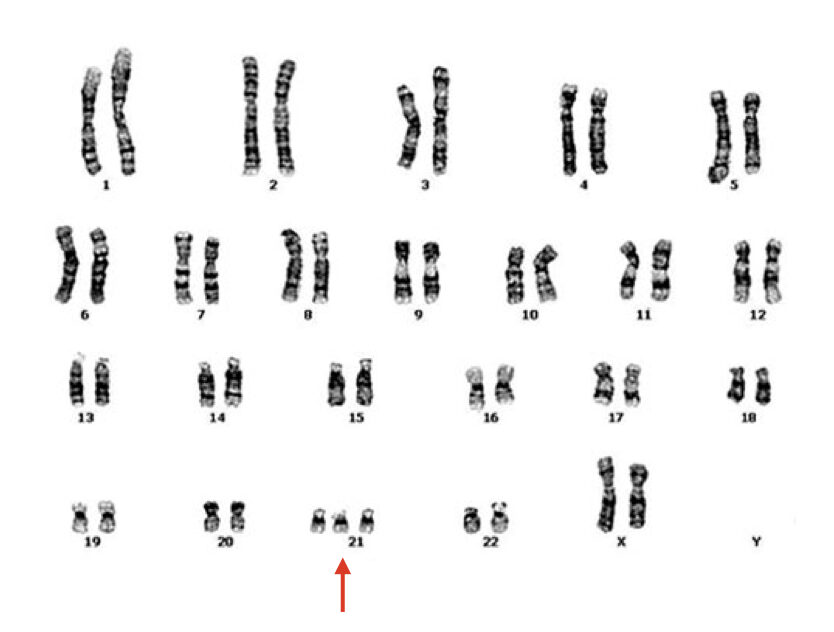
Chromosomal analysis:
Often known as karyotyping or cytogenetic analysis- chromosomal test is the final diagnosis test performed to identify the trisomy.
In karyotyping, chorionic villi sample (early in the pregnancy) or amniotic fluid (late in the pregnancy) is take for chromosomal analysis.
The cells are cultured in strict sterile conditions for getting metaphase chromosomes. Using the G-banding method, the numerical chromosomal abnormalities can be encountered using microscopic analysis.
NIPD- Cell-free DNA:
The risk of fetal or pregnancy loss is high in amniocentesis thus taking amniotic fluid or CV sample is not a good choice always.
In addition to this, a woman has to bear the pain during the sample collection.
Studies show that some amount of fetal DNA is also present in the maternal blood. By isolating fetal DNA from maternal blood, DS diagnostic test can be performed.
The fetal DNA is carefully isolated from the mother DNA and proceeds for DNA sequencing. Using the massive parallel shot-gun sequencing, the presence of the extra copy of the chromosome or chromosome part can be determined.
Although the present method is not globally accepted as a diagnostic test, scientists consider it as one of the safer screening methods.
Even after the cell-free DNA testing, cytogenetic analysis is must require to perform if diagnosed positive for the down syndrome.
Conclusively we can say that cytogenetic analysis technique is the final diagnostic test performed for validating the results of down syndrome, however, the indication of ultrasound analysis are also taken into account for giving final remarks.
Life expectancy:
The fetal mortality rate of with the trisomy 21 is very less unlike trisomy 18 and 13. Although the patient has to safe several mental, intellectual and developmental problems. The life expectancy of trisomy 21 is similar to normal people, one can live up to 60 years if well organised and proper treatment is given.
In recent days, patient with the trisomy 21 can go to school, like the normal students, even some also awarded higher school and college degrees.
They can earn their own bread by working for some organisation or themselves. I was associated with a local Down syndrome organisation, the patient here makes antiques and sell it in the exhibition and all these activities are done by down syndrome patients.
Besides, several intellectual, heart and gastrointestinal problems, a child with the trisomy 21 can live a normal life.
Due to the advancement in the technologies, the life expectancy of down syndrome is continuously increasing.
Suggestion for parents:
Social and emotional stigma is associated with genetic abnormalities and parents are blamed for that.
As a geneticist, we want to tell parents that none of the parents is responsible for the present condition. So do not blame each other for that. Try to support each other instead.
The Down syndrome is a condition, not a disease, fewer complications are detected immediately after birth.
Remember, with care and extensive treatment, a person with Down syndrome can live a long and healthy life, until and unless they are diagnosed with some severe health problems.
The trisomy 21 condition is non-inherited hence do not worry about it when you are planning a second baby.
For safer side, get your cytogenetic report done for finding translocation trisomy if any.
A child with Down syndrome can behave like a normal person if proper treatment is given. Occupational, speech, physical, mental and other therapies surely help them to do well.
Do not treat them as a mental patient instead, behave politely with them, a child with trisomy 21 are more sensitive and emotional.
One of the interesting thing about them is that they are well mannered and well organised compared to a normal child. They keep their every small thing organised.
Risk factor:
The present condition occurs randomly, even though, the risk factor is associated with the conditions given here:
Advanced maternal age:
The risk of Down syndrome increases with increment in maternal age. As per the scientific findings, the mother’s with age more than 35 years are at risk of giving birth to a baby with down syndrome.
However, the majority of the Down syndrome cases are of mother below 35 years of age.
Familial down syndrome:
Some translocation down syndrome can be inherited to consecutive generations. If one of the parents is detected with translocation trisomy 21 or any of their family member is detected with the translocation trisomy 21, the risk of occurrence of Down syndrome in their child are high.
Chromosomal testing is must be needed before planning the pregnancy.
Previous down syndrome child:
If your previous child was born with trisomy 21, there is a little risk associated with the second pregnancy, if it is translocation trisomy.
Prevention:
No prevention techniques are available for Down syndrome, indeed. By taking extensive care, counselling and proper treatments Down syndrome babies can live a healthy life.
In some serious conditions, surgeries and operations can help to improve their life expectancy.
Besides all theses, parents or their family has to face social, financial and emotional burden, further, it also increases the burden for society too.
The special children have to face many problems and criticism at school and the workplace and they have to face several health complications as well. Hence it is better to abort it.
Pregnancies with down syndrome can be aborted and it is legal in all countries.
Common Down syndrome FAQs:
What is trisomy 21?
The trisomy 21 is a type of chromosomal aberrations in which an extra copy of chromosome 21 causes severe health problems. It is also known as Down syndrome too.
What is a down syndrome?
The Down syndrome is a type of aneuploidy- trisomy of chromosome 21, a non-inherited genetic condition, occurs due to the imbalanced distribution of chromosomes.
The condition is described by John Langdon Down in 1866 therefore, in his honour it is known as Down syndrome.
Severe developmental, mental and intellectual problems are associated with it.
What causes down syndrome or trisomy 21?
The event called nondisjunction is the reason for the origin of trisomy 21. The event is totally random, non-inherited and occurs during the meiosis of germ cell.
How common the down syndrome is? Or
What is the incidence of Down syndrome?
The down syndrome is more common than the other type of trisomies, globally, 1 in 800 to 1 in 1500 babies born with down syndrome.
When was down syndrome discovered?
Down syndrome was discovered in 1866 by John Langdon Down, though it is present for more than 2500 years.
Interestingly, the cytogenetic indication of the Down syndrome was given by Lejeune J in 1959.
What are the symptoms of down syndrome?
The common symptoms of down syndrome are fattened face, mild to moderate mental retardation, poor muscle tones and absence of nasal bone. Some other symptoms of it are enlisted above.
How is Down syndrome diagnosed?
The Down syndrome is diagnosed using chromosomal analysis, ultrasound analysis and cell-free fetal DNA testing.
However, two or three marker test, maternal age and some of the physical features are taken into account for the diagnosis of trisomy 21 or Down syndrome.
Notably, the cytogenetic analysis- karyotyping or chromosomal analysis using amniocentesis is one of the gold standard and most trusted method used for the diagnosis of the present condition.
Is down syndrome inherited?
No, the Down syndrome occurs due to the uneven distribution of chromosome and the entire process occurs randomly.
However, in the case of the translocation trisomy 21, ~3% cases are inherited. This condition is also known as familial Down syndrome.
Due to the translocation of some portion of chromosome 21 to other chromosomes, it inherited from parents to their offspring, although the severity of the disease depends on the amount of the portion translocated.
Which children are at risk of down syndrome?
Mother’s age plays an important role in the development of the down syndrome. As the maternal age increases, the chance of Down syndrome or any type of chromosomal abnormality increase. Commonly women above 35 are at more risk with their pregnancy with Down syndrome.
Interestingly, the majority of reported cases of Down syndrome are of females age below 25.
Related articles:
- Trisomy 18- Definition, Symptoms, Pictures, Diagnosis And Life Expectancy.
- Trisomy 13(Patau Syndrome)- Definition, Causes, Symptoms, Life Expectancy And Diagnosis.
Conclusion:
I can say if your child born with the down syndrome, instead of blaming yourself, thank god for giving you the opportunity to serve the “angel child.”
The trisomy 21 is a condition, not a disease, unlike other genetic mutations. with great care and management, a child with the Down syndrome can live a normal life.
Sources:
Kazemi M, Salehi M, Kheirollahi M. Down Syndrome: Current Status, Challenges and Future Perspectives. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2016;5(3):125–133.