“Sanger sequencing is a gold-standard diagnostic technique and is extensively used in almost all the life sciences fields. Here are a few reasons why you should learn it.”
When comparing Sanger sequencing vs PCR and Sanger sequencing vs NGS, Sanger is a step ahead of PCR by detecting the nucleotide-level alterations that PCR can not identify.
However, it is one step behind the NGS which offers high-throughput sequencing with a broader range.
In the present era of high throughput and Next-generation sequencing, Sanger sequencing still has its own significance as a stand-alone sequencing technique. Even, the NGS results are oftentimes, validated using the Sanger!
Meaning, it was developed in 1977 but still it is a relevant, useful and recommended sequencing platform.
But why should we learn it, if we have NGS? Let me give you 6 reasons.
Stay tuned!
Key Topics:
Why should you learn Sanger sequencing?
In recent times, life sciences have bifurcated into either wet lab work or dry lab work. Those who don’t want to mess up with lab and experimentation things, choose bioinformatics and vice versa.
Techniques like PCR, rt-PCR, karyotyping or FISH methods rely on extensive wet lab work, optimization and troubleshooting whereas techniques like microarray or NGS rely on extensive data processing and analysis.
Sanger sequencing is the only technique available that relies on the least wet and dry lab work. Personnel with a moderate level of knowledge and skills can perform it and analyze the results.
It’s that simple!
And still! It is a gold standard, widespread, accurate, versatile and cost-effective technique. Thus, every life science aspirant should have to learn it. Let’s see what makes it stand alone.
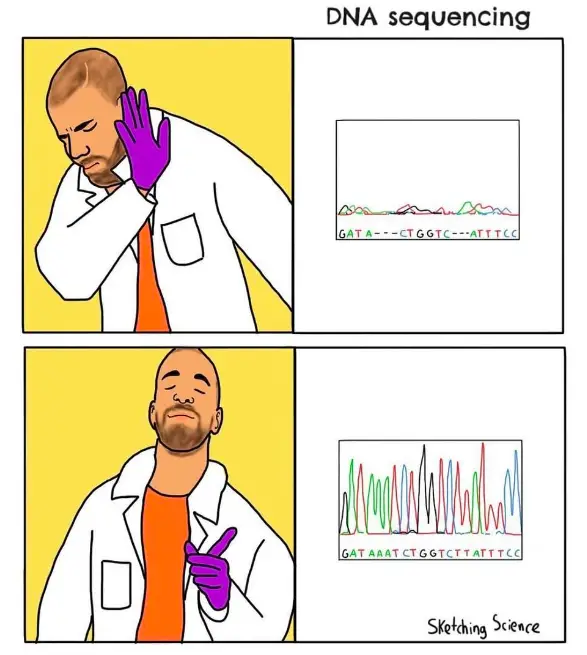
1. Gold Standard Method:
A few genetic techniques are widely adopted in healthcare and diagnostics. The chain termination technique is one among them. It is used to study inherited genetic conditions and well-studied mutations associated with health-related conditions.
Hence, it is used in pre- and post-natal diagnostics, screening and testing. So if someone wants to achieve a career in healthcare or diagnostics, they need to learn Sanger sequencing.
2. Sequencing level investigations:
The present technique provides sequence-level or more precisely nucleotide-level information, which the previous techniques like PCR or karyotyping can’t provide! Meaning, that we can investigate and know mutations like SNPs, insertions and deletions in the sequence.
So if someone wants
- To study a gene or sequence evolution (Evolutionary study)
- To study Inherited conditions (Biotechnology)
- To find out new alterations (Genetics)
- To study microbial gene or DNA sequence (Microbiology)
- To investigate the biological role of a gene (Biochemistry)
- To study a plant’s genes or resistance (Botany)
- To study animal genes and related inherited conditions (Zoology)
- To study evolutionary relationship between species (Ecology)
They need to learn Sanger sequencing.
3. Simple lab technique:
Life sciences students have a basic foundation of wet lab work. Using this knowledge, they can easily prepare the sequencing.
It’s just DNA extraction, PCR, sequencing and analysis. You just need to do pipetting as per the protocol that’s it. And you already know the role of ingredients like polymerase, nucleotide or buffer.
If you are new to DNA extraction or PCR, you can click the link and read our free resources to gain knowledge.
So it’s not rocket science for them.
4. Simplest data analysis:
For life science students, especially lab enthusiasts, bioinformatics and information technology can feel overwhelming. Thankfully, analyzing and interpreting Sanger sequencing data is much simpler and more straightforward.
You need to have some basic knowledge of installing and running software, that’s it. Complex coding, programming or back-end handling is not needed. You just need to observe the sequence and compare it with the reference.
And guess what! The software is equipped with all the steps and facilities. It’s like making an Instagram reel.
Let me tell you that Sanger sequencing data analysis is a ‘balanced system’ between manual and automated analysis. This means you can cross-validate automated results with manual investigations and manual results with automated investigations.
Isn’t that perfect for you?
Hurry! Limited spots available
Want to Master Sanger Sequencing?
Join our Beginner’s or Advanced Guide to Sanger sequencing certification course.
Understanding the theory: Learn the basics of Sanger sequencing
Understand the technique: learn reaction preparation, troubleshooting and more.
Hands-on software training for data analysis, including tools.
Real-world applications in diagnostics, forensics, and cancer research.
Dedicated “SeqMan Community
Join Dr. Tushar Chauhan, an expert with 10+ years of experience, and unlock your potential in genetic research.
Enroll Now and Start Your Journey Today!
5. Scale up your research work:
Thinking out of your boundaries is a bit difficult yet rewarding. The well-recognized, cited and appreciated research work you see in reputed journals covers almost every possible area related to their topic.
Let me give you an example,
If you are in biochemistry, you mostly focus on the pathways, their proteins and their consequences. But what if you also include the genes that encode those proteins, sounds crazy, Right?
That’s what you can do with your research work and scale up to the next level. Check out the table below to brainstorm some ideas.
| Life science field | General research idea | How to use Sanger sequencing |
| Microbiology | Study antibiotic resistance in bacteria. | Sequence resistance-related genes (e.g., bla, mecA) to detect mutations or confirm the presence of resistance genes. |
| Biotechnology | Verify gene modifications in genetically engineered organisms. | Sequence modified regions to confirm successful integration or specific changes in the target DNA. |
| Biochemistry | Explore genetic regulation of metabolic pathways. | Sequence genes encoding enzymes or regulators to identify mutations that impact metabolic function. |
| Ecology | Assess ecological diversity in populations. | Sequence mitochondrial DNA or specific genetic markers (e.g., COI) to study variation and conservation status. |
| Botany | Study disease resistance in plants. | Sequence genes related to resistance (e.g., R-genes) to identify polymorphisms or SNPs conferring disease resistance. |
| Zoology | Investigate genetic disorders in animals. | Sequence suspected genes to confirm mutations responsible for inherited diseases or traits. |
| Evolutionary study | Analyze species relationships and evolution. | Sequence conserved DNA regions to compare sequences, infer phylogenetic relationships, and map evolutionary changes. |
| Genetics | Detecting disease-causing mutations in humans. | Sequence target genes (e.g., BRCA1/BRCA2) to identify point mutations or small deletions causing genetic disorders. |
| Immunology | Study immune response in autoimmune diseases. | Sequence immune-related genes (e.g., HLA or TCR) to identify mutations impacting immune system regulation. |
Want more ideas for your field, you can email me or comment below.
Let’s move further.
6. Cost-effective:
Traditional research methods are outdated, while new-age methods like microarray or NGS are very expensive. So what if you have a limited budget for research? Or what if you want to test a patient’s sample?
Sanger sequencing is a cost-effective testing method. It’s super cheap, yet accurate and provides impressive data. In India, the standard rate for a 500 bp sequence is up to 1000 to 1500 INR.
If you do some work and send amplicons instead of a direct sample, the price will be further lowered up to 600 INR per sample. Meaning, with a few thousand rupees, you can get sequence-level information for your research work!
Isn’t that amazing?
Related articles:
- ddNTP in Sanger Sequencing- What Is It and Why We Use It?
- How to improve Sanger Sequencing Results?- 5 Technical Tips from Experts
- Sanger Sequencing vs PCR: Common and Technical Differences
- A Step-by-Step Process on How to Read Sanger Sequencing Gel?
- Advances in Sanger Sequencing- Manual vs Automated Sanger Sequencing
Wrapping up:
Sanger sequencing is a “one of a kind” technique that, in my view, will remain irreplaceable for at least the next 10 years. With current automation and availability of ready-to-use kits, it has outperformed many competitors.
Let me tell you one thing!
Underconfident NGS variants are also validated using Sanger sequencing. We will discuss the applications in the separate article, this is just an overview for students on how and why they have to use it.
I hope you like this article, check out our basic DNA sequencing course that comprises all the information on Sanger sequencing, before leaving this article.
Join now! : Sanger sequencing online course

Your writing has a way of resonating with me on a deep level. I appreciate the honesty and authenticity you bring to every post. Thank you for sharing your journey with us.
Somebody essentially lend a hand to make significantly posts I might state That is the very first time I frequented your web page and up to now I surprised with the research you made to create this particular put up amazing Excellent job