“Gel electrophoresis is the subsidiary genetic technique used to visualize, examine and study DNA for various purposes. It is used to study DNA- deoxyribose nucleic acid, RNA and proteins too.”
Or technically, we can
It is a technique employed to separate charged particles based on their size (to understand this concept, you need to read this article).
Standard, as well as computational techniques, are so useful in genetics and genomic studies. For instance, southern blotting, gel electrophoresis and restriction digestion are conventional whilst capillary electrophoresis, real-time PCR and microarray are computational ones.
Techniques like DNA cloning, PCR, restriction digestion, recombinant DNA uses gel electrophoresis to see, study, confirm and validate DNA and experiment.
DNA is a tiny thing! Even the RNA and protein too. We can’t see it by the naked eye, even under the conventional microscope. So how DNA studies are conducted?
Before answering this question, we have to understand the importance of two things. First, obviously, we have discussed- DNA can’t be seen. Seconds, few copies can’t be studied.
The bulk of DNA is required to study the DNA, but DNA can’t be replicated outside our body. The process of in vitro replication- polymerase chain reaction or the amplification process is used to make copies of DNA.
The machine is thermocycler- or PCR and a primary or initial technique in DNA studies while to evaluate results, gel electrophoresis is used, a secondary or additional technique with the PCR.
Spoiler! The present article is a brief overview of the technique ‘electrophoresis’. If you want more technical information, you can read our previous article. The present content is focused only on the gel electrophoresis only.
Key Topics:
What is gel electrophoresis?
The gel electrophoresis is a secondary genetic technique used in DNA studies and tests to run, evaluate and examine DNAs or genes.
Gel electrophoresis works on the simple principle of charge and current. As electrons migrate from negative to positives the charged particle migrates under the medium.
The medium is a liquid ‘buffer’ made up of the special chemicals that facilitates ease in the migration.
DNA or RNA- the types of nucleic acid have a net negative charge on their one end. With the current from negative to positive, a nucleic acid also migrates.
DNA can’t be seen, it doesn’t have any color so it can’t be seen during the electrophoresis. So how to track the migration of DNA?
Two types of chemicals- dyes; more precisely, used to monitor the running of DNA in electrophoresis. One is the BPB- the bromophenol blue and the other is the EtBr- the ethidium bromide. We will discuss it later on how both work.
First, let us understand how DNA is applied to the electrical field?
We use buffer to manage its migration, but we cant add DNA directly to buffer, it will be dispersed. Scientists need something solid, hollow and electrically susceptible thing! That can help to migrate DNA.
The “gel” a gelly, semi-solid and hollow synthetic polymer solves this problem and helps smooth-traveling of nucleic acid under the current. The gel for electrophoresis is made up of the ‘agarose’- having a definite sized pores which can travel current and DNA in a buffer.
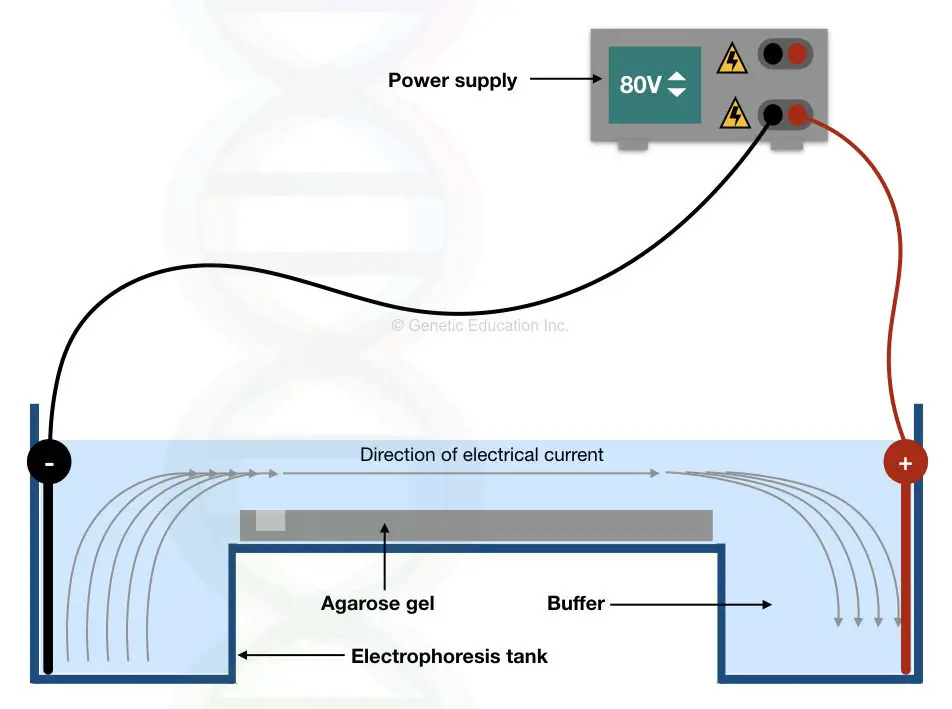
Comporevehnsively, electrophoresis assembly is a combination of current, gel, buffer and dyes that helps to run DNA.
Current– run DNA from negative to positive under the influence of electrical pulses
Agarose gel– provide space or work as a vehicle to run DNA under the current
Buffer– a medium that facilitates easy migration
Dyes– track and monitor the migration of DNA.
Gel electrophoresis is a simple assembly work on the principle of electronics having an electrical power supply, a chamber to fill the buffer and a gel tray that’s it!
The two types of dye play a major role in monitoring the migration otherwise we can’t see DNA.
The BPB runs along with the DNA so that it can’t come out from the gel (if DNA will run out, what we will study?), the EtBr- intercalates or binds to the bases of DNA and emits fluorescence under the UV light.
Unlike other genetic techniques, the electrophoresis technique is a simple one! The process and instrumentation setup are easy and handy having only two instruments- the power supply and the gel tank.
The power supply is a standard electrical device that provides constant current while the gel tank or electrophoresis apparatus is the instrument in which the DNA is run.
It has the tank to fill the buffer and the gel assembly to set up a gel. Once gel submerged in the buffer, through an electrical current the DNA migrates.
Related article: 10 Proven Tips to Success in Gel Electrophoresis of DNA.
What is gel electrophoresis used for?
Comprehensively, the gel electrophoresis is used to study, visualize, examine and evaluate DNA and RNA. Popularly it is combinedly used with the amplification to study the PCR amplicons or DNA amplicons.
By using gel electrophoresis, we can study mutations, disease and other alterations in DNA or gene. It’s employed to confirm the presence or absence of nucleic acid in the sample.
Gel electrophoresis is used in the study of gDNA, pDNA, amplicons of various sizes, bacterial DNA or plant DNA.
All the nucleic acid studies can be done using the popular variation known as agarose gel electrophoresis, however, protein can be studied using the PAGE- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis.
Gel electrophoresis separates charged particles based on their size.
One of the important points important to discuss here is that the charged particles migrate in a gel-based on their size. The larger sized particles or DNA runs slowly and smaller one migrates fasters.
This phenomenon is used to separate various sized particles and hence identify fragments of DNA of different sizes. For example, genes of different sizes are identified.
Read more: Plasmid DNA- Structure, Function, Isolation And Applications.
Standard applications of gel electrophoresis:
- Mutational studies
- Amplicon identification and studies
- Running gDNA.
- Separating DNA of various sizes.
- Sizing DNA fragments
- Disease studies
Read more:
- Role of EtBr in Agarose Gel Electrophoresis and Karyotyping.
- DNA Gel Loading Dye- Bromophenol Blue and Xylene Cyanol.
Conclusion:
Conclusively, the gel electrophoresis technique is used to study biomolecules like DNA, RNA and proteins and is a standard, routine and common genetic technique used in the genetic lab.
To know more about gel electrophoresis, aperture, buffer system, BPB, EtBr, and how to run it, you can read our previous article: Agarose gel electrophoresis.