“RFLP is a genetic marker popularly used in genetic research. In this article, learn about how to perform RFLP.”
Being a student of genetics, biotechnology or life science RFLP would be known to you. RFLP is a conventional and old-school genetic marker widely used in genetic research and even in diagnosis.
Certainly! Despite remarkable advancements in sequencing technology, especially in genome sequencing, the traditional method of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) remains relevant, applicable, and valuable. However, many students and researchers face challenges due to a lack of technical expertise in its utilization.
Allow me to highlight that RFLP is a significant technique in genetic engineering experiments. Therefore, acquiring knowledge of this technique would prove highly advantageous. I assure you that after reading this article, you will be equipped to design your own RFLP experiment confidently.
In this article, I will explain to you what the RFLP genetic marker is and how to use it in your experiment. The present article is a complete theory and technical guide on RFLP.
Stay tuned.
Disclaimer: The content presented herein has been compiled from reputable, peer-reviewed sources and is presented in an easy-to-understand manner for better comprehension. A comprehensive list of sources is provided after the article for reference.
Key Topics:
What is RFLP?
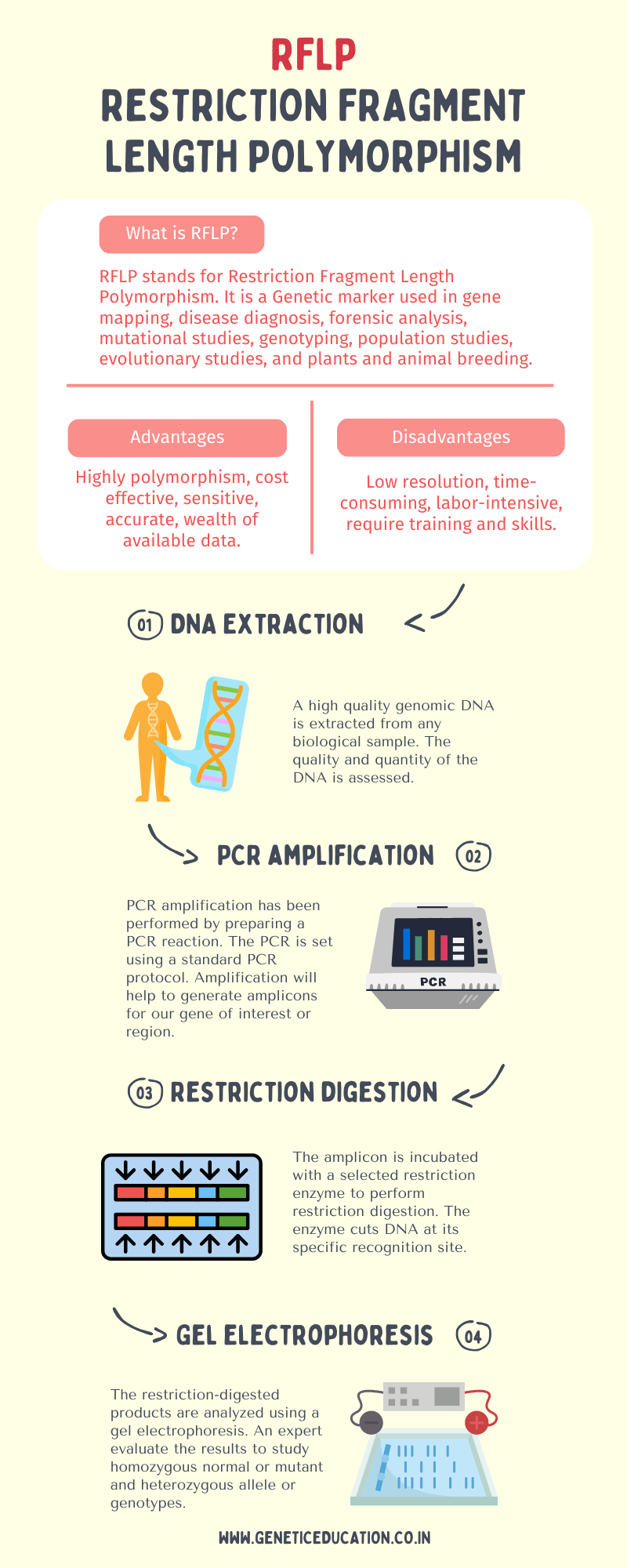
RFLP stands for Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. Put simply, we can say that using a restriction enzyme or restriction digestion protocol, polymorphism can be detected by generating varied lengthed fragments
RFLP is a combination of three different and important genetic techniques- PCR, restriction digestion and agarose gel electrophoresis. Here, PCR generates an amplicon for the gene of interest, digestion prepares varied lengthed fragments and gel electrophoresis detects polymorphism by size-based separation.
RFLP is a genetic marker used to detect polymorphism or alteration at a specific location in a sequence, within a gene, in an individual or from the entire population. Hence, it’s a significantly important tool for genetic research.
Genetic Marker
Molecular or genetic markers are unique DNA sequences found at specific locations within the gene which are capable of being inherited by the next generations and they are identifiable as well.
However, no definitive historical evidence exists regarding the inventor of this technique. Each genetic markers have several unique characteristics. Take a look at the characteristics of RFLP.
Characteristics of RFLP
Here are a few characteristics of RFLP that make it unique and usable in genetic science.
Heritability:
RFLP markers are heritable from parents to their offspring. The present characteristic is useful for tracing alleles across the generations. Heritability helps in predicting the outcomes during experimental design.
For instance, if we are designing the experiment to study one SNP for a disease, we already know what we will get in homozygous normal and mutant, and heterozygous conditions.
Mendelian inheritance:
RFLP also exhibits the classic Mendelian inheritance pattern. It can be inherited as homozygous dominant or recessive and heterozygous. Again, the present characteristic helps predict the outcomes.
Codominance:
One of the crucial characteristics that makes it useful in genetic research and diagnosis is the co-dominance. Both the alleles at a given locus are detectable in the heterozygous condition.
For instance, mutations in inherited genetic diseases like sickle cell anemia can be detected using RFLP. A restriction enzyme is selected in a way that it can cleave either the normal or mutant allele and gives two different fragments. We can determine the heterozygous condition by differential banding pattern.
Length polymorphism:
RFLP exhibits length polymorphism property. This means that upon digestion, different fragments are obtained across individuals or populations, depending on the presence of recognition sites on the target sequence.
Length polymorphism provides ease and flexibility in studying and interpreting the results.
Principle:
The simplest representation of the RFLP principle is as stated.
“PCR amplified DNA sequence or a gene is digestion using a specific endonuclease, producing DNA fragments of different lengths. The fragments are separated and studied using gel electrophoresis.”
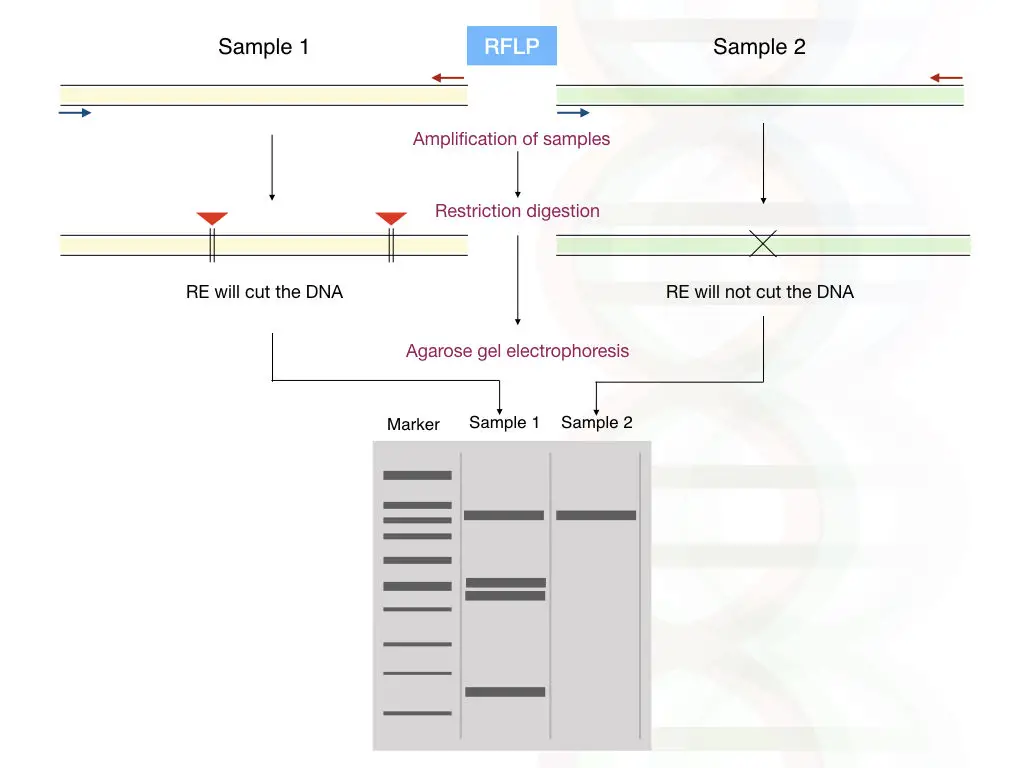
Restriction digestion of an amplified genomic segment or a gene by a specific restriction enzyme results in variations in the length of DNA fragments. Depending on the presence of recognition sites, DNA fragments of varying sizes are generated.
These fragments are separated by gel electrophoresis according to their molecular weights, allowing the visualization of distinct DNA banding patterns of DNA fragments for homozygous and heterozygous conditions on a gel (agarose or polyacrylamide gels).
The patterns of DNA fragments, or restriction fragments, reflect the presence or absence of restriction sites and polymorphic variations in the DNA sequence. By comparing the fragment patterns among individuals or populations, genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and insertions/deletions (indels), can be identified and analyzed.
How to Perform RFLP?
So far you get a theoretical idea about RFLP. Now let’s dive deeper into the topic and understand the step-by-step process of how to perform an RFLP experiment.
Note: We have prepared many demonstration articles and videos on our blog, when needed I will provide the link. Each demonstration is easy to understand and perform.
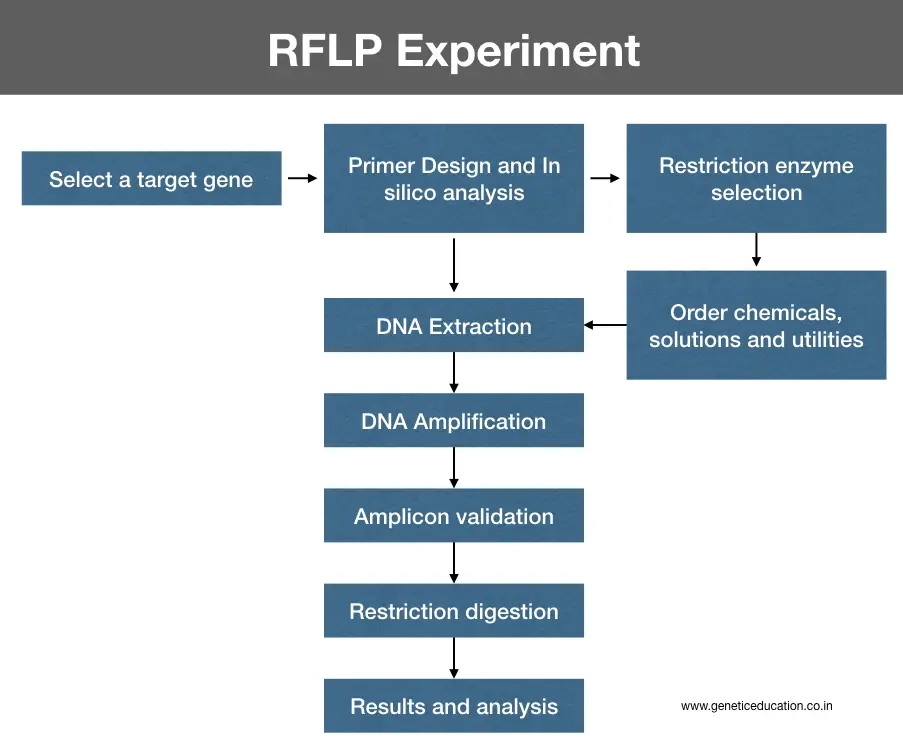
Step 1: Select a target gene
The experiment begins with selecting a gene of interest, a target or a sequence you wish to study. Now, you have to obtain information related to your GOI. Online platforms like NCBI can be used to collect such information.
In addition, you can also gather information on variations- SNPs, insertion, deletion and translocations, etc to prepare your RFLP experiment. For a complete demonstration follow this article: How to Find Information about a Gene of Interest?
Step 2: In silico analysis and primer designing
You have the sequence information now (if you followed the demonstration given in step 1), for your PCR amplification, you have to design and validate primers. For PCR primer design you can follow this tutorial: How to Design PCR Primers?
For in silico analysis of PCR products, you can follow this tutorial: How to Perform In silico PCR?
After these two analyses, you will get
- Forward and reverse primer sequences
- The annealing temperature for PCR amplification
- PCR conditions
- Amplicon size
Step 3: Select a restriction enzyme
Usually, what we do is, select the REase that cleaves on the normal allele and not the mutant allele. To do that, the recognition site must be located within the mutation site that we want to study.
Using an NEB cutter software, a restriction enzyme can be selected and ordered. We do not have to do anything special. Just simply copy the sequence we obtained from step 1 and paste it into the NEB cutter software.
It will give us the list of all the enzymes for cleaving the sequence at various locations. To perform an NEB cutter, you can follow this demonstration: How to Choose a Restriction Enzyme: A step-by-step Guide.
Note:
NEB cutter also has one facility, you can see the hypothetical gel image of what you will observe if you use a particular REase in your RFLP experiment.
Step 4: Ordering
Now, the prerequisites are done! It’s time to order all of your chemicals and requirements. It will take 15 to 30 days for everything.
Related article: How to Order, Use and Store PCR Primers?
Step 5: DNA extraction
During that time, you can isolate a good-quality DNA from your sample. Any sample that contains genomic DNA, can be used for the RFLP experiment. Use a decent DNA extraction protocol or ready-to-use kit.
This guide will help you to choose one: How to Choose a DNA Extraction Method?
Step 6: DNA amplification
Now prepare a PCR reaction, using a standard PCR reaction protocol provided by the kit manufacturer. Take necessary precautions to avoid false negative and positive results. This guide will help you with this: How to Prepare an Excellent Reaction Preparation.
After that, run a PCR protocol to amplify your target. The annealing temperature and other details are given during the primer design step. You can use it to set a protocol. Run the protocol for 30 to 35 cycles.
Step 7: Validate amplicons
In the next step, run the PCR amplicon on 2% agarose gel to confirm the positive amplification. It should have a single and clear amplicon, any non-specific amplification can interfere with the digestion reaction.
Amplicon size is given during the in silico analysis. You can use that information for validation purposes.
Step 8: Restriction digestion
Now, perform restriction digestion. The protocol and experimental conditions would be given with the restriction enzyme kit. Follow the guide and prepare the reaction. Incubate the reaction as per the instructions given in the manual.
Follow this demonstration for more detail: A Well-Establish Protocol For Restriction Digestion. A step-by-step process and reaction preparation protocol are given there.
Step 9: Results and analysis
RFLP results are a bit tricky to understand. To make things simple and easy to understand, we already have prepared an in-depth article on this topic. To understand the RFLP results, you can follow this guide: A Guide to Read and Understand Restriction Digestion Results.
Requirements for RFLP:
| Step | Chemicals, Reagents, or Kits | Instruments |
| DNA Extraction | DNA extraction kit | Microcentrifuge, Vortex mixer |
| DNA extraction buffers and solutions | Heat block or water bath | |
| Proteinase K | Centrifuge | |
| RNase | Pipettes | |
| Isopropanol or ethanol | ||
| PCR Amplification | PCR master mix | PCR tubes and tube strips |
| Primers specific to the target region | PCR tube rack | |
| dNTPs | Thermocycler | |
| Taq DNA polymerase | ||
| PCR reaction buffer | ||
| Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) | ||
| Restriction Digestion | Restriction enzyme(s) specific to the target site | Restriction enzyme buffer |
| Bovine serum albumin (BSA) | Microcentrifuge | |
| Double-distilled water (ddH2O) | Vortex mixer | |
| Restriction enzyme storage buffer | Heat block or water bath | |
| Thermocycler for heat inactivation | ||
| Analysis | Agarose gel | Gel electrophoresis apparatus |
| DNA staining dye (e.g., ethidium bromide, SYBR Safe) | UV transilluminator | |
| DNA size marker | Gel documentation system | |
| TAE or TBE buffer | Pipettes |
Advantages and Limitations:
| Advantages | Limitations |
| Widely Applicable and can be used across diverse organisms and genetic loci. | Low Resolution: Limited ability to detect small genetic variations. |
| High Polymorphism and displays extensive genetic variation. | Labor-Intensive: Requires multiple steps, making it time-consuming. |
| It’s cost-effective. Requires standard laboratory equipment and common reagents. | Limited by the amount and quality of DNA available. |
| A wealth of literature and established protocols are available. | Analysis may require specialized knowledge and training. |
| Highly sensitive and accurate. | Results may vary based on factors like temperature and enzyme activity. |
| Easy experimental setup. | Low throughput. |
Applications
Starting from disease diagnosis to plant and animal breeding, RFLP has been used in various fields since it evolved. Here are a few important applications of RFLP in various fields.
Genetic mapping:
The very first application of the present technique and for which it was developed is genetic mapping. Using the known recognition sites, various genes or DNA fragments are digested with a restriction enzyme and mapped on a chromosome.
To know more about gene mapping read this article: A Brief Introduction to Gene Mapping.
Genotyping and mutational studies:
Afterward, it entered into genetic research and scientists started using the technique for SNP genotyping, indels genotyping and mutational studies. The mutation-specific, disease-causing, wild-type and heterozygous genotypes can be investigated.
Such investigations help determine the frequency of an allele or genotype in the entire population and help determine pathogenic and non-pathogenic genotypes for the population.
Disease diagnosis:
RFLP then entered into the diagnosis of various and common genetic diseases. For example, thalassemia and sickle cell anemia. RFLP can effectively identify SNPs, smaller insertions and deletions.
A selected restriction enzyme can perform a cut at the SNP or indel site either on the normal allele or mutant allele. This can allow scientists to determine homozygous normal, mutant and heterozygous alleles from the sample.
Forensic analysis:
Before the development of STR-based forensic typing which is the most accurate technique nowadays, RFLP was used in forensic typing and analysis. It is also used to establish kinship relationships.
The sample from the crime scene has been digested with various restriction enzymes and analyzed on a gel to determine the differences between various samples through length polymorphism.
Genetic association studies:
RFLP has been widely used in genetic association studies to determine the correlation between genotypes and phenotypes. It’s also beneficial to establish an association between a genetic variant and a disease.
This way, phenotype-associated genotypes or alleles can be mapped on a chromosome.
Population studies:
As aforementioned, one of the pivotal applications of the present technique is in population-based genetic studies. The frequency and prevalence of a specific genotype or allele can be determined at a population level.
In addition, pathogenic variants associated with a particular population can be identified and studied. Such studies enable scientists to predict the disease risk for the population for a particular genotype.
Plant and animal breeding:
In plant and animal breeding programs, the present genetic marker has been widely accepted. Using a specific or group of restriction enzyme(s) scientists can validate breeding experiments.
RFLP in these programs helps study economically important plants and animals at a genetic level. In addition, economically important traits like quality characteristics, various resistance and yield potential can be studied.
Evolutionary studies:
RFLP is also an important tool for evolutionary studies. By performing the restriction digestion on amplified target fragments scientists can establish evolutionary relationships, and genetic relatedness, and study population structure and dynamics.
In addition, the genetic similarities between two different populations can also be studied. By preparing the phylogenetic tree scientists can study evolutionary events.
Other applications:
Lastly, RFLP is used in biotechnology experiments, gene cloning, genetic engineering and other related studies. It is also used in microbial genetic studies.
Wrapping up:
RFLP is a gold-standard genetic marker that is still relevant in modern times. In the present era, led by NGS-like high throughput sequencing technologies, scientists and healthcare providers are still using it for studying diseases and mutations.
Furthermore, RFLP-like markers are the first choice for small-scale master’s or PhD level research. However, the use and selection of restriction enzymes can be a challenging task which makes RFLP tedious and error prone.
I hope you like this article. Do share it and subscribe to our blog for more knowledge and information.
Resources:
Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism by NCBI.
Gawel, N.J., Jarret, R.L. & Whittemore, A.P. Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP)-based phylogenetic analysis of Musa . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 286–290 (1992).
Mittal B, Chaturvedi P, Tulsyan S. Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism. ScienceDirect. Published January 1, 2013. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780123749840013140.